Abstract
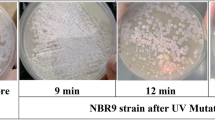
Two mutant strains of Amycolatopsis mediterranei VA17 and VA18 were isolated using physical (UV) and chemical (NTG) mutagens gave high rifamycin B than the parent type when grown in the same fermentation medium with a pH of 7.2, temperature 32 °C for a period of 12 days. The cultural conditions of both mutant strains are similar to the parent strain except temperature which was higher by 4 °C. By this mutation and selection study, rifamycin B production was improved from 1400 mg/l to 2450 mg/l.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkateswarlu, G., Murali, P., Sharma, G. et al. Improvement of rifamycin B production using mutant strains of Amycolatopsis mediterranei . Bioprocess Engineering 23, 315–318 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004499900068
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004499900068