Abstract
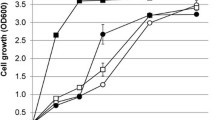
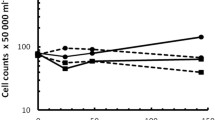
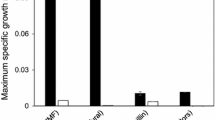
The evolutionary adaptation was carried out on the thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus NIRE-K1 at 45 °C up to 60 batches to enhance its xylose utilization capability. The adapted strain showed higher specific growth rate and 3-fold xylose uptake rate and short lag phase as compared to the native strain. During aerobic growth adapted yeast showed 2.81-fold higher xylose utilization than that of native. In anaerobic batch fermentation, adapted yeast utilized about 91 % of xylose in 72 h and produced 2.88 and 18.75 g l−1 of ethanol and xylitol, respectively, which were 5.11 and 5.71-fold higher than that of native. Ethanol yield, xylitol yield and specific sugar consumption rate obtained by the adapted cells were found to be 1.57, 1.65 and 4.84-fold higher than that of native yeast, respectively. Aforesaid results suggested that the evolutionary adaptation will be a very effective strategy in the near future for economic lignocellulosic ethanol production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar S, Mishra IM, Adhikari DK (2008) Bioethanol production from baggasse with cell recycle at high temperature. J Biotechnol 136:S459
Behera S, Arora R, Nandhagopal N, Kumar S (2014) Importance of chemical pretreatment for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew Sust Energy Rev 36:91–106
Long TM, Su YK, Headman J, Higbee A, Willis LB, Jeffries TW (2012) Cofermentation of glucose, xylose, and cellobiose by the beetle-associated yeast Spathaspora passalidarum. Appl Env Microbiol 78:5492–5500
Kumar S, Singh SP, Mishra IM, Adhikari DK (2009) Recent advances in production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic biomass. Chem Eng Technol 32:517–526
Kumar S, Singh SP, Mishra IM, Adhikari DK (2009) Ethanol and xylitol production from glucose and xylose at high temperature by Kluyveromyce sp. IIPE453. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1483–1489
Kumar S, Singh SP, Mishra IM, Adhikari DK (2010) Feasibility of ethanol production with enhanced sugar concentration in bagasse hydrolysate at high temperature using Kluyveromyces sp. IIPE453. Biofuels 1:697–704
Arora R, Behera S, Sharma NK, Singh R, Yadav YK, Kumar S (2014) Biochemical conversion of rice straw (Oryza sativa L.) to bioethanol using thermotolerant isolate K. marxianus NIRE-K3. In: Sharma NR, Thakur RC, Sharma M, Parihar L, Kumar G (eds) Proceeding of exploring and basic science for next generation frontiers. Elsevier, New Delhi, pp 143–146
Behera S, Arora R, Sharma NK, Kumar S (2014) Fermentation of glucose and xylose sugar for the production of ethanol and xylitol by the newly isolated NIRE-GX1 yeast. In: Kumar S, Sarma AK, Tyagi SK, Yadav YK (eds) Recent advances in bio-energy research, vol 3. SSS-NIRE, Kapurthala, pp 175–182
Kumar S, Dheeran P, Singh SP, Mishra IM, Adhikari DK (2015) Bioprocessing of bagasse hydrolysate for ethanol and xylitol production using thermotolerant yeast. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:39–47
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Karhuma K, Jeppsson M, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) Metabolic engineering for pentose utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:147–177
Runquist D, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Rådström P (2010) Comparison of heterologous xylose transporters in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:5
Sharma NK, Behera S, Arora R, Kumar S (2014) Genetic modification in yeast for simultaneous utilization of glucose and xylose. In: Kumar S, Sarma AK, Tyagi SK, Yadav YK (eds) Recent advances in bioenergy research, vol III. SSS-NIRE, Kapurthala, pp 194–207
Jeffries TW (1983) Utilization of xylose by bacteria, yeasts and fungi. Adv Biochem Eng Biotech 27:1–31
Wyman CE (1996) Handbook on bioethanol: production and utilization. Taylor Francis, Washington
Maleszka R, Schneider H (1982) Fermentation of d-xylose, xylitol and d-xylulose by yeasts. Can J Microbiol 28:360–363
Kotter P, Ciriacy M (1993) Xylose fermentation by Sacchaaromyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Katahira S, Mizuike A, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2006) Ethanol fermentation from lignocellulosic hydrolysate by a recombinant xylose- and cello-oligosaccharides assimilating yeast strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:1136–1143
Kuhad RC, Gupta R, Khasa YP, Singh A, Zhang YHP (2011) Bioethanol production from pentose sugars: current status and future prospects. Ren Sus Energy Rev 15:4950–4962
Sedlak M, Ho NW (2004) Characterization of the effectiveness of hexose transporters for transporting xylose during glucose and xylose co-fermentation by a recombinant Saccharomyces yeast. Yeast 21:671–684
Young E, Poucher A, Comer A, Bailey A, Alper H (2011) Functional survey for heterologous sugar transport proteins, using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a host. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3311–3319
Farwick A, Bruder S, Schadeweg V, Oreb M, Boles E (2014) Engineering of yeast hexose transporters to transport d-xylose without inhibition by d-glucose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:5159–5164
Yablochkova EN, Bolotnikova OI, Mikhaĭlova NP, Nemova NN, Ginak AI (2003) The activity of xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase in yeasts. Microbiol 72:414–417
Yablochkova EN, Bolotnikova OI, Mikhaĭlova NP, Nemova NN, Ginak AI (2004) Activity of the key enzymes in xylose assimilating yeasts at different rates of oxygen transfer to the fermentation medium. Microbiol 73:129–133
Arora R, Behera S, Kumar S (2015) Bioprospecting thermophilic/thermotolerant microbes for production of lignocellulosic ethanol: a future perspective. Renew Sust Energy Rev 51:699–717
Rodrussamee N, Lertwattanasakul N, Hirata K, Suprayogi Limtong S, Kosaka T, Yamada M (2011) Growth and ethanol fermentation ability on hexose and pentose sugars and glucose effect under various conditions in thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(1573):1586
Zhang B, Li L, Zhang J, Gao X, Wang D, Hong J (2013) Improving ethanol and xylitol fermentation at elevated temperature through substitution of xylose reductase in Kluyveromyces marxianus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:305–316
Signori L, Passolunghi S, Ruohonen L, Porro D, Branduardi P (2014) Effect of oxygenation and temperature on glucosexylose fermentation in Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS712 strain. Microb Cell Fact 13:51
Kuyper M, Toirkens MJ, Diderich JA, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005) Evolutionary engineering of mixed-sugar utilization by a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. FEMS Yeast Res 5:925–934
Zhou H, Cheng JS, Wang BL, Fink GR, Stephanopoulos G (2012) Xylose isomerase overexpression along with engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway and evolutionary engineering enable rapid xylose utilization and ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14:611–622
Kuyper M, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2004) Minimal metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient anaerobic xylose fermentation: a proof of principle. FEMS Yeast Res 4:655–664
Liu E, Hu Y (2010) Construction of a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain by combined approaches of genetic engineering, chemical mutagenesis and evolutionary adaptation. Biochem Eng J 48:204–210
Cadiere A, Ortiz-Julien A, Camarasa C, Dequin S (2011) Evolutionary engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae wine yeast strains with increased in vivo flux through the pentose phosphate pathway. Metab Eng 13:263–271
Koppram R, Albers E, Olsson L (2012) Evolutionary engineering strategies to enhance tolerance of xylose utilizing recombinant yeast to inhibitors derived from spruce biomass. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:32
Shen Y, Chen X, Peng B, Chen L, Hou J, Bao X (2012) An efficient xylose-fermenting recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain obtained through adaptive evolution and its global transcription profile. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1079–1091
Lee SM, Jellison T, Alper HS (2014) Systematic and evolutionary engineering of a xylose isomerase-based pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient conversion yields. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:122
Liu ZL, Slininger PJ, Dien BS, Berhow MA, Kurtzman CP, Gorsich SW (2004) Adaptive response of yeasts to furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and new chemical evidence for HMF conversion to 2, 5-bis-hydroxymethylfuran. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:345–352
Agbogbo FK, Haagensen FD, Milam D, Wenger KS (2008) Fermentation of acid pretreated corn stover to ethanol without detoxification using Pichia stipitis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 145:53–58
Zhu JJ, Yong Q, Xu Y, Chen S-X, Yu SY (2009) Adaptation fermentation of Pichia stipitis and combination detoxification on steam exploded lignocellulosic prehydrolyzate. Nat Sci 1:47–54
Wisselink HW, Toirkens MJ, Wu Q, Pronk JT, van Maris AJ (2009) A novel evolutionary engineering approach for accelerated utilization of glucose, xylose and arabinose mixtures by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:907–914
Diao L, Liu Y, Qian F, Yang J, Jiang Y, Yang S (2013) Construction of fast xylose-fermenting yeast based on industrial ethanol-producing diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae by rational design and adaptive evolution. BMC Biotechnol 13:110
Arora R, Behera S, Sharma NK, Kumar S (2015) A new search for thermotolerant yeast, its characterization and optimization using response surface methodology for ethanol production. Front Microbiol 6:1–16
Bailey JE, Ollis DF (1986) Biochemical engineering fundamentals. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sonderegger M, Sauer U (2003) Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for anaerobic growth on xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1990–1998
Beales N (2004) Adaptation of microorganisms to cold temperatures, weak acid preservatives, low pH and osmotic stress: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 3:1–20
Brejning J, Arneborg N, Jaspersen L (2005) Identification of genes and proteins induced during lag and early exponential phase of lager brewing yeasts. J Appl Microbiol 98:261–271
Vriesekoop F, Pamment NB (2005) Acetaldehyde addition and pre-adaptation to the stressor together virtually eliminated the ethanol-induced lag phase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Lett Appl Microbiol 41:424–427
Mihoub F, Mistou MY, Guillot A, Leveau JY, Boubetra A, Billaux F (2003) Cold adaptation of Escherichia coli: microbiological and proteomic approaches. Int J Food Microbiol 89:171–184
Landaeta R, Aroca G, Acevedo F, Teixeira JA, Mussatto SI (2013) Adaptation of a flocculent Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to lignocellulosic inhibitors by cell recycle batch fermentation. Appl Energy 102:124–130
Slininger PJ, Shea-Andersh MA, Thompson SR, Dien BS, Kurtzman CP, Balan V, da Costa Sousa L, Uppugundla N, Dale BE, Cotta MA (2015) Evolved strains of Scheffersomyces stipitis achieving high ethanol productivity on acid- and base-pretreated biomass hydrolyzate at high solids loading. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:60
Nigam JN (2001) Development of xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis for ethanol production through adaptation on hardwood hemicellulose acid prehydrolysate. J Appl Microbiol 90:208–215
Martin C, Marcet M, Almazan O, Jonsson LJ (2007) Adaptation of a recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to a sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate with high content of fermentation inhibitors. Biores Techn 98:1767–1773
Pereira SR, Sanchez I, Nogue V, Frazao CJ, Serafim LS, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Xavier AM (2015) Adaptation of Scheffersomyces stipitis to hardwood spent sulfite liquor by evolutionary engineering. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:50
Silva CJ, Roberto IC (2001) Improvement of xylitol production by Candida guilliermondii FTI 20037 previously adapted to rice straw hemicellulosic hydrolysate. Lett Appl Microbiol 32:248–252
Matsushika A, Oguri E, Sawayama S (2010) Evolutionary adaptation of recombinant shochu yeast for improved xylose utilization. J Biosci Bioeng 110:102–105
Wahlbom CF, van Zyl WH, Jönsson LJ, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Otero RR (2003) Generation of the improved recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae TMB 3400 by random mutagenesis and physiological comparison with Pichia stipitis CBS 6054. FEMS Yeast Res 3:319–326
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (N. K. Sharma) is very thankful to Sardar Swaran Singh National Institute of Bio-Energy, Kapurthala for providing Junior Research Fellowship and I. K. Gujral Punjab Technical University, Kapurthala for providing Ph.D. registration (Pro. reg. 1422002). Authors are also gratefully acknowledged the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Govt. of India for providing financial supports to carry out the research activities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
N. K. Sharma and S. Behera equal contributors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, N.K., Behera, S., Arora, R. et al. Enhancement in xylose utilization using Kluyveromyces marxianus NIRE-K1 through evolutionary adaptation approach. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39, 835–843 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1563-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1563-3