Abstract
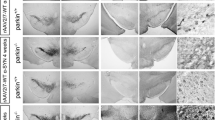
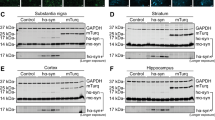
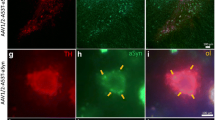
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is pathologically characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and alpha-synucleinopathy. We mimic the disease pathology with overexpression of either the human α-syn wildtype (α-syn-WT) or E46K mutant form (α-syn-E46K) in DA neurons of the SNpc in adult rats using AAV2/DJ as a viral vector for the first time. Transduction efficiency was compared to an equal virus titer expressing the green fluorescent protein (GFP). Motor skills of all animals were evaluated in the cylinder and amphetamine-induced rotation test over a total time period of 12 weeks. Additionally, stereological quantification of DA cells and striatal fiber density measurements were performed every 4 weeks after injection. Rats overexpressing α-syn-WT showed a progressive loss of DA neurons with 40% reduction after 12 weeks accompanied by a greater loss of striatal DA fibers. In contrast, α-syn-E46K led to this reduction after 4 weeks without further progress. Insoluble α-syn positive cytoplasmic inclusions were observed in both groups within DA neurons of the SNpc and VTA. In addition, both α-syn groups developed a characteristic worsening of the rotational behavior over time. However, only the α-syn-WT group reached statistically significant different values in the cylinder test. Summarizing these effects, we established a motor symptom animal model of PD by using AAV2/DJ in the brain for the first time. Thereby, overexpressing of α-syn-E46K mimicked a rather pre-symptomatic stage of the disease, while the α-syn-WT overexpressing animals imitated an early symptomatic stage of PD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert K, Voutilainen MH, Domanskyi A, Airavaara M (2017) AAV vector-mediated gene delivery to substantia nigra dopamine neurons: implications for gene therapy and disease models. Genes (Basel):8
Albert K, Voutilainen MH, Domanskyi A, Piepponen TP, Ahola S, Tuominen RK, Richie C, Harvey BK, Airavaara M (2018) Downregulation of tyrosine hydroxylase phenotype after AAV injection above substantia nigra: caution in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res
Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, de Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, Diep L, Keim PS, Shen X, Chataway T, Schlossmacher MG, Seubert P, Schenk D, Sinha S, Gai WP, Chilcote TJ (2006) Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 281:29739–29752
Azeredo da Silveira S, Schneider BL, Cifuentes-Diaz C, Sage D, Abbas-Terki T, Iwatsubo T, Unser M, Aebischer P (2009) Phosphorylation does not prompt, nor prevent, the formation of alpha-synuclein toxic species in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 18:872–887
Bergstrom BP, Garris PA (2003) “Passive stabilization” of striatal extracellular dopamine across the lesion spectrum encompassing the presymptomatic phase of Parkinson’s disease: a voltammetric study in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat. J Neurochem 87:1224–1236
Burger C, Gorbatyuk OS, Velardo MJ, Peden CS, Williams P, Zolotukhin S, Reier PJ, Mandel RJ, Muzyczka N (2004) Recombinant AAV viral vectors pseudotyped with viral capsids from serotypes 1, 2, and 5 display differential efficiency and cell tropism after delivery to different regions of the central nervous system. Mol Ther 10:302–317
Burton EA, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ (2003) Gene therapy progress and prospects: Parkinson’s disease. Gene Ther 10:1721–1727
Cookson MR, van der Brug M (2008) Cell systems and the toxic mechanism(s) of alpha-synuclein. Exp Neurol 209:5–11
Decressac M, Mattsson B, Bjorklund A (2012a) Comparison of the behavioural and histological characteristics of the 6-OHDA and alpha-synuclein rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 235:306–315
Decressac M, Mattsson B, Lundblad M, Weikop P, Bjorklund A (2012b) Progressive neurodegenerative and behavioural changes induced by AAV-mediated overexpression of alpha-synuclein in midbrain dopamine neurons. Neurobiol Dis 45:939–953
Dehay B, Fernagut PO (2016) Alpha-synuclein-based models of Parkinson’s disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 172:371–378
Emmer KL, Waxman EA, Covy JP, Giasson BI (2011) E46K human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop Lewy-like and tau pathology associated with age-dependent, detrimental motor impairment. J Biol Chem 286:35104–35118
Fearnley JM, Lees AJ (1991) Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain 114(Pt 5):2283–2301
Febbraro F, Sahin G, Farran A, Soares S, Jensen PH, Kirik D, Romero-Ramos M (2013) Ser129D mutant alpha-synuclein induces earlier motor dysfunction while S129A results in distinctive pathology in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 56:47–58
Finkelstein DI, Stanic D, Parish CL, Tomas D, Dickson K, Horne MK (2000) Axonal sprouting following lesions of the rat substantia nigra. Neuroscience 97:99–112
Fredenburg RA, Rospigliosi C, Meray RK, Kessler JC, Lashuel HA, Eliezer D, Lansbury PT Jr (2007) The impact of the E46K mutation on the properties of alpha-synuclein in its monomeric and oligomeric states. Biochemistry 46:7107–7118
Gasser T (2009) Molecular pathogenesis of Parkinson disease: insights from genetic studies. Expert Rev Mol Med 11:e22
Gaugler MN, Genc O, Bobela W, Mohanna S, Ardah MT, El-Agnaf OM, Cantoni M, Bensadoun JC, Schneggenburger R, Knott GW, Aebischer P, Schneider BL (2012) Nigrostriatal overabundance of alpha-synuclein leads to decreased vesicle density and deficits in dopamine release that correlate with reduced motor activity. Acta Neuropathol 123:653–669
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Gibb WR, Poewe WH (1986) The centenary of Friederich H. Lewy 1885-1950. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 12:217–222
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Davies SW (1998) Filamentous nerve cell inclusions in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8:619–632
Gombash SE, Manfredsson FP, Kemp CJ, Kuhn NC, Fleming SM, Egan AE, Grant LM, Ciucci MR, MacKeigan JP, Sortwell CE (2013) Morphological and behavioral impact of AAV2/5-mediated overexpression of human wildtype alpha-synuclein in the rat nigrostriatal system. PLoS One 8:e81426
Gorbatyuk OS, Li S, Sullivan LF, Chen W, Kondrikova G, Manfredsson FP, Mandel RJ, Muzyczka N (2008) The phosphorylation state of Ser-129 in human alpha-synuclein determines neurodegeneration in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:763–768
Gorbatyuk OS, Li S, Nguyen FN, Manfredsson FP, Kondrikova G, Sullivan LF, Meyers C, Chen W, Mandel RJ, Muzyczka N (2010) Alpha-synuclein expression in rat substantia nigra suppresses phospholipase D2 toxicity and nigral neurodegeneration. Mol Ther 18:1758–1768
Grimm D, Lee JS, Wang L, Desai T, Akache B, Storm TA, Kay MA (2008) In vitro and in vivo gene therapy vector evolution via multispecies interbreeding and retargeting of adeno-associated viruses. J Virol 82:5887–5911
Hardy J, Cai H, Cookson MR, Gwinn-Hardy K, Singleton A (2006) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 60:389–398
Huang X, Hartley AV, Yin Y, Herskowitz JH, Lah JJ, Ressler KJ (2013) AAV2 production with optimized N/P ratio and PEI-mediated transfection results in low toxicity and high titer for in vitro and in vivo applications. J Virol Methods 193:270–277
Ibanez P, Bonnet AM, Debarges B, Lohmann E, Tison F, Pollak P, Agid Y, Durr A, Brice A (2004) Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 364:1169–1171
Kirik D, Rosenblad C, Burger C, Lundberg C, Johansen TE, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ, Bjorklund A (2002) Parkinson-like neurodegeneration induced by targeted overexpression of alpha-synuclein in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurosci 22:2780–2791
Klein RL, Dayton RD, Leidenheimer NJ, Jansen K, Golde TE, Zweig RM (2006) Efficient neuronal gene transfer with AAV8 leads to neurotoxic levels of tau or green fluorescent proteins. Mol Ther 13:517–527
Koprich JB, Johnston TH, Reyes MG, Sun X, Brotchie JM (2010) Expression of human A53T alpha-synuclein in the rat substantia nigra using a novel AAV1/2 vector produces a rapidly evolving pathology with protein aggregation, dystrophic neurite architecture and nigrostriatal degeneration with potential to model the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 5:43
Koprich JB, Johnston TH, Huot P, Reyes MG, Espinosa M, Brotchie JM (2011) Progressive neurodegeneration or endogenous compensation in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease produced by decreasing doses of alpha-synuclein. PLoS One 6:e17698
Korecka J, Schouten M, Eggers R, Ulusoy A, Bossers K, Verhaagen J (2011) Comparison of AAV serotypes for gene delivery to dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Viral Gene Therapy 21. https://doi.org/10.5772/18939
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108
Lee J, Zhu WM, Stanic D, Finkelstein DI, Horne MH, Henderson J, Lawrence AJ, O'Connor L, Tomas D, Drago J, Horne MK (2008) Sprouting of dopamine terminals and altered dopamine release and uptake in Parkinsonian dyskinaesia. Brain 131:1574–1587
Lo Bianco C, Ridet JL, Schneider BL, Deglon N, Aebischer P (2002) Alpha -synucleinopathy and selective dopaminergic neuron loss in a rat lentiviral-based model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:10813–10818
Lotharius J, Barg S, Wiekop P, Lundberg C, Raymon HK, Brundin P (2002) Effect of mutant alpha-synuclein on dopamine homeostasis in a new human mesencephalic cell line. J Biol Chem 277:38884–38894
McFarland NR, Lee JS, Hyman BT, McLean PJ (2009) Comparison of transduction efficiency of recombinant AAV serotypes 1, 2, 5, and 8 in the rat nigrostriatal system. J Neurochem 109:838–845
Nair-Roberts RG, Chatelain-Badie SD, Benson E, White-Cooper H, Bolam JP, Ungless MA (2008) Stereological estimates of dopaminergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area, substantia nigra and retrorubral field in the rat. Neuroscience 152:1024–1031
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier Inc., London
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Ratzka A, Kalve I, Ozer M, Nobre A, Wesemann M, Jungnickel J, Koster-Patzlaff C, Baron O, Grothe C (2012) The colayer method as an efficient way to genetically modify mesencephalic progenitor cells transplanted into 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Transplant 21:749–762
Reimsnider S, Manfredsson FP, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ (2007) Time course of transgene expression after intrastriatal pseudotyped rAAV2/1, rAAV2/2, rAAV2/5, and rAAV2/8 transduction in the rat. Mol Ther 15:1504–1511
Rumpel R, Hohmann M, Klein A, Wesemann M, Baumgartner W, Ratzka A, Grothe C (2015) Transplantation of fetal ventral mesencephalic progenitor cells overexpressing high molecular weight fibroblast growth factor 2 isoforms in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Neuroscience 286:293–307
Schallert T, Fleming SM, Leasure JL, Tillerson JL, Bland ST (2000) CNS plasticity and assessment of forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke, cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology 39:777–787
Shibayama-Imazu T, Okahashi I, Omata K, Nakajo S, Ochiai H, Nakai Y, Hama T, Nakamura Y, Nakaya K (1993) Cell and tissue distribution and developmental change of neuron specific 14 kDa protein (phosphoneuroprotein 14). Brain Res 622:17–25
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K (2003) Alpha-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:841
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Stanic D, Finkelstein DI, Bourke DW, Drago J, Horne MK (2003) Timecourse of striatal re-innervation following lesions of dopaminergic SNpc neurons of the rat. Eur J Neurosci 18:1175–1188
Thenganatt MA, Jankovic J (2014) Parkinson disease subtypes. JAMA Neurol 71:499–504
Timmer M, Grosskreutz J, Schlesinger F, Krampfl K, Wesemann M, Just L, Bufler J, Grothe C (2006) Dopaminergic properties and function after grafting of attached neural precursor cultures. Neurobiol Dis 21:587–606
Ulusoy A, Febbraro F, Jensen PH, Kirik D, Romero-Ramos M (2010) Co-expression of C-terminal truncated alpha-synuclein enhances full-length alpha-synuclein-induced pathology. Eur J Neurosci 32:409–422
Ungerstedt U, Arbuthnott GW (1970) Quantitative recording of rotational behavior in rats after 6-hydroxy-dopamine lesions of the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res 24:485–493
Van der Perren A, Toelen J, Carlon M, Van den Haute C, Coun F, Heeman B, Reumers V, Vandenberghe LH, Wilson JM, Debyser Z, Baekelandt V (2011) Efficient and stable transduction of dopaminergic neurons in rat substantia nigra by rAAV 2/1, 2/2, 2/5, 2/6.2, 2/7, 2/8 and 2/9. Gene Ther 18:517–527
Van der Perren A, Toelen J, Casteels C, Macchi F, Van Rompuy AS, Sarre S, Casadei N, Nuber S, Himmelreich U, Osorio Garcia MI, Michotte Y, D’Hooge R, Bormans G, Van Laere K, Gijsbers R, Van den Haute C, Debyser Z, Baekelandt V (2015) Longitudinal follow-up and characterization of a robust rat model for Parkinson’s disease based on overexpression of alpha-synuclein with adeno-associated viral vectors. Neurobiol Aging 36:1543–1558
Van der Perren A, Casteels C, Van Laere K, Gijsbers R, Van den Haute C, Baekelandt V (2016) Development of an alpha-synuclein based rat model for Parkinson’s disease via stereotactic injection of a recombinant adeno-associated viral vector. J Vis Exp:53670
Wersinger C, Prou D, Vernier P, Niznik HB, Sidhu A (2003) Mutations in the lipid-binding domain of alpha-synuclein confer overlapping, yet distinct, functional properties in the regulation of dopamine transporter activity. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:91–105
Winner B, Jappelli R, Maji SK, Desplats PA, Boyer L, Aigner S, Hetzer C, Loher T, Vilar M, Campioni S, Tzitzilonis C, Soragni A, Jessberger S, Mira H, Consiglio A, Pham E, Masliah E, Gage FH, Riek R (2011) In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:4194–4199
Wu Z, Asokan A, Samulski RJ (2006) Adeno-associated virus serotypes: vector toolkit for human gene therapy. Mol Ther 14:316–327
Yamada M, Iwatsubo T, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H (2004) Overexpression of alpha-synuclein in rat substantia nigra results in loss of dopaminergic neurons, phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein and activation of caspase-9: resemblance to pathogenetic changes in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 91:451–461
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gomez Tortosa E, del Ser T, Munoz DG, de Yebenes JG (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173
Zigmond MJ, Abercrombie ED, Berger TW, Grace AA, Stricker EM (1990) Compensations after lesions of central dopaminergic neurons: some clinical and basic implications. Trends Neurosci 13:290–296
Zolotukhin S, Potter M, Zolotukhin I, Sakai Y, Loiler S, Fraites TJ Jr, Chiodo VA, Phillipsberg T, Muzyczka N, Hauswirth WW, Flotte TR, Byrne BJ, Snyder RO (2002) Production and purification of serotype 1, 2, and 5 recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. Methods 28:158–167
Acknowledgements
We thank Hella Brinkmann, Silke Fischer, Natascha Heidrich, Kerstin Kuhlemann and Maike Wesemann (Institute of Neuroanatomy and Cell Biology) for excellent technical assistance.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Konrad-Adenauer-Stiftung (Friederike Freiin von Hövel).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the German Animal Protection Act (33.12-42502-04-15/1993). This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Hövel, F.F., Rumpel, R., Ratzka, A. et al. AAV2/DJ-mediated alpha-synuclein overexpression in the rat substantia nigra as early stage model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Tissue Res 378, 1–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03013-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03013-x