Abstract
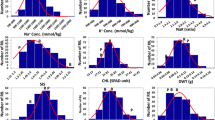
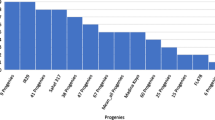
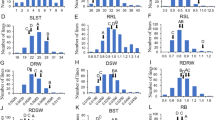
Breeding for salt tolerance is the most promising approach to enhance the productivity of saline prone areas. However, polygenic inheritance of salt tolerance in rice acts as a bottleneck in conventional breeding for salt tolerance. Hence, we set our goals to construct a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based molecular map employing high-throughput SNP marker technology and to investigate salinity tolerant QTLs with closest flanking markers using an elite rice background. Seedling stage salinity responses were assessed in a population of 281 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from the cross between At354 (salt tolerant) and Bg352 (salt susceptible), by 11 morpho-physiological indices under a hydroponic system. Selected extreme 94 RILs were genotyped using Illumina Infinium rice 6K SNP array and densely saturated molecular map spanning 1460.81 cM of the rice genome with an average interval of 1.29 cM between marker loci was constructed using 1135 polymorphic SNP markers. The results revealed 83 significant QTLs for 11 salt responsive traits explaining 12.5–46.7 % of phenotypic variation in respective traits. Of them, 72 QTLs responsible for 10 traits were co-localized together forming 14 QTL hotspots at 14 different genomic regions. The all QTL hotspots were flanked less than 1 Mb intervals and therefore the SNP loci associated with these QTL hotspots would be important in candidate gene discovery for salt tolerance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrama HAS, Moussa ME (1996) Mapping QTLs in breeding for drought tolerance in maize. Euphytica 91:89–97
Ahmadi J, Fotokian M (2011) Identification and mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) using SSR markers. Iran J Biotechnol 9(1):21–30
Ahmadi N, Negrao S, Katsantonis D, Frouin J, Ploux J, Letourmy P, Droc G, Babo P, Trindade H, Bruschi G, Greco R, Oliveira MM, Piffanelli P, Courtois B (2011) Targeted association analysis identified japonica rice varieties achieving Na+/K+ homeostasis without the allelic make-up of the salt tolerant indica variety Nona Bokra. Theor Appl Genet 123:881–895
Banuelos MA, Garciadeblas B, Cubero B, Rodriguez-Navarro A (2002) Inventory and functional characterization of the HAK potassium transporters of rice. Plant Physiol 130:784–795
Bonilla P, Dvorak J, Mackill DJ, Deal K, Gregorio G (2002) RLFP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Philipp Agric Sci 85:68–76
Boonburapong B, Buaboocha T (2007) Genome-wide identification and analyses of the rice calmodulin and related potential calcium sensor proteins. BMC Plant Biol 7. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-7-4
Champoux MC, Wang G, Sarkarung S, Mackill DJ, O-Toole JC, Huang N, McCouch SR (1995) Locating genes associated with root morphology and drought avoidance in rice via linkage to molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:969–981
Chen F, Li Q, Sun L, He Z (2006) The rice 14-3-3 gene family and its involvement in responses to biotic and abiotic stress. DNA Res 13:53–63
Chen X, WangY Lv B, Li J, Luo L, Lu S, Zhang X, Ma H, Ming F (2014) The NAC family transcription factor OsNAP confers abiotic stress response through the ABA Pathway. Plant Cell Physiol 55(3):604–619
Churchill G, Doerg R (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142:285–294
Flowers TJ, Koyama ML, Flowers SA, Sudhakar C, Singh KP, Yeo AR (2000) QTL: their place in engineering tolerance of rice to salinity. J Exp Bot 51(342):99–106
Food and Agriculture Organization (2016) Soils portal; extent of salt-affected soils. http://www.fao.org/soils-portal/soilmanagement/management-ofsome-problem-soils/salt-affected-soils/more-information-on-salt-affected-soils/en. Accessed 20 Jun 2015
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Hara N, Toki S, Tanaka Y (2010) Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes. Planta 233(1):175–188
Gimhani DR, Kottearachchi NS, Samarasinghe WLG (2014) Microsatellite marker based hybridity assessment for salinity tolerance in rice. J Agricul Sci 9(2):96–100. doi:10.4038/jas.v9i2.6914
Golldack D, Quigley F, Michalowski CB, Kamasani UR, Bohnert HJ (2003) Salinity stress-tolerant and sensitive rice (Oryza sativa L.) regulate AKT1-type potassium channel transcripts differently. Plant Mol Biol 51:71–81
Gregorio GB (1997) Tagging salinity tolerance genes in rice using amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP). PhD thesis, University of the Philippines, Los Banos
Gregorio GB, Senadhira D, Mendoza RD (1997) Screening rice for salinity tolerance. IRRI Discussion Paper Series No 22-International Rice Research Institute Los Banos Laguna Philippines, 13
Gupta B, Huang B (2014) Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological biochemical and molecular characterization. Int J Genom 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/701596
Haq TU, Gorham J, Akhtar J, Akhtar N, Steele KA (2010) Dynamic quantitative trait loci for salt stress components on chromosome 1 of rice. Funcl Plant Biol 37:634–645
Horie T, Karahara I, Katsuhara M (2012) Salinity tolerance mechanisms in glycophytes: an overview with the central focus on rice plants. Rice 5. doi:10.1186/1939-8433-5-11
Huang XY, Chao DY, Gao JP, Zhu MZ, Shi M, Lin HX (2009) A previously unknown zinc finger protein, DST, regulates drought and salt tolerance in rice via stomatal aperture control. Genes Dev 23(15):1805–1817
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (IRGSP) (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436(7052):793–800
Ismail AM, Heuer S, Thomson MJ, Wissuwa M (2007) Genetic and genomic approaches to develop rice germplasm for problem soils. Plant Mol Biol 65:547–570
Jena KK, Mackill DJ (2008) Molecular markers and their use in marker-assisted selection in rice. Crop Sci 48:1266–1276
Joehanes R, Nelson JC (2008) QGene 4.0 an extensible Java QTL-analysis platform. Bioinformatics 24:2788–2789
Kim DM, Ju HG, Kwon TR, Oh CS, Ahn SN (2009) Mapping QTLs for salt tolerance in an introgression line population between japonica cultivars in rice. J Crop Sci Biotech 12(3):121–128
Koyama LM, Levesley A, Koebner RMD, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 125:406–422
Lebreton C, Lazic-Jancic V, Steed A, Pekic S (1995) Identification of QTL for drought responses in maize and their use in testing causal relationships between traits. J Exp Bot 46(7):853–865
Lee SY, Ahn JH, Cha YS, Yun DW, Lee MC, Ko JC, Lee KS, Eun MY (2007) Mapping QTLs related to salinity tolerance of rice at the young seedling stage. Plant Breed 126(1):43–46
Li W, He M, Wang J, Wang Y (2013) Zinc finger protein (ZEP) in plants—a review. Plant Omics Journal 6(6):474–480
Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004) QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 108(2):253–260
Maas EV, Hoffman GJ (1977) Crop salt tolerance-current assessment. J Irrig Drain Div ASCE 103(2):115–134
Mackill DJ (2007) Molecular markers and marker-assisted selection in rice. In: Varshney RK, Tuberosa R (eds) Genomics assisted crop improvement. Springer, New York, pp 147–168
Marathi B, Guleria S, Mohapatra T, Parsad R, Mariappan N, Kurungara VK, Atwal SS, Prabhu KV, Singh NK, Singh AK (2012) QTL analysis of novel genomic regions associated with yield and yield related traits in new plant type based recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 12. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-12-137
Martinez-Atienza J, Jiang X, Garciadeblas B, Mendoza I, Zhu JK, Pardo JM, Quintero FJ (2007) Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 143:1001–1012
Matsukura S, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, Todaka D, Ito Y, Maruyama K, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010) Comprehensive analysis of rice DREB2-type genes that encode transcription factors involved in the expression of abiotic stress-responsive genes. Mol Genet Genom 283:185–196
McCouch SR, Committee on Gene Symbolization Nomenclature and Linkage Rice Genetics Cooperative (CGSNL) (2008) Gene nomenclature system for rice. Rice 1:72–84
McCouch SR, Chen X, Panaud O, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho Y, Huang N, Ishii T, Blair M (1997) Microsatellite marker development mapping and applications in rice genetics and breeding. Plant Mol Biol 35(1):89–99
Minitab 17 Statistical Software (2010) (Computer software) Minitab Inc, State College PA
Moradi F, Ismail AM (2007) Responses of photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and ROS scavenging system to salt stress during seedling and reproductive stages in rice. Ann Bot 99:1161–1173
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant. DNA Nucl Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nguyen VT, Nguyen BD, Sarkarung S, Martinez C, Paterson AH, Nguyen HT (2002) Mapping of genes controlling aluminum tolerance in rice: comparison of different genetic backgrounds. Mol Genet Genom 267:772–780
Prasad SR, Bagli PG, Hittalmani S, Shashidhar HE (1999) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with seedling tolerance of salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr Sci 78:162–164
Qi D, Guo G, Lee M, Zhang J, Cao G, Zhang S, Suh S, Zhou Q, Han L (2008) Identification of quantitative trait loci for the dead leaf rate and the seedling dead rate under alkaline stress in rice. J Genet Genom 35:299–305
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li GL, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37:1141–1146
Sabouri H, Sabouri A (2008) New evidence of QTLs attributed to salinity tolerance in rice. Afr J Biotechnol 7(24):4376–4383
Sabouri H, Rezai AM, Moumeni A, Kavousi M, Katouzi M, Sabouri A (2009) QTLs mapping of physiological traits related to salt tolerance in young rice seedlings. Biologia Plantaru 53(4):657–662
Sandhu N, Singh A, Dixit S, Cruz MS, Maturan PC, Jain RK, Kumar A (2014) Identification and mapping of stable QTL with main and epistasis effect on rice grain yield under upland drought stress. BMC Genet 15:63. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-15-63
Sanguineti MC, Tuberosa R, Landi P, Salvi S (1999) QTL analysis of drought-related traits and grain yield in relation to genetic variation for leaf abscisic acid concentration in field-grown maize. J Exp Bot 50:1289–1297
Schadt EE, Monks SA, Drake TA, Lusis AJ, Che N, Collnayo V, Ruff TG, Milligan SB, Lamb JR, Cavet G, Linsley PA, Mao M, Stoughton RB, Friend SH (2003) Genetics of gene expression surveyed in maize mouse and man. Nature 422(6929):297–302
Singh RK, Flowers TJ (2010) The physiology and molecular biology of the effects of salinity on rice. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop stress, 3rd edn. Taylor and Francis, Florida, pp 901–942
Singh BD, Singh AK (2015) Marker assisted plant breeding: Principles and practices. Springer
Singh RK, Gregorio GB, Jain RK (2007) QTL mapping for salinity tolerance in rice. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 13:87–99
Sirisena DN, Rathnayake WMUK, Herath HMA (2010) Productivity enhancement of saline paddy fields in Angiththamkulam Yaya, Sri Lanka a case study. Pedologist 96–100
Sun LJ, Huang L, Li DY, Zhang HJ, Song FM (2014) Comprehensive expression analysis suggests overlapping of rice OsWRKY transcription factor genes during abiotic stress responses. Plant Physiol J 50(11):1651–1658
Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS (2013) Using multivariate statistics. Pearson, California
Takehisa H, Shimodate T, Fukuta Y, Ueda T, Yano M, Ymaya T, Kameya T (2004) Identification of quantitative trait loci for plant growth of rice in paddy field flooded with salt water. Field Crop Res 89(1):85–95
Tan C, Han Z, Yu H, Zhan W, Xie W, Chen X, Zhao H, Zhou F, Xing Y (2013) QTL scanning for rice yield using a whole genome SNP array. J Genet Genomics 40(12):629–638
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100(5):697–712
Thomson MJ (2014) High-throughput SNP genotyping to accelerate crop improvement. Plant Breed Biotech 2(3):195–212
Thomson MJ, De-Ocampo M, Egdane J, Rahman MA, Sajise AG, Adorada DL, Tumimbang-Raiz E, Blumward E, Seraj ZI, Singh RK, Gregorio GB, Ismail AM (2010) Characterizing the Saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice. Rice 3(2):148–160
Thomson MJ, Zhao K, Wright M, McNally KL, Rey J, Tung C, Reynolds A, Scheffler B, Eizenga G, McClung A, Kim H, Ismail AM, De-Ocampo M, Mojica C, Reveche MY, Dilla-Ermita CJ, Mauleon R, Leung H, Bustamante C, McCouch SR (2011) High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping for breeding applications in rice using the BeadXpress platform. Mol Breed 29(4):875–886
Tuberosa R, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Giuliani MM (2002) Identification of QTLs for root characteristics in maize grown in hydroponics and analysis of their overlap with QTLs for grain yield in the field at two water regimes. Plant Mol Biol 48(5):697–712
Veldboom LR, Lee M, Woodman WL (1994) Molecular-marker facilitated studies in an elite maize population: linkage analysis and determination of QTL for morphological traits. Theor Appl Genet 88:7–16
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC
Wijerathna YMAM, Kottearachchi NS, Gimhani DR, Sirisena DN (2014) Exploration of relationship between fragrant gene and growth performances of fragrant rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling under salinity stress. J Exp Biol Agricul Sci 1(2):7–12
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan J, Tanksley SD (1996) Identification of QTLs affecting traits of agronomic importance in a recombinant inbred population derived from a sub specific rice cross. Theor Appl Genet 92:230–244
Xiao YN, Li XH, George ML, Li MS (2005) Quantitative trait locus analysis of drought tolerance and yield in maize in China. Plant Mol Biol Rep 23:155–165
Xing Y, Tan Y, Hua J, Sun X, Xu C, Zhang Q (2002) Characterization of the main effects epistatic effects and their environmental interactions of QTLs on the genetic basis of yield traits in rice. Theor Appl Genet 105:248–257
Ye C, Argayoso MA, Redon ED, Sierra SN, Laza MA, Dilla CJ, Mo Y, Thomson MJ, Chin J, Delavin CB, Diaz GQ, Hernandez JE (2011) Mapping QTL for heat tolerance at flowering stage in rice using SNP markers. Plant Breed 131(1):33–41
Yeo AR, Flowers TJ (1986) Salinity resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and a pyramiding approach to breeding varieties for saline soils. Aust J Plant Physiol 13:161–173
Yeo AR, Yeo ME, Flowers SA, Flowers TJ (1990) Screening of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for physiological characters contributing to salinity resistance, and their relationship to overall performance. Theor Appl Genet 79:377–384
Zeng L, Shannon MC (2000) Salinity effects on the seedling growth and yield components of rice. Crop Sci 40:996–1003
Zheng BS, Yang L, Zhang WP, Mao CZ, Wu YR, Yi KK, Liu FY, Wu P (2003) Mapping QTLs and candidate genes for rice root traits under different water-supply conditions and comparative analysis across three populations. Theor Appl Genet 107(8):1505–1515
Acknowledgments
Global Rice Science scholarship 2011, awarded by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) is greatly appreciated for providing financial support and research facilities. National Science Foundation (NSF) in Sri Lanka is also acknowledged for financial support during initial phase of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Global Rice Science scholarship 2011, awarded by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and the National Science Foundation (NSF) in Sri Lanka (NSF/RG/2011/BT/02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gimhani, D.R., Gregorio, G.B., Kottearachchi, N.S. et al. SNP-based discovery of salinity-tolerant QTLs in a bi-parental population of rice (Oryza sativa). Mol Genet Genomics 291, 2081–2099 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1241-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1241-9