Abstract
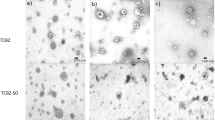
A study has been carried out to investigate whether the action of triclabendazole (TCBZ) against Fasciola hepatica is altered by inhibition of drug metabolism. The cytochrome P450 (CYP 450) enzyme pathway was inhibited using ketoconazole (KTZ) to see whether a TCBZ-resistant isolate could be made more sensitive to TCBZ action. The Oberon TCBZ-resistant and Cullompton TCBZ-susceptible isolates were used for these experiments. The CYP 450 system was inhibited by a 2-h pre-incubation in ketoconazole (40 μM), then incubated for a further 22 h in NCTC medium containing either KTZ, KTZ + nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) (1 nM), KTZ + NADPH + TCBZ (15 μg/ml), or KTZ + NADPH + triclabendazole sulphoxide (TCBZ.SO; 15 μg/ml). Changes to fluke ultrastructure following drug treatment and metabolic inhibition were assessed using transmission electron microscopy. After treatment with either TCBZ or TCBZ.SO on their own, there was greater disruption to the TCBZ-susceptible than TCBZ–resistant isolate. However, co-incubation with KTZ + TCBZ, but more particularly KTZ + TCBZ.SO, led to more severe changes to the TCBZ-resistant isolate than with each drug on its own: in the syncytium, for example, there was severe swelling of the basal infolds and their associated mucopolysaccharide masses, accompanied by an accumulation of secretory bodies just below the apex. Golgi complexes were greatly reduced or absent in the tegumental cells and the synthesis, production, and transport of secretory bodies were badly disrupted. With the TCBZ-susceptible Cullompton isolate, there was limited potentiation of drug action. The results support the concept of altered drug metabolism in TCBZ-resistant flukes and this process may play a role in the development of drug resistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez LI, Solana HD, Mottier ML, Virkel GL, Fairweather I, Lanusse CE (2005) Altered drug influx/efflux and enhanced metabolic activity in triclabendazole-resistant liver flukes. Parasitology 131:501–510
Alvarez AI, Merino G, Molina AJ, Pulido MM, McKellar QA, Prieto JG (2006) Role of ABC transporters in veterinary drug research and parasite resistance. Curr Drug Deliv 3:199–206
Alvinerie M, Dupuy J, Kiki-Mvouaka S, Sutra J-F, Lespine A (2008) Ketoconazole increases the plasma levels of ivermectin in sheep. Vet Parasitol 157:117–122
Anderson HR, Fairweather I (1995) Fasciola hepatica: ultrastructural changes to the tegument of juvenile flukes following incubation in vitro with the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide. Int J Parasitol 25:319–333
Bartley DJ, Mc Allister H, Bartley Y, Dupuy J, Menez C, Alvinerie M, Jackson F, Lespine A (2009) P-glycoprotein interfering agents potentiate ivermectin susceptibility in ivermectin sensitive and resistant isolates of Teladorsagia circumcinta and Haemonchus contortus. Parasitology 136:1081–1088
Benchaoui HA, McKellar QA (1996) Interaction between fenbendazole and piperonyl butoxide: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic implications. J Pharm Pharmacol 48:753–759
Bourrie M, Meunier V, Berger Y, Fabre G (1996) Cytochrome P450 isoform inhibitors as a tool for the investigation of metabolic reactions catalyzed by human liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:321–332
Buchanan JF, Fairweather I, Brennan GP, Trudgett A, Hoey EM (2003) Surface and internal tegumental changes induced by treatment in vitro with the sulphoxide metabolite of albendazole (“Valbazen”). Parasitology 126:141–153
Cvilink V, Lamka J, Skálová L (2009) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and metabolism of anthelmintics in helminths. Drug Metab Rev 41:8–26
Devine C, Brennan GP, Lanusse CE, Alvarez LI, Trudgett A, Hoey E, Fairweather I (2009) Effect of the metabolic inhibitor, methimazole on the drug susceptibility of a triclabendazole-resistant isolate of Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 136:183–192
Devine C, Brennan GP, Lanusse CE, Alvarez LI, Trudgett A, Hoey E, Fairweather I (2010a) Inhibition of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism enhances ex vivo susceptibility of Fasciola hepatica to triclabendazole. Parasitology 137:871–880
Devine C, Brennan GP, Lanusse CE, Alvarez LI, Trudgett A, Hoey E, Fairweather I (2010b) Potentiation of triclabendazole sulphoxide-induced tegumental disruption by methimazole in a triclabendazole-resistant isolate of Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 106:1351–1363
Devine C, Brennan GP, Lanusse CE, Alvarez LI, Trudgett A, Hoey E, Fairweather I (2010c) Enhancement of the drug susceptibility of a triclabendazole-resistant isolate of Fasciola hepatica using the metabolic inhibitor ketoconazole. Parasitol Res 107:337–353
Devine C, Brennan GP, Lanusse CE, Alvarez LI, Trudgett A, Hoey EM, Fairweather I (2011a) Piperonyl butoxide enhances triclabendazole action against triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 138:224–236
Devine C, Brennan GP, Lanusse CE, Alvarez LI, Trudgett A, Hoey E, Fairweather I (2011b) Enhancement of triclabendazole action in vivo against a triclabendazole–resistant isolate of Fasciola hepatica by co-treatment with ketoconazole. Vet Parasitol. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.12.002
Dupuy J, Larrieu G, Sutra JF, Lespine A, Alvinerie M (2003) Enhancement of moxidectin bioavailability in lamb by a natural flavonoid: quercetin. Vet Parasitol 112:337–347
Fairweather I (2011) Liver fluke isolates: a question of provenance. Vet Parasitol 176:1–8
Fairweather I, Anderson HR, Threadgold LT (1986) Fasciola hepatica: tegumental changes induced in vitro by the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide. Exp Parasitol 62:336–348
Fairweather I, Threadgold LT, Hanna REB (1999) Development of Fasciola hepatica in the mammalian host. In: Dalton JP (ed) Fasciolosis. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 47–111
Fairweather I, Meaney M, Savage J, Brennan G, Hoey E, Trudgett A (2009) Do drug efflux pumps play a role in the resistance of Fasciola hepatica to triclabendazole? 23rd International Conference of the WAAVP, Calgary Canada, August 2009. Abst. CS35.2
Halferty L, Brennan GP, Trudgett A, Hoey EM, Fairweather I (2009a) The relative activity of triclabendazole metabolites against the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol 159:126–138
Halferty L, O’Neill JF, Brennan GP, Keiser J, Fairweather I (2009b) Electron microscopical study to assess the in vitro effects of the synthetic trioxolane OZ78 against the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 136:1325–1337
Hennessy DR, Lacey E, Steel JW, Prichard RK (1987) The kinetics of triclabendazole disposition in sheep. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 10:64–72
Hugnet C, Lespine A, Alvinerie M (2007) Multiple oral dosing of ketoconazole increases dog exposure to ivermectin. J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci 10:311–318
James CE, Davey MW (2009) Increased expression of ABC transport proteins is associated with ivermectin resistance in the model nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Int J Parasitol 39:213–220
James CE, Hudson AL, Davey MW (2009) An update on P-glycoprotein and drug resistance in Schistosoma mansoni. Trends Parasitol 25:538–539
Kageyama M, Namiki H, Fukushima H, Ito Y, Shibata N, Takada K (2005) In vivo effects of cyclosporine A and ketoconazole on the pharmacokinetics of representative substrates for P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 28:316–322
Kerboeuf D, Blackhall W, Kaminsky R, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G (2003) P-glycoprotein in helminths: function and perspectives for anthelmintic treatment and reversal of resistance. Int J Antimicrob Agents 22:332–346
Kim RB, Wandel C, Leake B, Cvetkovic M, Fromm MF, Dempsye PJ, Roden MM, Belas F, Chaudhary AK, Roden DM, Wood AJ, Wilkinson GR (1999) Interrelationship between substrates and inhibitors of human CYP3A and P-glycoprotein. Pharm Res 16:408–414
Lanusse CE, Prichard RK (1993) Clinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of benzimidazole anthelmintics in ruminants. Drug Metab Rev 25:235–279
Lanusse CE, Gascon LH, Prichard RK (1995) Influence of the antithyroid compound methimazole on the plasma disposition of fenbendazole and oxfendazole in sheep. Res Vet Sci 58:222–226
Lespine A, Alvinerie M, Vercruysse J, Prichard RK, Geldhof P (2008) ABC transporter modulation: a strategy to enhance the activity of macrocyclic lactone anthelmintics. Trends Parasitol 24:293–298
Lespine A, Dupuy J, Alvinerie M, Comera C, Nagy T, Krajcsi P, Orlowski S (2009) Interaction of macrocyclic lactones with the multidrug transporters: the bases of the pharmacokinetics of lipid-like drugs. Curr Drug Metab 10:272–288
Lifschitz A, Entrocasso C, Alvarez L, Lloberas M, Ballent M, Manazza G, Virkel G, Borda B, Lanusse C (2010) Interference with P-glycoprotein improves ivermectin activity against adult resistant nematodes in sheep. Vet Parasitol 172:291–298
López-García ML, Torrado S, Torrado S, Martínez AR, Bolás F (1998) Methimazole-mediated enhancement of albendazole oral bioavailability and anthelmintic effects against parenteral stages of Trichinella spiralis in mice: the influence of the dose-regime. Vet Parasitol 75:209–219
McConville M, Brennan GP, McCoy M, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Ibarra F, Fairweather I (2006) Adult triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: surface and subsurface tegumental responses to in vitro treatment with the sulphoxide metabolite of the experimental fasciolicide compound alpha. Parasitology 133:195–208
McConville M, Brennan GP, McCoy M, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Ibarra F, Fairweather I (2007) Immature triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: tegumental responses to in vitro treatment with the sulphoxide metabolite of the experimental fasciolicide compound alpha. Parasitol Res 100:365–377
McConville M, Brennan GP, Flanagan A, Edgar HWJ, McCoy M, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Fairweather I (2008) Surface and internal tegumental changes in juvenile Fasciola hepatica following treatment in vivo with the experimental fasciolicide, compound alpha. Vet Parasitol 153:52–64
McConville M, Brennan GP, Flanagan A, Edgar HWJ, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Fairweather I (2009) Ultrastructural changes to the tegumental system and the gastrodermal cells in adult Fasciola hepatica following in vivo treatment with the experimental fasciolicide, compound alpha. Parasitology 136:665–680
McKinstry BD (2008) Ultrastructural changes observed in Fasciola hepatica following treatment with nitroxynil and triclabendazole, alone and in combination. PhD Thesis, The Queen’s University of Belfast
McKinstry B, Brennan GP, Halferty L, Forbes AB, Fairweather I (2007) Ultrastructural changes induced in the tegument and gut of Fasciola hepatica following in vivo and in vitro drug treatment with nitroxynil (Trodax). Parasitol Res 101:929–941
McKinstry B, Halferty L, Brennan GP, Fairweather I (2009) Morphological response of triclabendazole-resistant isolates of Fasciola hepatica to treatment in vitro with nitroxynil (Trodax). Parasitol Res 104:645–655
Meaney M, Fairweather I, Brennan GP, Forbes AB (2004) Transmission electron microscope study of the ultrastructural changes induced in the tegument and gut of Fasciola hepatica following treatment with clorsulon. Parasitol Res 92:232–241
Meaney M, Haughey S, Brennan GP, Fairweather I (2005) Ultrastructural observations on oral ingestion and trans-tegumental uptake of clorsulon by the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 95:201–212
Meaney M, Allister J, McKinstry B, McLauglin K, Brennan GP, Forbes AB, Fairweather I (2007) Fasciola hepatica: ultrastructural effects of a combination of triclabendazole and clorsulon against mature fluke. Parasitol Res 100:1091–1104
Messerli SM, Kasinathan RS, Morgan W, Spranger S, Greenberg RM (2009) Schistosoma mansoni P-glycoprotein levels increase in response to praziquantel exposure and correlate with reduced praziquantel susceptibility. Mol Biochem Parasitol 167:54–59
Molento MB, Prichard RK (1999) Effects of the multidrug-reversing agents verapamil and CL 347,099 on the efficacy of ivermectin or moxidectin against unselected and drug-selected strains of Haemonchus contortus in jirds. Parasitol Res 85:1007–1011
Mottier L, Virkel G, Solana H, Alvarez L, Salles J, Lanusse C (2004) Triclabendazole biotransformation and comparative diffusion of the parent drug and its oxidized metabolites into Fasciola hepatica. Xenobiotica 34:1043–1047
Mottier L, Alvarez L, Ceballos L, Lanusse C (2006) Drug transport mechanisms in helminth parasites: passive diffusion of benzimidazole anthelmintics. Exp Parasitol 113:49–57
Newton DJ, Wang RW, Lu AYH (1995) Cytochrome P450 inhibitors: evaluation of specificities in the in vitro metabolism of therapeutic agents by human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 23:154–158
O’Neill JF, Johnston RC, Halferty L, Brennan GP, Keiser J, Fairweather I (2009) Adult triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: morphological responses to in vivo treatment with artemether in the rat model. J Helminthol 83:151–163
Pelkonen O, Turpeinen M, Hakkola M, Honkakoski P, Hukkanen J, Raunio H (2008) Inhibition and induction of human cytochrome P450 enzymes: current status. Arch Toxicol 82:667–715
Prichard RK, Roulet A (2007) ABC transporters and β-tubulin in macrocyclic lactone resistance: prospects for marker development. Parasitology 134:1123–1132
Robinson MW, Lawson J, Trudgett A, Hoey EM, Fairweather I (2004) The comparative metabolism of triclabendazole sulphoxide by triclabendazole-susceptible and triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 92:205–210
Rogan MT, Threadgold LT (1984) Fasciola hepatica: tegumental changes as a result of lectin binding. Exp Parasitol 57:248–260
Sánchez-Bruni SFS, Fusé LA, Moreno L, Saumell CA, Álvarez LI, Fiel C, McKellar QA, Lanusse CE (2005) Changes to oxfendazole chiral kinetics and anthelmintic efficacy induced by piperonyl butoxide in horses. Equine Vet J 37:257–262
Siegsmund MJ, Cardarelli C, Akasentjevich I, Sugimoto Y, Pastan I, Gottesman MM (1994) Ketoconazole effectively reverses multidrug resistance in highly resistant KB cells. J Urol 151:485–491
Skuce PJ, Fairweather I (1990) The effect of the hydrogen ionophore closantel upon the pharmacology and ultrastructure of the adult fluke Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 76:241–250
Skuce PJ, Anderson HR, Fairweather I (1987) The interaction between the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide (DAMD) and cytochemically demonstrable Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the tegument of Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 74:161–167
Stitt A, Fairweather I (1994) The effect of the sulphoxide metabolite of triclabendazole (‘Fasinex’) on the tegument of mature and immature stages of the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 108:555–567
Threadgold LT, Brennan G (1978) Fasciola hepatica: basal infolds and associated vacuoles of the tegument. Exp Parasitol 46:300–316
Toner E, McConvery F, Brennan GP, Meaney M, Fairweather I (2009) A scanning electron microscope study on the route of entry of triclabendazole into the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 136:523–535
Toner E, Brennan GP, McConvery F, Meaney M, Fairweather I (2010a) A transmission electron microscope study on the route of entry of triclabendazole into the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 137:855–870
Toner E, Brennan GP, Hanna REB, Edgar HWJ, Fairweather I (2010b) Time-dependent changes to the tegumental system and gastrodermis of adult Fasciola hepatica following treatment in vivo with triclabendazole in the sheep host. Vet Parasitol 174:218–227
Virkel G, Lifschitz A, Sallovitz J, Pis A, Lanusse C (2006) Assessment of the main metabolism pathways for the flukicidal compound triclabendazole in sheep. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 29:213–223
Virkel G, Lifschitz A, Sallovitz J, Ballent M, Scarcella S, Lanusse C (2009) Inhibition of cytochrome P450 activity enhances the systemic availability of triclabendazole metabolites in sheep. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 32:79–86
Wang EJ, Lew K, Casciano N, Clement RP, Johnson WW (2002) Interaction of common azole antifungals with P glycoprotein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:160–165
Ward KW, Stelman GJ, Morgan JA, Zeigler KS, Azzarano LM, Kehler JR, McSurdy-Freed JE, Proksch JW, Smith BR (2004) Development of an in vivo preclinical screen model to estimate absorption and first-pass hepatic extraction of xenobiotics. II. Use of ketoconazole to identify P-glycoprotein/CYP3A-limited bioavailability in the monkey. Drug Metab Dispos 32:172–177
Wisedpanichkij R, Chaijaroenkul W, Sangsuwan P, Tantisawat J, Boonprasert K, Na-Bangchang K (2009) In vitro antimalarial interactions between mefloquine and cytochrome P450 inhibitors. Acta Trop 112:12–15
Wolstenholme AJ, Fairweather I, Prichard R, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Sangster NC (2004) Drug resistance in veterinary helminths. Trends Parasitol 20:469–476
Xu M, Molento M, Blackhall W, Ribeiro P, Beech R, Prichard R (1998) Ivermectin resistance in nematodes may be caused by alteration of P-glycoprotein homolog. Mol Biochem Parasitol 91:327–335
Zhang Y, Hsieh Y, Izumi T, Lin ET, Benet LZ (1998) Effects of ketoconazole on the intestinal metabolism, transport and oral bioavailability of K02, a novel vinylsulfone peptidomimetic cysteine protease inhibitor and a P450 3A, P-glycoprotein dual substrate, in male Sprague–Dawley rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:246–252
Zhang W, Ramamoorthy Y, Kilicarslan T, Nolte H, Tyndale RF, Sellers EM (2002) Inhibition of cytochromes P450 by antifungal imidazole derivatives. Drug Metab Dispos 30:314–318
Acknowledgements
This investigation was supported by a DARDNI Postgraduate Studentship to Catherine Devine. It was also partially supported by a grant from the European Union (DELIVER grant, no. FOOD-CT-200X-023025) and by a BBSRC/Defra grant (C00082X/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2554-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devine, C., Brennan, G.P., Lanusse, C.E. et al. Inhibition of triclabendazole metabolism in vitro by ketoconazole increases disruption to the tegument of a triclabendazole-resistant isolate of Fasciola hepatica . Parasitol Res 109, 981–995 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2304-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2304-9