Abstract
Purpose
To determine the rate of success of small-incision levator resection technique for correction of congenital ptosis.
Methods
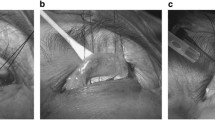
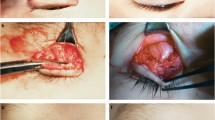
Patients with congenital ptosis who were candidates for levator resection were enrolled if their levator function was not poor (< 5 mm). Incisions were made on upper eyelid crease with a length of 10–12 mm. After resection of adequate length of levator muscle, two sutures were used to fix it to tarsal plate. Sliding the incision to medial and lateral sides provided a wider field of access to allow the surgeon to place the sutures above nasal and temporal borders of limbus. Success was defined as margin reflex distance-1 (MRD-1) ≥ 3 mm and inter-eyelid difference of MRD-1 less than 1 mm, which was considered excellent if inter-eyelid difference was < 0.5 mm and good if the latter parameter was between 0.5 and 1 mm.
Results
Fifty eyes of 47 congenital ptosis cases (16 males and 31 females) were included. Average age was 21.7 ± 9.7 years (range, 3–44 years). Mean preoperative levator function and MRD-1 were 11.26 ± 2.79 and 1.78 ± 0.92 mm, respectively, while postoperative MRD-1 increased to 3.95 ± 0.82 mm (P < 0.001). The result was failure (undercorrection) in 12 cases (25.5%), good in 9 patients (19.2%), and excellent in 26 cases (55.3%).
Conclusions
Small-incision levator resection has previously been studied for correction of aponeurotic ptosis and proved to yield successful outcome. The findings of this study suggest that small-incision technique can be effectively used in correction of congenital ptosis, as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehta S, Belliveau MJ, Oestreicher JH (2013) Oculoplastic surgery. Clin Plast Surg 40(4):631–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2013.08.005
Dortzbach R, Woog JJ (1990) Small-incision techniques in ophthalmic plastic surgery. Ophthalmic Surg 21(9):615–622
Lucarelli MJ, Lemke BN (1999) Small incision external levator repair: technique and early results. Am J Ophthalmol 127(6):637–644
Frueh BR, Musch DC, McDonald HM (2004) Efficacy and efficiency of a small-incision, minimal dissection procedure versus a traditional approach for correcting aponeurotic ptosis. Ophthalmology 111(12):2158–2163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.07.019
Baroody M, Holds JB, Sakamoto DK, Vick VL, Hartstein ME (2004) Small incision transcutaneous levator aponeurotic repair for blepharoptosis. Ann Plast Surg 52(6):558–561
Bernardini FP, de Conciliis C, Devoto MH (2006) Mini-invasive ptosis surgery. Orbit 25(2):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830600671425
Ahuero AE, Winn BJ, Sires BS (2012) Standardized suture placement for mini-invasive ptosis surgery. Arch Facial Plast Surg 14(6):408–412. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfacial.2012.388
Elabjer BK, Busic M, Elabjer E, Bosnar D, Sekelj S, Krstonijevic EK (2009) Microincision aponeurotic ptosis surgery of upper lid. Coll Antropol 33(3):915–918
Kasaee A, Yazdani-Abyaneh A, Tabatabaie SZ, Jafari AK, Ameri A, Eshraghi B, Samarai V, Mireshghi M, Rajabi MT (2010) Assessing amblyogenic factors in 100 patients with congenital ptosis. Int J Ophthalmol 3(4):328–330. https://doi.org/10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2010.04.12
Gire J, Robert PY, Denis D, Adenis JP (2011) Small-incision, minimal dissection procedure (Frueh’s procedure) in correction of involutional and congenital ptosis: a retrospective study of 119 cases. J Fr Ophtalmol 34(7):439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfo.2011.01.017
Ranno S, Sacchi M, Gonzalez MO, Ravula MT, Nucci P (2014) Evaluation of levator function for efficacy of minimally invasive and standard techniques for involutional ptosis. Am J Ophthalmol 157 (1):209–213 e201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2013.08.005
Scoppettuolo E, Chadha V, Bunce C, Olver JM, Wright M, Bopss (2008) British Oculoplastic Surgery Society (BOPSS) national ptosis survey. Br J Ophthalmol 92 (8):1134–1138. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2007.132746
Kashkouli MB, Jamshidian-Tehrani M (2014) Minimum incision no skin suture external dacryocystorhinostomy. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 30(5):405–409. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000131
Berry-Brincat A, Willshaw H (2009) Paediatric blepharoptosis: a 10-year review. Eye (Lond) 23(7):1554–1559. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2008.311
Doxanas MT (1992) Simplified aponeurotic ptosis surgery. Ophthalmic Surg 23(8):512–515
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval/research involving human participants
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eshraghi, B., Ghadimi, H. Small-incision levator resection for correction of congenital ptosis: a prospective study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 256, 1747–1750 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-4008-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-4008-7