Abstract
Background
The study of cerebral underpinnings of schizophrenia may benefit from the high temporal resolution of electromagnetic techniques, but its spatial resolution is low. However, source imaging approaches such as low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (LORETA) allow for an acceptable compromise between spatial and temporal resolutions.
Methods
We combined LORETA with 32 channels and 3-Tesla diffusion magnetic resonance (Dmr) to study cerebral dysfunction in 38 schizophrenia patients (17 first episodes, FE), compared to 53 healthy controls. The EEG was acquired with subjects performing an odd-ball task. Analyses included an adaptive window of interest to take into account the interindividual variability of P300 latency. We compared source activation patters to distractor (P3a) and target (P3b) tones within- and between-groups.
Results
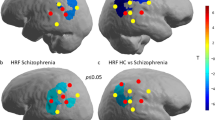
Patients showed a reduced activation in anterior cingulate and lateral and medial prefrontal cortices, as well as inferior/orbital frontal regions. This was also found in the FE patients alone. The activation was directly related to IQ in the patients and controls and to working memory performance in controls. Symptoms were unrelated to source activation. Fractional anisotropy in the tracts connecting lateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate regions predicted source activation in these regions in the patients.
Conclusions
These results replicate the source activation deficit found in a previous study with smaller sample size and a lower number of sensors and suggest an association between structural connectivity deficits and functional alterations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachiller A, Poza J, Gomez C, Molina V, Suazo V, Hornero R (2015) A comparative study of event-related coupling patterns during an auditory oddball task in schizophrenia. J Neural Eng 12:016007
Bachiller A, Romero S, Molina V, Alonso JF, Mananas MA, Poza J, Hornero R (2015) Auditory p3a and p3b neural generators in schizophrenia: an adaptive sloreta p300 localization approach. Schizophr Res 169:318–325
Baiano M, David A, Versace A, Churchill R, Balestrieri M, Brambilla P (2007) Anterior cingulate volumes in schizophrenia: a systematic review and a meta-analysis of mri studies. Schizophr Res 93:1–12
Bledowski C, Prvulovic D, Hoechstetter K, Scherg M, Wibral M, Goebel R, Linden DE (2004) Localizing p300 generators in visual target and distractor processing: a combined event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci 24:9353–9360
Bora E, Fornito A, Radua J, Walterfang M, Seal M, Wood SJ, Yucel M, Velakoulis D, Pantelis C (2011) Neuroanatomical abnormalities in schizophrenia: a multimodal voxelwise meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Schizophr Res 127:46–57
Campanella S, Gomez C, Rossion B, Liard L, Debatisse D, Dubois S, Delinte A, Bruyer R, Crommelinck M, Guerit JM (1999) A comparison between group-average and individual evoked potential analysis. Neurophysiol Clin 29:325–338
Dien J, Spencer KM, Donchin E (2003) Localization of the event-related potential novelty response as defined by principal components analysis. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 17:637–650
Donchin E, Coles M (1988) P300 component, a manifestation of cognitive updating? Behav Brain Sci 11:357–427
Goldman Rakic PS (1994) Working memory dysfunction in schizophrenia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 6:348–357
Gómez-Pilar J, Poza J, Bachiller A, Gómez C, Molina V, Hornero R (2015) Neural network reorganization analysis during an auditory oddball task in schizophrenia using wavelet entropy. Entropy 17:5241–5256
Higuchi Y, Sumiyoshi T, Kawasaki Y, Matsui M, Arai H, Kurachi M (2008) Electrophysiological basis for the ability of olanzapine to improve verbal memory and functional outcome in patients with schizophrenia: A loreta analysis of p300. Schizophr Res 101:320–330
Jung HT, Kim DW, Kim S, Im CH, Lee SH (2012) Reduced source activity of event-related potentials for affective facial pictures in schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Res 136:150–159
Kawasaki Y, Sumiyoshi T, Higuchi Y, Ito T, Takeuchi M, Kurachi M (2007) Voxel-based analysis of p300 electrophysiological topography associated with positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 94:164–171
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (panss) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Kim DW, Shim M, Kim JI, Im CH, Lee SH (2014) Source activation of p300 correlates with negative symptom severity in patients with schizophrenia. Brain Topogr 27:307–317
Lancaster JL, Woldorff MG, Parsons LM, Liotti M, Freitas CS, Rainey L, Kochunov PV, Nickerson D, Mikiten SA, Fox PT (2000) Automated talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum Brain Mapp 10:120–131
Lenartowicz A, Escobedo-Quiroz R, Cohen JD (2010) Updating of context in working memory: an event-related potential study. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 10:298–315
Mazziotta J, Toga A, Evans A, Fox P, Lancaster J, Zilles K, Woods R, Paus T, Simpson G, Pike B, Holmes C, Collins L, Thompson P, MacDonald D, Iacoboni M, Schormann T, Amunts K, Palomero-Gallagher N, Geyer S, Parsons L, Narr K, Kabani N, Le Goualher G, Boomsma D, Cannon T, Kawashima R, Mazoyer B (2001) A probabilistic atlas and reference system for the human brain: International consortium for brain mapping (icbm). Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356:1293–1322
Molina V, Lubeiro A, Soto O, Rodriguez M, Alvarez A, Hernandez R, de Luis-Garcia R (2017) Alterations in prefrontal connectivity in schizophrenia assessed using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 76:107–115
Mucci A, Galderisi S, Kirkpatrick B, Bucci P, Volpe U, Merlotti E, Centanaro F, Catapano F, Maj M (2007) Double dissociation of n1 and p3 abnormalities in deficit and nondeficit schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 92:252–261
Nichols TE, Holmes AP (2002) Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp 15:1–25
Pae JS, Kwon JS, Youn T, Park HJ, Kim MS, Lee B, Park KS (2003) Loreta imaging of p300 in schizophrenia with individual mri and 128-channel eeg. Neuroimage 20:1552–1560
Pascual-Marqui RD (2002) Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sloreta): technical details. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 24(Suppl D):5–12
Passingham D, Sakai K (2004) The prefrontal cortex and working memory: physiology and brain imaging. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:163–168
Pettersson-Yeo W, Allen P, Benetti S, McGuire P, Mechelli A (2011) Dysconnectivity in schizophrenia: where are we now? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:1110–1124
Polich J (2007) Updating p300: an integrative theory of p3a and p3b. Clin Neurophysiol 118:2128–2148
Qin P, Northoff G (2011) How is our self related to midline regions and the default-mode network? Neuroimage 57:1221–1233
Saas LA, Parnas J (2007) Explaining schizophrenia: The relevance of phenomenology. In: Cheung Chung M, K.W.M. F, Graham G (eds) Reconceiving schizophrenia. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 63–92
Sabeti M, Moradi E, Katebi S (2011) Analysis of neural sources of p300 event-related potential in normal and schizophrenic participants. Adv Exp Med Biol 696:589–597
Segarra N, Bernardo M, Gutierrez F, Justicia A, Fernadez-Egea E, Allas M, Safont G, Contreras F, Gascon J, Soler-Insa PA, Menchon JM, Junque C, Keefe RS (2011) Spanish validation of the brief assessment in cognition in schizophrenia (bacs) in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls. Eur Psychiatry 26:69–73
Soltani M, Knight RT, Yamaguchi S, Chao LL, Nielsen-Bohlman L (2000) Neural origins of the p300. Crit Rev Neurobiol 14:199–224
Strobel A, Debener S, Sorger B, Peters JC, Kranczioch C, Hoechstetter K, Engel AK, Brocke B, Goebel R (2008) Novelty and target processing during an auditory novelty oddball: a simultaneous event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroimage 40:869–883
Sumiyoshi T, Higuchi Y, Kawasaki Y, Matsui M, Kato K, Yuuki H, Arai H, Kurachi M (2006) Electrical brain activity and response to olanzapine in schizophrenia: a study with loreta images of p300. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1299–1303
Volpe U, Mucci A, Bucci P, Merlotti E, Galderisi S, Maj M (2007) The cortical generators of p3a and p3b: a loreta study. Brain Res Bull 73:220–230
Wang J, Tang Y, Li C, Mecklinger A, Xiao Z, Zhang M, Hirayasu Y, Hokama H, Li H (2010) Decreased p300 current source density in drug-naive first episode schizophrenics revealed by high density recording. Int J Psychophysiol 75:249–257
Wheeler AL, Voineskos AN (2014) A review of structural neuroimaging in schizophrenia: from connectivity to connectomics. Frontiers Hum Neurosci 8:653
Winterer G, Mulert C, Mientus S, Gallinat J, Schlattmann P, Dorn H, Herrmann WM (2001) P300 and loreta: comparison of normal subjects and schizophrenic patients. Brain Topogr 13:299–313
Wronka E, Kaiser J, Coenen AM (2012) Neural generators of the auditory evoked potential components p3a and p3b. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 72:51–64
Acknowledgements
This study has been partially supported by the “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias” from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI11/02708, PI11/02203 and PI15/00299), Consejería de Educación de Castilla y Leon VA057P17 and the Gerencia Regional de Salud de Castilla y León (GRS 1485/A/17 and GRS 1263/A/16) grants to V. Molina; Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO), Spain, under contract DPI2017-83989-R and Fundación BBVA grants for researchers and cultural creators 2016; a predoctoral research fellowship from the Consejería de Educación—Junta de Castilla to A. Lubeiro and Grant TEC2013-44194-P from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad of Spain. CIBER-BBN is an initiative of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina, V., Bachiller, A., de Luis, R. et al. Topography of activation deficits in schizophrenia during P300 task related to cognition and structural connectivity. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 269, 419–428 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0877-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0877-3