Abstract
Purpose
Anticipating the possibility of olfactory recovery after functional endoscopic surgery (FES) in nasal polyposis (NP) is difficult. The main objective of this study was to assess the predictive factors of recovering the sense of smell after radical bilateral ethmoidectomy. Secondary objectives were to identify other predictors of olfactory recovery.
Methods
Open prospective study was conducted at the Nantes University Hospital including all patients with NP operated on in the Ear, Nose, and Throat Department between January 2011 and September 2017. These patients underwent functional endoscopic surgery (radical ethmoidectomy) after medical treatment failure. Olfaction was quantified prospectively and systematically during the preoperative consultation using a visual analog scale. Multivariate analysis evaluated the presence of predictive factors of postoperative olfactory recovery.
Results
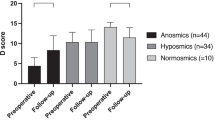
One hundred nineteen patients were included in the study. Overall, olfaction was partially improved after surgery. For patients who presented greater than 50% recovery of olfaction after systemic corticosteroid therapy before surgery, we observed a predictive better rate of olfactory recovery after surgery (p < 0.001). Age over 65 years, a history of sinonasal surgery, associated asthma, and bacterial colonization were not associated with less postoperative olfactory recovery.
Conclusion
This study identified an objective factor that may influence olfactory recovery after FES using a therapeutic trial for olfactory recovery after oral corticosteroid treatment taken before surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klossek JM, Neukirch F, Pribil C, Jankowski R, Serrano E, Chanal I et al (2005) Prevalence of nasal polyposis in France: a cross-sectional, case–control study. Allergy 60(2):233–237
Hosemann W, Goertzen W, Wohlleben R, Wolf S, Wigand ME (1993) Olfaction after endoscopic endonasal ethmoidectomy. Am J Rhinol 7(1):11–15
Litvack JR, Fong K, Mace J, James KE, Smith TL (2008) Predictors of olfactory dysfunction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 118(12):2225–2230
Bonfils P, Malinvaud D, Bozec H, Halimi P (2004) Olfactory disorders. Ann Oto-Laryngol Chir Cervico Faciale Bull Soc Oto-Laryngol Hopitaux Paris 121(2):67–74
Vento SI, Ertama LO, Hytönen ML, Wolff CH, Malmberg CH (2000) Nasal polyposis: clinical course during 20 years. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 85(3):209–214
Hummel T, Nordin S (2005) Olfactory disorders and their consequences for quality of life. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 125(2):116–121
Danielides V, Katotomichelakis M, Balatsouras D, Riga M, Simopoulou M, Kantas E et al (2009) Evaluation of prognostic factors for olfaction in nasal polyposis treated by endoscopic sinus surgery. Rhinology 47(2):172–180
Hermann P, Tran Ba Huy P (1999) Physiologie de l’olfaction. In: Les troubles du goût et de l’odorat. Société française d’oto-rhino-laryngologie et de chirurgie de la face et du cou. chapitre III: 81–124
Miwa T, Furukawa M, Tsukatani T, Costanzo RM, DiNardo LJ, Reiter ER (2001) Impact of olfactory impairment on quality of life and disability. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127(5):497–503
Li Z, Guo J, Zhou J, Yan F, Yang Z, Ding Z (2015) Meta-analysis of the olfaction effectiveness of glucocorticoid in the management of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 29(21):1868–1872
Hissaria P, Smith W, Wormald PJ, Taylor J, Vadas M, Gillis D et al (2006) Short course of systemic corticosteroids in sinonasal polyposis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with evaluation of outcome measures. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118(1):128–133
Van Zele T, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, Beule A, Wormald PJ, Mayr S et al (2010) Oral steroids and doxycycline: two different approaches to treat nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(5):1069–1076.e4
Doty RL, Shaman P, Applebaum SL, Giberson R, Siksorski L, Rosenberg L (1984) Smell identification ability: changes with age. Science 226(4681):1441–1443
Conley DB, Robinson AM, Shinners MJ, Kern RC (2003) Age-related olfactory dysfunction: cellular and molecular characterization in the rat. Am J Rhinol 17(3):169–175
Benninger MS, Holy CE (2014) The impact of endoscopic sinus surgery on health care use in patients with respiratory comorbidities. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 151(3):508–515
Perry BF, Kountakis SE (2003) Subjective improvement of olfactory function after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Otolaryngol 24(6):366–369
Brämerson A, Johansson L, Ek L, Nordin S, Bende M (2004) Prevalence of olfactory dysfunction: the Skövde population-based study. Laryngoscope 114(4):733–737
Bachert C, Zhang N, Patou J, van Zele T, Gevaert P (2008) Role of staphylococcal superantigens in upper airway disease. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 8(1):34–38
Van Zele T, Vaneechoutte M, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C (2008) Detection of enterotoxin DNA in Staphylococcus aureus strains obtained from the middle meatus in controls and nasal polyp patients. Am J Rhinol 22(3):223–227
Day N, Mainardi J-L, Malinvaud D, Bonfils P (2009) Bacteriological study of ethmoid specimens from patients with nasal polyposis after ethmoidal surgery. Ann Oto-Laryngol Chir Cervico Faciale Bull Soc Oto-Laryngol Hopitaux Paris 126(4):196–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The protocol was reviewed and approved by the local independent ethics committee, and the study was conducted in accordance with French legislative and regulatory measures, and the European Good Clinical Practice Directive 2005/28/EC (1964 Helsinki declaration).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rives, P., Espitalier, F., Michel, G. et al. Prospective evaluation of oral corticosteroid as a predictor of postoperative olfactory recovery after functional endoscopic surgery for nasal polyposis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 3359–3366 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05537-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05537-y