Abstract
Purpose
Stress has been suspected to play a role in rhinitis. The role of stress on nasal patency has been not yet elucidated. The aim was to evaluate the potential effects of stress on nasal patency in healthy subjects.
Methods
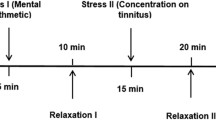
We conducted a prospective pilot study including 12 healthy subjects. Experimental protocol was divided in three periods (pre-task, task and recovery). In the task period, subjects were exposed to the “Trier Social Stress Test” (TSST), a standardized laboratory stressor. Different parameters including Spielberger State Anxiety Inventory (SSAI) score, visual analogic scale (VAS) of nasal patency feeling, heart rate, acoustic rhinometry measurements have been compared between the three different periods. The study population was divided into two groups according to the Spielberger Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) score: A “non anxious” group and a “weakly anxious” group.
Results
Seven subjects were in the “non anxious” group and five in the “weakly anxious” group. TSST significantly increased heart rate in all volunteers. SSAI score was significantly increased (p = 0.04) after the task period (36.6 ± 11.3) when compared to the SSAI score in pre-task period (31.9 ± 12.6). VAS score of nasal patency feeling significantly decreased from pre-task to task and recovery periods. Mean minimal cross-sectional areas and mean volumes of the nasal cavities were not significantly different between the three periods, except in “weakly anxious” group, but the small number of subjects does not allow to draw a definite conclusion.
Conclusion
We observed that stress influenced the feeling of nasal patency in healthy subjects. However, the objective effects of stress on nasal geometry were globally non-significant except in “weakly anxious” group. This latter result of our pilot study needs to be confirmed in a larger cohort.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narducci F, Snape WJ Jr, Battle WM, London RL, Cohen S (1985) Increased colonic motility during exposure to a stressful situation. Dig Dis Sci 30(1):40–44
Benson H, Beary JF, Carol MP (1974) The relaxation response. Psychiatry 37(1):37–46
Pohjavaara P, Telaranta T, Vaisanen E (2003) The role of the sympathetic nervous system in anxiety: Is it possible to relieve anxiety with endoscopic sympathetic block? Nord J Psychiatry 57(1):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/08039480310000266
Kahana-Zweig R, Geva-Sagiv M, Weissbrod A, Secundo L, Soroker N, Sobel N (2016) Measuring and characterizing the human nasal cycle. PLoS One 11(10):e0162918. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162918
Eccles R (1978) The central rhythm of the nasal cycle. Acta Otolaryngol 86(5–6):464–468
Xiao Y, Han D, Zang H, Wang D (2016) The effectiveness of nasal surgery on psychological symptoms in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and nasal obstruction. Acta Otolaryngol 136(6):626–632. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2016.1143120
Kirschbaum C, Pirke KM, Hellhammer DH (1993) The ‘Trier Social Stress Test’—a tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology 28(1–2):76–81. doi:119004
Brugel-Ribere L, Fodil R, Coste A, Larger C, Isabey D, Harf A, Louis B (2002) Segmental analysis of nasal cavity compliance by acoustic rhinometry. J Appl Physiol (1985) 93(1):304–310. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00085.2002
Spielberger CD, Lushene R, Vagg PR, Jacobs GA (1983) Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory. In Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory, Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene R, Vagg PR, Jacobs GA (eds). Publisher CA:Consulting Psychologists Press
Louis B, Fodil R, Jaber S, Pigeot J, Jarreau PH, Lofaso F, Isabey D (2001) Dual assessment of airway area profile and respiratory input impedance from a single transient wave. J Appl Physiol (1985) 90(2):630–637
Louis B, Glass G, Kresen B, Fredberg J (1993) Airway area by acoustic reflection: the two-microphone method. J Biomech Eng 115(3):278–285
Julian LJ (2011) Measures of anxiety: State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Anxiety (HADS-A). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63(Suppl 11):S467–S472. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.20561
Wang M, Lung MA (2003) Adrenergic mechanisms in canine nasal venous systems. Br J Pharmacol 138(1):145–155. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0705020
Delaney JP, Brodie DA (2000) Effects of short-term psychological stress on the time and frequency domains of heart-rate variability. Percept Mot Skills 91(2):515–524. https://doi.org/10.2466/pms.2000.91.2.515
Sharpley CF, Kamen P, Galatsis M, Heppel R, Veivers C, Claus K (2000) An examination of the relationship between resting heart rate variability and heart rate reactivity to a mental arithmetic stressor. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 25(3):143–153
Steptoe A, Kearsley N, Walters N (1993) Cardiovascular activity during mental stress following vigorous exercise in sportsmen and inactive men. Psychophysiology 30(3):245–252
Steptoe A, Moses J, Mathews A, Edwards S (1990) Aerobic fitness, physical activity, and psychophysiological reactions to mental tasks. Psychophysiology 27(3):264–274
Fichera LV, Andreassi JL (2000) Cardiovascular reactivity during public speaking as a function of personality variables. Int J Psychophysiol 37(3):267–273
Girdler SS, Turner JR, Sherwood A, Light KC (1990) Gender differences in blood pressure control during a variety of behavioral stressors. Psychosom Med 52(5):571–591
Djupesland PG, Rotnes JS (2001) Accuracy of acoustic rhinometry. Rhinology 39(1):23–27
Corboz MR, Rivelli MA, Mingo GG, McLeod RL, Varty L, Jia Y, Hey JA (2008) Mechanism of decongestant activity of alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 21(3):449–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pupt.2007.06.007
Eccles R, Jawad MS, Morris S (1990) The effects of oral administration of (-)-menthol on nasal resistance to airflow and nasal sensation of airflow in subjects suffering from nasal congestion associated with the common cold. J Pharm Pharmacol 42(9):652–654
Papon JF, Brugel-Ribere L, Fodil R, Croce C, Larger C, Rugina M, Coste A, Isabey D, Zerah-Lancner F, Louis B (2006) Nasal wall compliance in vasomotor rhinitis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 100(1):107–111. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00575.2005
Buske-Kirschbaum A, Ebrecht M, Kern S, Gierens A, Hellhammer DH (2008) Personality characteristics in chronic and non-chronic allergic conditions. Brain Behav Immun 22(5):762–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2007.12.002
Devillier P, Dessanges JF, Rakotosihanaka F, Ghaem A, Boushey HA, Lockhart A, Marsac J (1988) Nasal response to substance P and methacholine in subjects with and without allergic rhinitis. Eur Respir J 1(4):356–361
Knipping S, Holzhausen HJ, Riederer A, Schrom T (2009) Allergic and idiopathic rhinitis: an ultrastructural study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266(8):1249–1256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0898-z
Acknowledgements
The authors deeply thank Felicity Nielson for careful rereading of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was not sponsored by any external financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest in connection to this study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The experimental protocol was approved by the local research ethics committee (IRB).
Research involving human participants
Experimental protocol was approved by the local research ethics committee (IRB).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Kermadec, H., Bequignon, E., Zerah-Lancner, F. et al. Nasal response to stress test in healthy subjects: an experimental pilot study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 1391–1396 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05343-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05343-6