Abstract
Gacyclidine, a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, is a phencyclidine derivative with neuroprotective properties. It has been previously safely administered intravenously to acute traumatic brain-injured patients. Experiments in guinea pigs have shown that local administration of gacyclidine to the cochlea can suppress salicylate-induced tinnitus. Thus, we thought that patients with therapy-resistant sensorineural tinnitus might benefit from a local therapy with gacyclidine. As a compassionate treatment, we administered aqueous gacyclidine solution via a Durect RWμCathTM into the round window niche in six patients with unilateral deafness associated with tinnitus. The response of each patient to the drug treatment was given a numerical value by the use of a visual analogue scale (VAS) on a scale of 0–10 for tinnitus intensity, where 0 represented no tinnitus and 10 represented unbearable tinnitus-intensity or -annoyance (subjective). After constant perfusion of gacyclidine for 40–63 h, four out of six patients experienced a temporary relief from their tinnitus. No serious side effects were recorded in any of the cases. Gacyclidine might present a potent drug for the suppression of sensorineural tinnitus in humans and therefore should be considered for future double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trials. For lasting effective treatment, controlled intracochlear and long-term delivery of the drug seems to be necessary. Further studies investigating the toxicological effects of gacyclidine intracochlear perfusion as well as different dosages and therapy durations are under way to ensure the safety of the drug for long-term human use and warrant clinical trials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson G, Lyttkens L (1996) Acupuncture for tinnitus: time to stop? Scand Audiol 25:273–275
Chen Z, Ulfendahl M, Ruan R, Tan L, Duan M (2003) Acute treatment of noise trauma with local caroverine application in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol 123:905–909
Chen Z, Ulfendahl M, Ruan R, Tan L, Duan M (2004) Protection of auditory function against noise trauma with local caroverine administration in guinea pigs. Hear Res 197:131–136
Costa E (1998) From GABAA receptor diversity emerges a unified vision of GABAergic inhibition. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 38:321–350
Czuczwar SJ, Patsalos PN (2001) The new generation of GABA enhancers. Potential in the treatment of epilepsy. CNS Drugs 15:339–350
Denk DM, Heinzl H, Franz P, Ehrenberger K (1997) Caroverine in tinnitus treatment. A placebo-controlled blind study. Acta Otolaryngol 117:825–830
Dobie RA, Sakai CS, Sullivan MD, Katon WJ, Russo J (1993) Antidepressant treatment of tinnitus patients: report of a randomized clinical trial and clinical prediction of benefit. Am J Otol 14:18–23
Duckert LG, Rees TS (1984) Placebo effect in tinnitus management. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 92:697–699
Ehrenberger K (2005) Topical administration of caroverine in somatic tinnitus treatment: proof-of-concept study. Int Tinnitus J 11:34–37
Feldblum S, Arnaud S, Simon M, Rabin O, D’Arbigny P (2000) Efficacy of a new neuroprotective agent, gacyclidine, in a model of rat spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 17:1079–1093
Galici R, Pinna G, Stephens DN, Schneider HH, Turski L (1998) Tolerance to and dependence on alprazolam are due to changes in GABAa receptor function and are independent of exposure to experimental set-up. Restor Neurol Neurosci 12:233–237
Goldstein BA, Shulman A (2003) Tinnitus outcome profile and tinnitus control. Int Tinnitus J 9:26–31
Guitton MJ, Caston J, Ruel J, Johnson RM, Pujol R, Puel JL (2003) Salicylate induces tinnitus through activation of cochlear NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 23:3944–3952
Henry JA, Schechter MA, Loovis CL, Zaugg TL, Kaelin C, Montero M (2005) Clinical management of tinnitus using a “progressive intervention” approach. J Rehabil Res Dev 42:95–116
Hesse G (2008) Neurootologic and psychosomatic habituation therapy. Treatment approaches in chronic tinnitus. HNO 56:686–693
Hester TO, Theilman G, Green W, Jones RO (1998) Cyclandelate in the management of tinnitus: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:329–332
Hirbec H, Gaviria M, Vignon J (2001) Gacyclidine: a new neuroprotective agent acting at the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. CNS Drug Rev 7:172–198
Hirbec H, Kamenka JM, Privat A, Vignon J (2001) Characterization of ‘non-N-methyl-d-aspartate’ binding sites for gacyclidine enantiomers in the rat cerebellar and telencephalic structures. J Neurochem 77:190–201
Hirbec H, Mausset AL, Kamenka JM, Privat A, Vignon J (2002) Re-evaluation of phencyclidine low-affinity or “non-NMDA” binding sites. J Neurosci Res 68:305–314
Holgers KM, Axelsson A, Pringle I (1994) Ginkgo biloba extract for the treatment of tinnitus. Audiology 33:85–92
Hulshof JH, Vermeij P (1987) The effect of nicotinamide on tinnitus: a double-blind controlled study. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 12:211–214
Hulshof JH, Vermeij P (1985) The value of carbamazepine in the treatment of tinnitus. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 47:262–266
Hulshof JH, Vermeij P (1986) The value of flunarizine in the treatment of tinnitus. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 48:33–36
Hulshof JH, Vermeij P (1985) The value of tocainide in the treatment of tinnitus. A double-blind controlled study. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 241:279–283
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vockler J, Dikranian K, Tenkova TI, Stefovska V, Turski L, Olney JW (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283:70–74
Johnson RM, Brummett R, Schleuning A (1993) Use of alprazolam for relief of tinnitus. A double-blind study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:842–845
Kay NJ (1981) Oral chemotherapy in tinnitus. Br J Audiol 15:123–124
Kopke RD, Coleman JK, Liu J, Campbell KC, Riffenburgh RH (2002) Candidate’s thesis: enhancing intrinsic cochlear stress defenses to reduce noise-induced hearing loss. Laryngoscope 112:1515–1532
Krystal JH, D’Souza DC, Mathalon D, Perry E, Belger A, Hoffman R (2003) NMDA receptor antagonist effects, cortical glutamatergic function, and schizophrenia: toward a paradigm shift in medication development. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 169:215–233
Lenarz T (1986) Treatment of tinnitus with lidocaine and tocainide. Scand Audiol Suppl 26:49–51
Lenarz T, Gulzow J (1985) Tinnitus therapy with lidocaine and tocainide. Laryngol Rhinol Otol (Stuttg) 64:604–608
Lepeintre JF, D’Arbigny P, Mathe JF, Vigue B, Loubert G, Delcour J, Kempf C, Tadie M (2004) Neuroprotective effect of gacyclidine. A multicenter double-blind pilot trial in patients with acute traumatic brain injury. Neurochirurgie 50:83–95
Moller AR (1997) A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of baclofen in the treatment of tinnitus. Am J Otol 18:268–269
Muly SM, Gross JS, Potashner SJ (2004) Noise trauma alters d-[3H]aspartate release and AMPA binding in chinchilla cochlear nucleus. J Neurosci Res 75:585–596
Newman CW, Sandridge SA, Jacobson GP (1998) Psychometric adequacy of the tinnitus handicap inventory (THI) for evaluating treatment outcome. J Am Acad Audiol 9:153–160
Niedzielski AS, Safieddine S, Wenthold RJ (1997) Molecular analysis of excitatory amino acid receptor expression in the cochlea. Audiol Neurootol 2:79–91
Nordang L, Cestreicher E, Arnold W, Anniko M (2000) Glutamate is the afferent neurotransmitter in the human cochlea. Acta Otolaryngol 120:359–362
Oestreicher E, Arnold W, Ehrenberger K, Felix D (1998) Memantine suppresses the glutamatergic neurotransmission of mammalian inner hair cells. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 60:18–21
Oestreicher E, Arnold W, Ehrenberger K, Felix D (1999) New approaches for inner ear therapy with glutamate antagonists. Acta Otolaryngol 119:174–178
Oestreicher E, Ehrenberger K, Felix D (2002) Different action of memantine and caroverine on glutamatergic transmission in the mammalian cochlea. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 59:18–25
Oliver D, Ludwig J, Reisinger E, Zoellner W, Ruppersberg JP, Fakler B (2001) Memantine inhibits efferent cholinergic transmission in the cochlea by blocking nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of outer hair cells. Mol Pharmacol 60:183–189
Olney JW (2002) New insights and new issues in developmental neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicology 23:659–668
Paaske PB, Pedersen CB, Kjems G, Sam IL (1991) Zinc in the management of tinnitus. Placebo-controlled trial. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 100:647–649
Perucca E, Jackson P (1985) A controlled study of the suppression of tinnitus by lidocaine infusion: (relationship of therapeutic effect with serum lidocaine levels). J Laryngol Otol 99:657–661
Pujol R, Puel JL (1999) Excitotoxicity, synaptic repair, and functional recovery in the mammalian cochlea: a review of recent findings. Ann N Y Acad Sci 884:249–254
Rosenberg SI, Silverstein H, Rowan PT, Olds MJ (1998) Effect of melatonin on tinnitus. Laryngoscope 108:305–310
Rowland LM, Astur RS, Jung RE, Bustillo JR, Lauriello J, Yeo RA (2005) Selective cognitive impairments associated with NMDA receptor blockade in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:633–639
Schwab B, Lenarz T, Heermann R (2004) Use of the round window micro cath for inner ear therapy—results of a placebo-controlled, prospective study on chronic tinnitus. Laryngorhinootologie 83:164–172
Schwarz JB, Gibbons SE, Graham SR, Colbry NL, Guzzo PR, Le VD, Vartanian MG, Kinsora JJ, Lotarski SM, Li Z, Dickerson MR, Su TZ, Weber ML, El-Kattan A, Thorpe AJ, Donevan SD, Taylor CP, Wustrow DJ (2005) Novel cyclopropyl beta-amino acid analogues of pregabalin and gabapentin that target the alpha2-delta protein. J Med Chem 48:3026–3035
Sekiya T, Shimamura N, Hatayama T, Suzuki S (2000) Effectiveness of preoperative administration of an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist to enhance cochlear neuron resistance to intraoperative traumatic stress: an experimental study. J Neurosurg 93:90–98
Simpson JJ, Donaldson I, Davies WE (1998) Use of homeopathy in the treatment of tinnitus. Br J Audiol 32:227–233
Soholm B (1998) Clinical improvement of memory and other cognitive functions by Ginkgo biloba: review of relevant literature. Adv Ther 15:54–65
Spangler EL, Bresnahan EL, Garofalo P, Muth NJ, Heller B, Ingram DK (1991) NMDA receptor channel antagonism by dizocilpine (MK-801) impairs performance of rats in aversively motivated complex maze tasks. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:949–958
Stahl SM (2004) Anticonvulsants and the relief of chronic pain: pregabalin and gabapentin as alpha(2)delta ligands at voltage-gated calcium channels. J Clin Psychiatry 65:596–597
Stoney PJ, Callaghan DE, Walker FS, Stephens SD (1991) A controlled trial of azapropazone in tinnitus. Br J Audiol 25:415–417
Sugimoto M, Uchida I, Mashimo T (2003) Local anaesthetics have different mechanisms and sites of action at the recombinant N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Br J Pharmacol 138:876–882
Sullivan M, Katon W, Russo J, Dobie R, Sakai C (1993) A randomized trial of nortriptyline for severe chronic tinnitus. Effects on depression, disability, and tinnitus symptoms. Arch Intern Med 153:2251–2259
Taylor CP (1997) Mechanisms of action of gabapentin. Rev Neurol (Paris) 153(Suppl 1):S39–S45
Vandame D, Desmadryl G, Becerril Ortega J, Teigell M, Crouzin N, Buisson A, Privat A, Hirbec H (2007) Comparison of the pharmacological properties of GK11 and MK801, two NMDA receptor antagonists: towards an explanation for the lack of intrinsic neurotoxicity of GK11. J Neurochem 103:1682–1696
Westerberg BD, Roberson JB Jr, Stach BA (1996) A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of baclofen in the treatment of tinnitus. Am J Otol 17:896–903
Zenner HP, Ruppersberg JP, Busch A (2000) Method for treating diseases of the inner ear using adamantane derivatives. US Patent No. 6,066,652
Acknowledgments
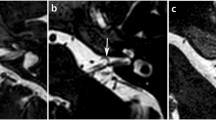
We herein thank NeuroSystec-Company for providing gacyclidine, Thomas J. Lobl for valuable comments and Isaac Ruperto Ayala for the illustration in Fig. 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The compassionate treatment has been sponsored by the Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wenzel, G.I., Warnecke, A., Stöver, T. et al. Effects of extracochlear gacyclidine perfusion on tinnitus in humans: a case series. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267, 691–699 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-1126-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-1126-1