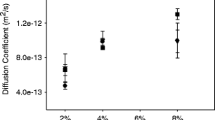
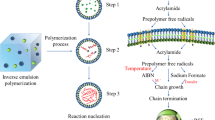
Abstract
The emulsification of amphiphilic polymer is inevitably affected by the salinity environment in the preparation and flooding process. The variation of emulsions in stability and rheology has a significant influence on the efficiency of polymer flooding. Thus, the effect of NaCl and CaCl2 on the emulsification behavior of hydrophobically modified polyacrylamide (HMPAM) was investigated. A novel dynamic multiple light scattering method was proposed to analyze the variation of emulsion stability. Then, the emulsions with addition of salt were systematically researched in terms of oil droplet size, polymer adsorption, and rheology properties. With the increase of NaCl concentration, the emulsion stability with 1500 mg L−1 HMPAM (above the critical aggregation concentration) decreases monotonically; with the increase of CaCl2 concentration, the emulsion stability rises at first then decreases. It is found that the structural viscosity of the polymer solution is the dominant factor in stabilizing the crude oil emulsion. Modulation effect of the salt ions on the emulsion stability is achieved by regulating the aggregate structure in the aqueous solution. Oscillation-shear-oscillation rheological experiments were conducted to investigate the rheological properties of emulsions. The results show that the viscoelasticity of emulsion system at high salt concentration decreases after high-rate shearing and the recovery of the viscoelasticity is slowed down due to the inhibition of hydrophobic association. This study provides theoretical guidance for elucidating the regulation rules and mechanism of salts on the amphiphilic polymer-containing crude oil emulsions.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirasaki GJ, Miller CA, Puerto M (2008) Recent advances in surfactant EOR. SPE J 16(4):889–907
Zolfaghari R, Fakhru’l-Razi A, Abdullah LC, Elnashaie SS, Pendashteh A (2016) Demulsification techniques of water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsions in petroleum industry. Sep Purif Technol 170:377–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.06.026
Abidin AZ, Puspasari T, Nugroho WA (2012) Polymers for enhanced oil recovery technology. Procedia Chem 4(12):11–16
Lu C, Liu H, Zhao W, Lu K, Liu Y, Tian J, Tan X (2016) Experimental investigation of in-situ emulsion formation to improve viscous-oil recovery in steam-injection process assisted by viscosity reducer. SPE J.
Guo J, Liu Q, Li M, Wu Z, Christy AA (2006) The effect of alkali on crude oil/water interfacial properties and the stability of crude oil emulsions. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects 273(1–3):213–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.10.015
Zhou Y, Wang D, Wang Z, Cao R (2017) The formation and viscoelasticity of pore-throat scale emulsion in porous media. Pet Explor Dev 1:110–116
Islam M, Ali S (1994) Numerical simulation of emulsion flow through porous media. J Can Petrol Technol 33(03). https://doi.org/10.2118/94-03-08
Schmidt DP, Soo H, Radke CJ (2013) Linear oil displacement by the emulsion entrapment process. Soc Pet Eng J 24(3):351–360
Lu H, Feng Y, Huang Z (2008) Association and effective hydrodynamic thickness of hydrophobically associating polyacrylamide through porous media. J Appl Polym Sci 110(3):1837–1843. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.28596
Morgan SE, Mccormick CL (1990) Water-soluble polymers in enhanced oil recovery. Prog Polym Sci 15(1):103–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6700(90)90017-U
Xie K, Lu XG, Li Q, Jiang WD, Yu Q (2016) Analysis of reservoir applicability of hydrophobically associating polymer. SPE J 21(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.2118/174553-PA
Perrin P, Lafuma F (1998) Low hydrophobically modified poly(acrylic acid) stabilizing macroemulsions: relationship betwee n copolymer structure and emulsions properties. J Colloid Interf Sci 197(2):317–326. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1997.5224
Robins MM (1991) Effect of polysaccharide on flocculation and creaming in oil-in-water emulsions. In: ACS Symposium series-American Chemical Society (USA),
Seright RS, Fan TG, Wavrik K, Wan H, Gaillard N, Favero C (2011) Rheology of a new sulfonic associative polymer in porous media. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 14(6):726–734. https://doi.org/10.2118/141355-PA
Tadros TF, Vandamme A, Levecke B, Booten K, Stevens C (2004) Stabilization of emulsions using polymeric surfactants based on inulin. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 108:207–226
Sun W, Sun D, Wei Y, Liu S, Zhang S (2007) Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by hydrophobically modified hydroxyethyl cellulose: adsorption and thickening effect. J Colloid Interf Sci 311(1):228–236
Akiyama E, Yamamoto T, Yago Y, Hotta H, Ihara T, Kitsuki T (2007) Thickening properties and emulsification mechanisms of new derivatives of polysaccharide in aqueous solution: 2. The effect of the substitution ratio of hydrophobic/hydrophilic moieties. J Colloid Interf Sci 311(2):438–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.03.009
Xu B, Kang W, Meng L, Yang R, Liu S, Zhang L (2013) Synthesis, aggregation behavior and emulsification characteristic of a multi-sticker amphiphilic polymer. J Macromol Sci A 50(3):302–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2013.755855
Ji Y, Kang W, Hu L, Yang R, Meng L, Fan H (2014) Study on shearing resistance and the stability of O/W emulsion of the inclusive and hydrophobic association systems by activation energy methodology. J Polym Res 21(8):517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0517-1
Xu B, Kang WL, Meng LW, Yang RM, Liu SR, Zhang L (2013) Synthesis, aggregation behavior and emulsification characteristic of a multi-sticker amphiphilic polymer. J Macromol Sci A 50(3):302–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2013.755855
Yang Q, Xin X, Wang L, Lu H, Ren H, Tan Y, Xu G (2014) Modification of the stability of oil-in-water nano-emulsions by polymers with different structures. Colloid Polymer Sci 292(6):1297–1306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3185-0
Lu Y, Kang W, Jiang J, Chen J, Xu D, Zhang P, Zhang L, Feng H, Wu H (2017) Study on the stabilization mechanism of crude oil emulsion with an amphiphilic polymer using the β-cyclodextrin inclusion method. RSC Adv 7(14):8156–8166. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA28528G
Bera A, Mandal A, Guha B (2013) Synergistic effect of surfactant and salt mixture on interfacial tension reduction between crude oil and water in enhanced oil recovery. J Chem Eng Data 59(1):89–96
Nguyen D, Sadeghi N, Houston C (2012) Chemical interactions and demulsifier characteristics for enhanced oil recovery applications. Energy Fuel 26(5):2742–2750. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef201800b
Tam KC, Guo L, Jenkins RD, Bassett DR (1999) Viscoelastic properties of hydrophobically modified alkali-soluble emulsion in salt solutions. Polymer 40(23):6369–6379. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00857-X
Chen H, Wu X, Ye Z, Han L, Luo P (2012) Self-assembly behavior of hydrophobically associating polyacrylamide in salt solution. Acta Phys -Chim Sin 28(4):903–908
Gharibzahedi SMT, Mousavi SM, Hamedi M, Ghasemlou M (2012) Response surface modeling for optimization of formulation variables and physical stability assessment of walnut oil-in-water beverage emulsions. Food Hydrocolloid 26(1):293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.06.006
Tadros T (2004) Application of rheology for assessment and prediction of the long-term physical stability of emulsions. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 108:227–258
Lemarchand C, Couvreur P, Vauthier C, Costantini D, Gref R (2003) Study of emulsion stabilization by graft copolymers using the optical analyzer Turbiscan. Int J Pharm 254(1):77–82
Wiśniewska M (2010) Influences of polyacrylic acid adsorption and temperature on the alumina suspension stability. Powder Technol 198(2):258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2009.11.016
Vie R, Azema N, Quantin J, Touraud E, Fouletier M (2007) Study of suspension settling: a approach to determine suspension classification and particle interactions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 298(3):192–200
Balastre M, Argillier J, Allain C, Foissy A (2002) Role of polyelectrolyte dispersant in the settling behaviour of barium sulphate suspension. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 211(2):145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(02)00240-6
Kang W, Xu B, Wang Y, Li Y, Shan X, An F, Liu J (2011) Stability mechanism of W/O crude oil emulsion stabilized by polymer and surfactant. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 384(1):555–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.05.017
Yang Q, Xin X, Wang L, Lu H, Ren H, Tan Y, Xu G (2014) Modification of the stability of oil-in-water nano-emulsions by polymers with different structures. Colloid Polym Sci 292(6):1297–1306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3185-0
Skinner L, Sambles J (1972) The kelvin equation—a review. J Aerosol Sci 3(3):199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-8502(72)90158-9
Gouldby SJ, Gunning PA, Hibberd DJ, Robins MM (1991) Creaming in flocculated oil in water emulsions. Food Polymers Gels Colloids 82:244
Meng L, Kang W, Zhang L, Yang R (2012) Rheological rules and influencing factors of amphiphilici polymer solution. Polymer Mater Sci Eng 28(10):55–58
Lin Y, Skaff H, Emrick T, Dinsmore A, Russell TP (2003) Nanoparticle assembly and transport at liquid-liquid interfaces. Science 299(5604):226–229
Lin Y, Böker A, Skaff H, Cookson D, Dinsmore A, Emrick T, Russell TP (2005) Nanoparticle assembly at fluid interfaces: structure and dynamics. Langmuir 21(1):191–194
Yang F, Liu S, Xu J, Lan Q, Wei F, Sun D (2006) Pickering emulsions stabilized solely by layered double hydroxides particles: the effect of salt on emulsion formation and stability. J Colloid Interf Sci 302(1):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.06.015
Kundu P, Agrawal A, Mateen H, Mishra IM (2013) Stability of oil-in-water macro-emulsion with anionic surfactant: effect of electrolytes and temperature. Chem Eng Sci 102:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2013.07.050
Rı́os G, Pazos C, Coca J (1998) Destabilization of cutting oil emulsions using inorganic salts as coagulants. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 138(2):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(97)00083-6
Ghannam MT, Esmail N (2005) Yield stress behavior for crude oil–polymer emulsions. J Pet Sci Eng 47(3):105–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2005.03.001
Ghannam MT (2004) Creep–recovery experimental investigation of crude oil–polymer emulsions. J Appl Polym Sci 92(1):226–237. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.13645
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Science and Technology Major Projects of China (2017ZX05009-004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51774309), and Science Foundation of China University of Petroleum, Beijing (No. 2462015YJRC033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Wu, H., Meng, Z. et al. Salt effect on hydrophobically modified polyacrylamide-containing crude oil emulsions: stability and rheology study. Colloid Polym Sci 296, 515–527 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4267-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4267-1