Abstract
Purpose
Several foods and nutrients have been independently associated with systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressure values. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of combined dietary habits on SBP and DBP values in a large cohort of healthy adults, with a cross-sectional design. Adherence of participants to four a priori dietary patterns was considered: the Healthy Eating Index 2010 (HEI-2010); the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH); the Greek Mediterranean Diet Score (MDS); and the Italian Mediterranean Index (IMI).
Methods
Overall, 13,597 volunteers (35–64 years) were enrolled in 1993–1998 in the EPIC-Florence cohort. Information on dietary habits, anthropometry, smoking status, education, physical activity habits, previous diagnosis of hypertension and SBP and DBP measurements were collected at baseline. Multivariate regression models were performed on 10,163 individuals (7551 women) after excluding subjects with prevalent hypertension.
Results
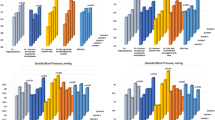
IMI, DASH and HEI-2010 were significantly and inversely associated with SBP and DBP values in the total population. The strongest association emerged between IMI and SBP (β − 1.80 excellent adherence vs low adherence, 95% CI − 2.99; − 0.61, p trend 0.001) and DBP (β − 1.12, 95% CI − 1.869; − 0.39, p trend 0.001) values. In sub-group analyses, an inverse association also emerged between IMI and SBP and DBP values among females and between DASH and DBP among males. MDS was not associated with SBP or DBP.
Conclusion
Overall, this study, carried out in a large cohort of healthy adults from Tuscany (Central Italy), showed inverse significant associations between specific a priori dietary patterns, identifying general models of health-conscious diet, and blood pressure values.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 October 2018
In the original publication of the article have been published in an incorrect form. The correct form is given below.
References
World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases (2014). WHO, Geneva. http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-status-report-2014/en/. Accessed 6 November 2017
ESH/ESC Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension (2013) Practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC): ESH/ESC Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 31(10):1925e38
Lafortune L, Martin S, Kelly S, Kuhn I, Remes O, Cowan A, Brayne C (2016) Behavioural risk factors in mid-life associated with successful ageing, disability, dementia and frailty in later life: a rapid systematic review. PLoS One 11(2):e0144405. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144405
Rasmussen BM, Vessby B, Uusitupa M, Berglund L, Pedersen E, Riccardi G, Rivellese AA, Tapsell L, Hermansen K, KANWU Study Group (2006) Effects of dietary saturated, monounsaturated, and n-3 fatty acids on blood pressure in healthy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 83(2):221–226
Hodge A, Bassett J (2016) What can we learn from dietary pattern analysis? Public Health Nutr 19(2):191–194
Guenther PM, Casavale KO, Reedy J, Kirkpatrick SI, Hiza HA, Kuczynski KJ, Kahle LL, Krebs-Smith SM (2013) Update of the healthy eating index: HEI-2010. J Acad Nutr Diet 113(4):569–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2012.12.016
Appel LJ, Moore TJ, Obarzanek E, Vollmer WM, Svetkey LP, Sacks FM, Bray GA, Vogt TM, Cutler JA, Windhauser MM, Lin PH, Karanja N (1997) A clinical trial of the effects of dietary patterns on blood pressure. DASH Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med 336(16):1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199704173361601
Trichopoulou A, Orfanos P, Norat T, Bueno-de-Mesquita B, Ocké MC, Peeters PH, van der Schouw YT, Boeing H, Hoffmann K, Boffetta P, Nagel G, Masala G, Krogh V, Panico S, Tumino R, Vineis P, Bamia C, Naska A, Benetou V, Ferrari P, Slimani N, Pera G, Martinez-Garcia C, Navarro C, Rodriguez-Barranco M, Dorronsoro M, Spencer EA, Key TJ, Bingham S, Khaw KT, Kesse E, Clavel-Chapelon F, Boutron-Ruault MC, Berglund G, Wirfalt E, Hallmans G, Johansson I, Tjonneland A, Olsen A, Overvad K, Hundborg HH, Riboli E, Trichopoulos D (2005) Modified Mediterranean diet and survival: EPIC-elderly prospective cohort study. BMJ 330(7498):991. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38415.644155.8F
Agnoli C, Krogh V, Grioni S, Sieri S, Palli D, Masala G, Sacerdote C, Vineis P, Tumino R, Frasca G, Pala V, Berrino F, Chiodini P, Mattiello A, Panico S (2011) A priori-defined dietary patterns are associated with reduced risk of stroke in a large Italian cohort. J Nutr 141(8):1552–1558. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.140061
Riboli E, Hunt KJ, Slimani N, Ferrari P, Norat T, Fahey M, Charrondière UR, Hémon B, Casagrande C, Vignat J, Overvad K, Tjønneland A, Clavel-Chapelon F, Thiébaut A, Wahrendorf J, Boeing H, Trichopoulos D, Trichopoulou A, Vineis P, Palli D, Bueno-De-Mesquita HB, Peeters PH, Lund E, Engeset D, González CA, Barricarte A, Berglund G, Hallmans G, Day NE, Key TJ, Kaaks R, Saracci R (2002) European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC): study populations and data collection. Public Health Nutr 5(6B):1113–1124. https://doi.org/10.1079/PHN2002394
Palli D, Berrino F, Vineis P, Tumino R, Panico S, Masala G, Saieva C, Salvini S, Ceroti M, Pala V, Sieri S, Frasca G, Giurdanella MC, Sacerdote C, Fiorini L, Celentano E, Galasso R, Decarli A, Krogh V, EPIC-Italy (2003) A molecular epidemiology project on diet and cancer: the EPIC-Italy Prospective Study. Design and baseline characteristics of participants. Tumori 89(6):586–593
Pala V, Sieri S, Palli D, Salvini S, Berrino F, Bellegotti M, Frasca G, Tumino R, Sacerdote C, Fiorini L, Celentano E, Galasso R, Krogh V (2003) Diet in the Italian EPIC cohorts: presentation of data and methodological issues. Tumori 89(6):594–607
Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (2017) Banca Dati di Composizione degli Alimenti per Studi Epidemiologici in Italia (BDA). http://www.bda-ieo.it/. Accessed 11 Aug 2017
Pols MA, Peeters PH, Ocké MC, Slimani N, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Collette HJ (1997) Estimation of reproducibility and relative validity of the questions included in the EPIC Physical Activity Questionnaire. Int J Epidemiol 26(Suppl 1):S181–S189
InterAct Consortium, Peters T, Brage S, Westgate K, Franks PW, Gradmark A, Tormo Diaz MJ, Huerta JM, Bendinelli B, Vigl M, Boeing H, Wendel-Vos W, Spijkerman A, Benjaminsen-Borch K, Valanou E, de Lauzon Guillain B, Clavel-Chapelon F, Sharp S, Kerrison N, Langenberg C, Arriola L, Barricarte A, Gonzales C, Grioni S, Kaaks R, Key T, Khaw KT, May A, Nilsson P, Norat T, Overvad K, Palli D, Panico S, Ramón Quirós J, Ricceri F, Sanchez MJ, Slimani N, Tjonneland A, Tumino R, Feskins E, Riboli E, Ekelund U, Wareham N (2012) Validity of a short questionnaire to assess physical activity in 10 European countries. Eur J Epidemiol 27(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-011-9625
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Boudier HA, Zanchetti A, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Erdine S, Kiowski W, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Lindholm LH, Viigimaa M, Adamopoulos S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Bertomeu V, Clement D, Erdine S, Farsang C, Gaita D, Lip G, Mallion JM, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, O’Brien E, Ponikowski P, Redon J, Ruschitzka F, Tamargo J, van Zwieten P, Waeber B, Williams B, Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension; European Society of Cardiology (2007) 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the european society of hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 25(6):1105–1187. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e3281fc975a
U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. and US Department of Health and Human Services (2010) Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010, 7th edn. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture (2005) Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 6th edn. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Fung TT, Chiuve SE, McCullough ML, Rexrode KM, Logroscino G, Hu FB (2008) Adherence to a DASH-style diet and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in women. Arch Intern Med 168(7):713–720. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.168.7.713
Masala G, Bendinelli B, Occhini D, Bruno RM, Caini S, Saieva C, Ungar A, Ghiadoni L, Palli D (2017) Physical activity and blood pressure in 10,000 Mediterranean adults: the EPIC-Florence cohort. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 27(8):670–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2017.06.003
Lelong H, Blacher J, Menai M, Galan P, Fezeu L, Hercberg S, Kesse-Guyot E (2016) Association between blood pressure and adherence to French dietary guidelines. Am J Hypertens 29(8):948–958. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpw017
Harrington JM, Fitzgerald AP, Kearney PM, McCarthy VJ, Madden J, Browne G, Dolan E, Perry IJ (2013) DASH diet score and distribution of blood pressure in middle-aged men and women. Am J Hypertens 26(11):1311–1320. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpt106
Dauchet L, Kesse-Guyot E, Czernichow S, Bertrais S, Estaquio C, Péneau S, Vergnaud AC, Chat-Yung S, Castetbon K, Deschamps V, Brindel P, Hercberg S (2007) Dietary patterns and blood pressure change over 5-y follow-up in the SU.VI.MAX cohort. Am J Clin Nutr 85(6):1650–1656
Agnoli C, Grioni S, Sieri S, Palli D, Masala G, Sacerdote C, Vineis P, Tumino R, Giurdanella MC, Pala V, Berrino F, Mattiello A, Panico S, Krogh V (2013) Italian Mediterranean Index and risk of colorectal cancer in the Italian section of the EPIC cohort. Int J Cancer 132(6):1404–1411. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27740
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) (2017) Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: a pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19·1 million participants. Lancet 389(10064):37–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31919-5
Drouin-Chartier JP, Brassard D, Tessier-Grenier M, Côté JA, Labonté M, Desroches S, Couture P, Lamarche B (2016) Systematic review of the association between dairy product consumption and risk of cardiovascular-related clinical outcomes. Adv Nutr 7(6):1026–1040. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.01140
Drouin-Chartier JP, Côté JA, Labonté M, Brassard D, Tessier-Grenier M, Desroches S, Couture P, Lamarche B (2016) Comprehensive review of the impact of dairy foods and dairy fat on cardiometabolic risk. Adv Nutr 7(6):1041–1051. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.011619
Roerecke M, Kaczorowski J, Tobe SW, Gmel G, Hasan OSM, Rehm J (2017) The effect of a reduction in alcohol consumption on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2(2):e108–e120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(17)30003-8
Cook NR, Cohen J, Hebert PR, Taylor JO, Hennekens CH (1995) Implications of small reductions in diastolic blood pressure for primary prevention. Arch Intern Med 155(7):701–709
Hebert PR, Moser M, Mayer J, Glynn RJ, Hennekens CH (1993) Recent evidence on drug therapy of mild to moderate hypertension and decreased risk of coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med 153(5):578–581
MacMahon S, Peto R, Cutler J, Collins R, Sorlie P, Neaton J, Abbott R, Godwin J, Dyer A, Stamler J (1990) Blood pressure, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Part 1, Prolonged differences in blood pressure: prospective observational studies corrected for the regression dilution bias. Lancet 335(8692):765–774
Blumenthal JA, Babyak MA, Hinderliter A, Watkins LL, Craighead L, Lin PH, Caccia C, Johnson J, Waugh R, Sherwood A (2010) Effects of the DASH diet alone and in combination with exercise and weight loss on blood pressure and cardiovascular biomarkers in men and women with high blood pressure: the ENCORE study. Arch Intern Med 170(2):126–135. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2009.470
Ndanuko RN, Tapsell LC, Charlton KE, Neale EP, Batterham MJ (2016) Dietary patterns and blood pressure in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Adv Nutr 7(1):76–89. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.009753
Appleby PN, Davey GK, Key TJ (2002) Hypertension and blood pressure among meat eaters, fish eaters, vegetarians and vegans in EPIC-Oxford. 5(5):645–54. https://doi.org/10.1079/PHN2002332
Psaltopoulou T, Naska A, Orfanos P, Trichopoulos D, Mountokalakis T, Trichopoulou A (2004) Olive oil, the Mediterranean diet, and arterial blood pressure: the Greek European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Am J Clin Nutr 80(4):1012–1018
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the cooperation of all study participants and staff members. The EPIC study was supported by the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Milan, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
The EPIC study has been approved by the Ethical Review Board of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC, Lyon) and by the local Florence Ethical Committee and has, therefore, been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
At enrolment, all participants in the EPIC study signed an informed consent form and agreed to provide detailed information on their dietary and lifestyle habits and their health status.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bendinelli, B., Masala, G., Bruno, R.M. et al. A priori dietary patterns and blood pressure in the EPIC Florence cohort: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Nutr 58, 455–466 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1758-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1758-2