Abstract
Purpose
Obesity is usually associated with low-grade inflammation, which impairs insulin action. The amino acid, taurine (TAU), regulates glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism and presents anti-inflammatory actions. Here, we evaluated whether inflammatory markers are altered in the serum and retroperitoneal adipose tissue of monosodium glutamate (MSG) obese rats, supplemented or not with TAU.
Methods
Male Wistar rats received subcutaneous injections of MSG (4 mg/kg body weight/day, MSG group) or hypertonic saline (CTL) during the first 5 days of life. From 21 to 120 days of age, half of each of the MSG and CTL groups received 2.5 % TAU in their drinking water (CTAU and MTAU).
Results
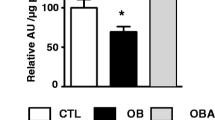
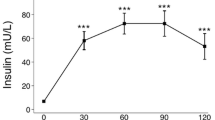
At 120 days of age, MSG rats were obese and hyperinsulinemic. TAU supplementation reduced fat deposition without affecting insulinemia in MTAU rats. MSG rats presented increased pIκ-Bα/Iκ-Bα protein expression in the retroperitoneal adipose tissue. TAU supplementation decreased the ratio of pIκ-Bα/Iκ-Bα protein, possibly contributing to the increased Iκ-Bα content in MTAU adipose tissue. Furthermore, MSG obesity or supplementation did not alter TNF-α, IL-1β or IL-6 content in adipose tissue. In contrast, MSG rats presented lower serum TNF-α, IL-4 and IL-10 concentrations, and these alterations were prevented by TAU treatment.
Conclusion
MSG obesity in rats was not associated with alterations in pro-inflammatory markers in retroperitoneal fat stores; however, reductions in the serum concentrations of anti-inflammatory cytokines and of TNF-α were observed. TAU treatment decreased adiposity, and this effect was associated with the normalization of circulating TNF-α and IL-4 concentrations in MTAU rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trujillo ME, Scherer PE (2006) Adipose tissue-derived factors: impact on health and disease. Endocr Rev 27:762–778
Wajchenberg BL (2000) Tecido Adiposo como Glândula Endócrina. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia & Metabologia 44(1):13–20
Leggate M, Carter WG, Evans MJ, Vennard RA, Sribala-Sundaram S, Nimmo MA (2012) Determination of inflammatory and prominent proteomic changes in plasma and adipose tissue after high-intensity intermittent training in overweight and obese males. J Appl Physiol (1985) 112:1353–1360
Yamakawa T, Tanaka S, Yamakawa Y, Kiuchi Y, Isoda F, Kawamoto S, Okuda K, Sekihara H (1995) Augmented production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in obese mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 75:51–56
Pickup JC, Chusney GD, Thomas SM, Burt D (2000) Plasma interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and blood cytokine production in type 2 diabetes. Life Sci 67:291–300
Roman-Ramos R, Almanza-Perez JC, Garcia-Macedo R, Blancas-Flores G, Fortis-Barrera A, Jasso EI, Garcia-Lorenzana M, Campos-Sepulveda AE, Cruz M, Alarcon-Aguilar FJ (2011) Monosodium glutamate neonatal intoxication associated with obesity in adult stage is characterized by chronic inflammation and increased mRNA expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 108:406–413
Trajcevski KE, O’Neill HM, Wang DC, Thomas MM, Al-Sajee D, Steinberg GR, Ceddia RB, Hawke TJ (2013) Enhanced lipid oxidation and maintenance of muscle insulin sensitivity despite glucose intolerance in a diet-induced obesity mouse model. PLoS One 8:e71747
Haase J, Weyer U, Immig K, Kloting N, Bluher M, Eilers J, Bechmann I, Gericke M (2014) Local proliferation of macrophages in adipose tissue during obesity-induced inflammation. Diabetologia 57:562–571
Schmid JA, Birbach A (2008) IkappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta/IKK2/IKBKB)–a key molecule in signaling to the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 19:157–165
Park YS, Lillehoj EP, Kato K, Park CS, Kim KC (2012) PPARgamma inhibits airway epithelial cell inflammatory response through a MUC1-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 302:L679–L687
Lira FS, Yamashita AS, Rosa JC, Koyama CH, Caperuto EC, Batista ML Jr, Seelaender MC (2012) Exercise training decreases adipose tissue inflammation in cachectic rats. Horm Metab Res 44:91–98
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259:87–91
Chae GN, Kwak SJ (2003) NF-kappaB is involved in the TNF-alpha induced inhibition of the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by reducing PPARgamma expression. Exp Mol Med 35:431–437
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239–252
Morse D, Pischke SE, Zhou Z, Davis RJ, Flavell RA, Loop T, Otterbein SL, Otterbein LE, Choi AM (2003) Suppression of inflammatory cytokine production by carbon monoxide involves the JNK pathway and AP-1. J Biol Chem 278:36993–36998
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Shozawa C, Sano K, Kamei Y, Kasaoka S, Hosokawa Y, Ezaki O (2006) Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) deficiency creates a vicious circle promoting obesity. Endocrinology 147:3276–3284
Nardelli TR, Ribeiro RA, Balbo SL, Vanzela EC, Carneiro EM, Boschero AC, Bonfleur ML (2011) Taurine prevents fat deposition and ameliorates plasma lipid profile in monosodium glutamate-obese rats. Amino Acids 41:901–908
Chang YY, Chou CH, Chiu CH, Yang KT, Lin YL, Weng WL, Chen YC (2011) Preventive effects of taurine on development of hepatic steatosis induced by a high-fat/cholesterol dietary habit. J Agric Food Chem 59:450–457
Gentile CL, Nivala AM, Gonzales JC, Pfaffenbach KT, Wang D, Wei Y, Jiang H, Orlicky DJ, Petersen DR, Pagliassotti MJ, Maclean KN (2011) Experimental evidence for therapeutic potential of taurine in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R1710–R1722
Carneiro EM, Latorraca MQ, Araujo E, Beltra M, Oliveras MJ, Navarro M, Berna G, Bedoya FJ, Velloso LA, Soria B, Martin F (2009) Taurine supplementation modulates glucose homeostasis and islet function. J Nutr Biochem 20:503–511
Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Amaral AG, Vanzela EC, Rocco SA, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2009) Taurine supplementation enhances nutrient-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic mice islets. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 25:370–379
Marcinkiewicz J, Mak M, Bobek M, Biedron R, Bialecka A, Koprowski M, Kontny E, Maslinski W (2005) Is there a role of taurine bromamine in inflammation? Interactive effects with nitrite and hydrogen peroxide. Inflamm Res 54:42–49
Marcinkiewicz J, Kurnyta M, Biedron R, Bobek M, Kontny E, Maslinski W (2006) Anti-inflammatory effects of taurine derivatives (taurine chloramine, taurine bromamine, and taurolidine) are mediated by different mechanisms. Adv Exp Med Biol 583:481–492
Marcinkiewicz J, Kontny E (2014) Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 46:7–20
Olney JW (1969) Brain lesions, obesity, and other disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate. Science 164:719–721
Olney JW, Adamo NJ, Ratner A (1971) Monosodium glutamate effects. Science 172:294
Alarcon-Aguilar FJ, Almanza-Perez J, Blancas G, Angeles S, Garcia-Macedo R, Roman R, Cruz M (2008) Glycine regulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in lean and monosodium glutamate-obese mice. Eur J Pharmacol 599:152–158
Patil S, Prakash T, Kotresha D, Rao NR, Pandy N (2011) Antihyperlipidemic potential of Cedrus deodara extracts in monosodium glutamate induced obesity in neonatal rats. Indian J Pharmacol 43:644–647
Hirata AE, Alvarez-Rojas F, Carvalheira JB, Carvalho CR, Dolnikoff MS, Abdalla Saad MJ (2003) Modulation of IR/PTP1B interaction and downstream signaling in insulin sensitive tissues of MSG-rats. Life Sci 73:1369–1381
Balbo SL, Grassiolli S, Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Gravena C, Brito Mdo N, Andreazzi AE, Mathias PC, Torrezan R (2007) Fat storage is partially dependent on vagal activity and insulin secretion of hypothalamic obese rat. Endocrine 31:142–148
Matysková R, Maletínská L, Maixnerová J, Pirník Z, Kiss A, Zelezná B (2008) Comparison of the obesity phenotypes related to monosodium glutamate effect on arcuate nucleus and/or the high fat diet feeding in C57BL/6 and NMRI mice. Physiol Res 57:727–734
Zhang N, Huan Y, Huang H, Song GM, Sun SJ, Shen ZF (2010) Atorvastatin improves insulin sensitivity in mice with obesity induced by monosodium glutamate. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:35–42
Almanza-Perez JC, Alarcon-Aguilar FJ, Blancas-Flores G, Campos-Sepulveda AE, Roman-Ramos R, Garcia-Macedo R, Cruz M (2010) Glycine regulates inflammatory markers modifying the energetic balance through PPAR and UCP-2. Biomed Pharmacother 64:534–540
Brandelero S Jr, Bonfleur ML, Ribeiro RA, Vanzela EC, Nassar CA, Nassar PO, Balbo SL (2012) Decreased TNF-alpha gene expression in periodontal ligature in MSG-obese rats: a possible protective effect of hypothalamic obesity against periodontal disease? Arch Oral Biol 57:300–306
Bernardis LL, Patterson BD (1968) Correlation between ‘Lee index’ and carcass fat content in weanling and adult female rats with hypothalamic lesions. J Endocrinol 40:527–528
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K (2011) Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:85–97
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB (2006) Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116:1793–1801
Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A (2007) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology 132:2169–2180
Barua M, Liu Y, Quinn MR (2001) Taurine chloramine inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and TNF-alpha gene expression in activated alveolar macrophages: decreased NF-kappaB activation and IkappaB kinase activity. J Immunol 167:2275–2281
Chen LF, Greene WC (2004) Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:392–401
Chiu YH, Zhao M, Chen ZJ (2009) Ubiquitin in NF-kappaB signaling. Chem Rev 109:1549–1560
Henkel T, Zabel U, van Zee K, Muller JM, Fanning E, Baeuerle PA (1992) Intramolecular masking of the nuclear location signal and dimerization domain in the precursor for the p50 NF-kappa B subunit. Cell 68:1121–1133
DiDonato JA, Hayakawa M, Rothwarf DM, Zandi E, Karin M (1997) A cytokine-responsive IkappaB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Nature 388:548–554
Hatada EN, Krappmann D, Scheidereit C (2000) NF-kappaB and the innate immune response. Curr Opin Immunol 12:52–58
Kanayama A, Inoue J, Sugita-Konishi Y, Shimizu M, Miyamoto Y (2002) Oxidation of Ikappa Balpha at methionine 45 is one cause of taurine chloramine-induced inhibition of NF-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem 277:24049–24056
Barbarroja N, Lopez-Pedrera C, Garrido-Sanchez L, Mayas MD, Oliva-Olivera W, Bernal-Lopez MR, El Bekay R, Tinahones FJ (2012) Progression from high insulin resistance to type 2 diabetes does not entail additional visceral adipose tissue inflammation. PLoS One 7:e48155
Ahmad R, Al-Mass A, Atizado V, Al-Hubail A, Al-Ghimlas F, Al-Arouj M, Bennakhi A, Dermime S, Behbehani K (2012) Elevated expression of the toll like receptors 2 and 4 in obese individuals: its significance for obesity-induced inflammation. J Inflamm (Lond) 9:48
Kawasaki N, Asada R, Saito A, Kanemoto S, Imaizumi K (2012) Obesity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes chronic inflammation in adipose tissue. Sci Rep 2:799
Chaparro-Huerta V, Rivera-Cervantes MC, Flores-Soto ME, Gomez-Pinedo U, Beas-Zarate C (2005) Proinflammatory cytokines and apoptosis following glutamate-induced excitotoxicity mediated by p38 MAPK in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. J Neuroimmunol 165:53–62
Dolnikoff MS, Kater CE, Egami M, de Andrade IS, Marmo MR (1988) Neonatal treatment with monosodium glutamate increases plasma corticosterone in the rat. Neuroendocrinology 48:645–649
Scheinman RI, Gualberto A, Jewell CM, Cidlowski JA, Baldwin AS (1995) Characterization of mechanisms involved in transrepression of NF-kappa B by activated glucocorticoid receptors. Mol Cell Biol 15:943–953
Marcinkiewicz J, Wojas-Pelc A, Walczewska M, Lipko-Godlewska S, Jachowicz R, Maciejewska A, Bialecka A, Kasprowicz A (2008) Topical taurine bromamine, a new candidate in the treatment of moderate inflammatory acne vulgaris: a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol 18:433–439
Marcinkiewicz J (2009) Taurine bromamine: a new therapeutic option in inflammatory skin diseases. Pol Arch Med Wewn 119:673–676
Lin S, Hirai S, Yamaguchi Y, Goto T, Takahashi N, Tani F, Mutoh C, Sakurai T, Murakami S, Yu R, Kawada T (2013) Taurine improves obesity-induced inflammatory responses and modulates the unbalanced phenotype of adipose tissue macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res 57:2155–2165
Das J, Vasan V, Sil PC (2012) Taurine exerts hypoglycemic effect in alloxan-induced diabetic rats, improves insulin-mediated glucose transport signaling pathway in heart and ameliorates cardiac oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258:296–308
Kim C, Cha YN (2014) Taurine chloramine produced from taurine under inflammation provides anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects. Amino Acids 46:89–100
Devi SL, Viswanathan P, Anuradha CV (2010) Regression of liver fibrosis by taurine in rats fed alcohol: effects on collagen accumulation, selected cytokines and stellate cell activation. Eur J Pharmacol 647:161–170
Kern S, Robertson SA, Mau VJ, Maddocks S (1995) Cytokine secretion by macrophages in the rat testis. Biol Reprod 53:1407–1416
Ziccardi P, Nappo F, Giugliano G, Esposito K, Marfella R, Cioffi M, D’Andrea F, Molinari AM, Giugliano D (2002) Reduction of inflammatory cytokine concentrations and improvement of endothelial functions in obese women after weight loss over 1 year. Circulation 105:804–809
Castrogiovanni D, Gaillard RC, Giovambattista A, Spinedi E (2008) Neuroendocrine, metabolic, and immune functions during the acute phase response of inflammatory stress in monosodium L-glutamate-damaged, hyperadipose male rat. Neuroendocrinology 88:227–234
Tsao CH, Shiau MY, Chuang PH, Chang YH, Hwang J (2014) Interleukin-4 regulates lipid metabolism by inhibiting adipogenesis and promoting lipolysis. J Lipid Res 55:385–397
Chang YH, Ho KT, Lu SH, Huang CN, Shiau MY (2012) Regulation of glucose/lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity by interleukin-4. Int J Obes (Lond) 36:993–998
Kaminski A, Welters HJ, Kaminski ER, Morgan NG (2010) Human and rodent pancreatic beta-cells express IL-4 receptors and IL-4 protects against beta-cell apoptosis by activation of the PI3 K and JAK/STAT pathways. Biosci Rep 30:169–175
Limaos EA, Silveira VL, Dolnikoff MS (1988) Inflammatory edema induced by carrageenin in monosodium glutamate-treated rats. Braz J Med Biol Res 21:837–839
Skultetyova I, Kiss A, Jezova D (1998) Neurotoxic lesions induced by monosodium glutamate result in increased adenopituitary proopiomelanocortin gene expression and decreased corticosterone clearance in rats. Neuroendocrinology 67:412–420
Perello M, Moreno G, Gaillard RC, Spinedi E (2004) Glucocorticoid-dependency of increased adiposity in a model of hypothalamic obesity. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 25:119–126
Acknowledgments
This study forms part of the M.Sc Thesis of Luis Carlos Caetano. We are grateful to Fernanda Michelly Nicoli for animal care and Nicola Conran for editing English. This study was supported by Grants from Conselho Nacional para o Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq process number: 480523/2012-7), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP).
Authorship
LCC, TRN, CL, JNS executed the experiments; SLB and MLB contributed to conception and experimental design, data interpretation and manuscript writing; RAR interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript; EMC intellectually contributed and provided materials and reagents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caetano, L.C., Bonfleur, M.L., Ribeiro, R.A. et al. Taurine supplementation regulates Iκ-Bα protein expression in adipose tissue and serum IL-4 and TNF-α concentrations in MSG obesity. Eur J Nutr 56, 705–713 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-1114-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-1114-8