Abstract
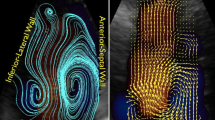
Mitral valve morphology after mitral valve surgery affects postoperative intraventricular flow patterns and long-term cardiac performance. We visualized ventricular flow by echocardiography vector flow mapping (VFM) to reveal the impact of different mitral valve procedures. Eleven cases of mechanical mitral valve replacement (nine in the anti-anatomical and two in the anatomical position), three bioprosthetic mitral valve replacements, and four mitral valve repairs were evaluated. The mean age at the procedure was 57.4 ± 17.8 year, and the echocardiography VFM in the apical long-axis view was performed 119.9 ± 126.7 months later. Flow energy loss (EL), kinetic pressure (KP), and the flow energy efficiency ratio (EL/KP) were measured. The cases with MVR in the anatomical position and with valve repair had normal vortex directionality (“Clockwise”; N = 6), whereas those with MVR in the anti-anatomical position and with a bioprosthetic mitral valve had the vortex in the opposite direction (“Counterclockwise”; N = 12). During diastole, vortex direction had no effect on EL (“Clockwise”: 0.080 ± 0.025 W/m; “Counterclockwise”: 0.083 ± 0.048 W/m; P = 0.31) or KP (“Clockwise”: 0.117 ± 0.021 N; “Counterclockwise”: 0.099 ± 0.057 N; P = 0.023). However, during systole, the EL/KP ratio was significantly higher in the “Counterclockwise” vortex than that in the “Clockwise” vortex (1.056 ± 0.463 vs. 0.617 ± 0.158; P = 0.009). MVP and MVR with a mechanical valve in the anatomical position preserve the physiological vortex, whereas MVR with a mechanical valve in the anti-anatomical position and a bioprosthetic mitral valve generate inefficient vortex flow patterns, resulting in a potential increase in excessive cardiac workload.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- EL:
-
Energy loss
- KP:
-
Kinetic pressure
- LV:
-
Left ventricle
- LVDd:
-
Left ventricular diastolic dimension
- LVDs:
-
Left ventricular systolic dimension
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- MR:
-
Mitral regurgitation
- MS:
-
Mitral stenosis
- MVP:
-
Mitral valve plasty
- MVR:
-
Mitral valve replacement
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PIV:
-
Particle imaging velocimetry
- TTE:
-
Transthoracic echocardiography
- VFM:
-
Vector flow mapping
References
Sengupta PP, Pedrizzetti G, Kilner PJ, Kheradvar A, Ebbers T, Tonti G, Fraster AG, Narula J (2012) Emerging trends in CV flow visualization. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 5: 305–316
Hong GR, Kim M, Pedrissetti G, Vannan MA (2013) Current clinical application of intracradiac flow analysis using echocardiography. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 21:155–162
Sughimoto K, Shimamura Y, Tezuka C, Tsubota KI, Liu H, Okumura K, Masuda Y, Haneishi H (2016) Effects of arterial blood flow on walls of the abdominal aorta: distributions of wall shear stress and oscillatory shear index determined by phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Heart Vessels 31:1168–1175
Koyama S, Kitamura T, Itatani K, Yamamoto T, Miyazaki S, Oka N, Nakashima K, Horai T, Ono M, Miyaji K (2016) Impact of top end anastomosis design on patency and flow stability in coronary artery bypass grafting. Heart Vessels 31:643–648
Faludi R, Szulik M, D’hooge J, Herijgers P, Rademakers F, Pedrizzetti G, Voigt JU (2010) Left ventricular flow patterns in healthy subjects and patients with prosthetic mitral valves: an in vivo study using echocardiographic particle image velocimetry. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 139:1501–1510
Itatani K (2014) When the blood flow becomes bright. Intraventricular flow patterns: from normality to pathology. Eur Heart J 35:747–752
Itatani K, Okata T, Uejima T, Tanaka T, Ono M, Miyaji K, Takenaka K (2013) Intraventricular flow velocity vector visualization based on the continuity equation and measurements of vorticity and wall shear stress. Jpn J Appl Phys 52:07HF16
Honda T, Itatani K, Miyaji K, Ishii M (2014) Assessment of the vortex flow in the post-stenotic dilatation above the pulmonary valve stenosis in an infant using echocardiography vector flow mapping. Eur Heart J 35:306
Kim HB, Hertzberg JR, Shandas R (2004) Echo PIV for flow field measurements in vivo. Biomed Sci Instrum 40:357–363
Prinz C, Faludi R, Walker A, Amzulescu M, Gao H, Uejima T, Fraser AG, Voigt JU (2012) Can echocardiographic particle image velocimetry correctly detect motion patterns as they occur in blood inside heart chambers? A validation study using moving phantoms. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 10:24
Ohtsuki S, Tanaka M (2006) The flow velocity distribution from Doppler information on a plane in three-dimensional flow. J Vis 9:69–82
Garcia D, Del Alamo JC, Tanne D, Yotti R, Cortina C, Bertrand E, Antoranz JC, Perez-David E, Rieu R, Fernandez-Aviles F, Bermejo J (2010) Two-dimensional intraventricular flow mapping by distal processing conventional color-Doppler echocardiography images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29:1701–1713
Föll D, Taeger S, Bode C, Jung B, Markl M (2013) Age, gender, blood pressure, and ventricular geometry influence normal 3D blood flow characteristics in the left heart. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 14:366–373
Mangual JO, De Luca A, Kraigher-Krainer E, Toncelli L, Shah A, Solomon S, Galanti G, Domenichini F, Pedrizzetti G (2013) Comparative numerical study on left ventricular fluid dynamics after dilated cardiomyopathy. J Biomech 46:1611–1617
Fukuda N, Itatani K, Kimura K, Ebihara A, Negishi K, Uno K, Miyaji K, Kurabayashi M, Takenaka K (2014) Prolonged vortex formation during the ejection period in the left ventricle with low ejection fraction: a study by vector flow mapping. J Med Ultrasonic 41:301–310
Mangual JO, Domenichini F, Pedrizzetti G (2012) Describing the highly three dimensional Right Ventricle flow. Ann Biomed Eng 40:1790–1801
Akutsu T, Imai R, Deguchi Y (2005) Effect of the flow field of mechanical bileaflet mitral prostheses on valve closing. J Artif Organ 8:161–170
Hong GR, PedrizzettiG, Tonti G, Li P, Wei Z, Kim JK, Baweja A, Liu S, Chung N, Houle H, Narula J, Vannan MA (2008) Characterization and quantification of vortex flow in the human left ventricle by contrast echocardiography using vector particle image velocimetry. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 1:705–717
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Keiichi Itatani was an endowed chair of Kitasato University, financially supported by Hitachi-Aloka Medical Co., Ltd. (Oct 2012–Jun 2015). He is also an endowed chair of Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, financially supported by Medtronic Japan Inc. (Apr 2016-present). He has a stock option of Cardio Flow Design Inc. The other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakashima, K., Itatani, K., Kitamura, T. et al. Energy dynamics of the intraventricular vortex after mitral valve surgery. Heart Vessels 32, 1123–1129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-0967-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-0967-6