Abstract
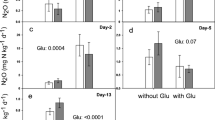
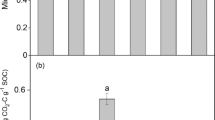
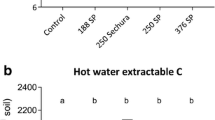
This study examines the effect of soil P status and N addition on the decomposition of 14C-labelled glucose to assess the consequences of reduced fertilizer inputs on the functioning of pastoral systems. A contrast in soil P fertility was obtained by selecting two hill pasture soils with different fertilizer history. At the two selected sites, representing low (LF) and high (HF) fertility status, total P concentrations were 640 and 820 mg kg–1 and annual pasture production was 4,868 and 14,120 kg DM ha–1 respectively. Soils were amended with 14C-labelled glucose (2,076 mg C kg–1 soil), with and without the addition of N (207 mg kg–1 soil), and incubated for 168 days. During incubation, the amounts of 14CO2 respired, microbial biomass C and 14C, microbial biomass P, extractable inorganic P (Pi) and net N mineralization were determined periodically. Carbon turnover was greatly influenced by nutrient P availability. The amount of glucose-derived 14CO2 production was high (72%) in the HF and low (67%) in the LF soil, as were microbial biomass C and P concentrations. The 14C that remained in the microbial biomass at the end of the 6-month incubation was higher in the LF soil (15%) than in the HF soil (11%). Fluctuations in Pi in the LF soil during incubation were small compared with those in HF soil, suggesting that P was cycling through microbial biomass. The concentrations of Pi were significantly greater in the HF samples throughout the incubation than in the LF samples. Net N mineralization and nitrification rates were also low in the LF soils, indicating a slow turnover of microorganisms under limited nutrient supply. Addition of N had little effect on biomass 14C and glucose utilization. This suggests that, at limiting P fertility, C turnover is retarded because microbial biomass becomes less efficient in the utilization of substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 October 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saggar, S., Hedley, C., Giddens, K. et al. Influence of soil phosphorus status and nitrogen addition on carbon mineralization from 14C-labelled glucose in pasture soils. Biol Fertil Soils 32, 209–216 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000237
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000237