Abstract
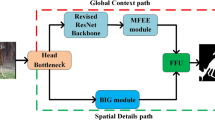
Salient object detection aims to detect distinct objects which attract human most. It has achieved substantial progress using deep convolutional neural networks in which conventional deconvolution operation is used as recovering the size of image in dense prediction tasks and cross-entropy loss is applied to compute the difference between saliency map and ground truth in pixel level. Different from conventional deconvolution operation, hybrid upsampling block is proposed to retain the detail of object by increasing the receptive field and spatial information when recovering the image size, and hybrid loss which consists of cross-entropy loss and area loss is proposed to train the network optimized by area constraint. At last, an encoder-decoder network based on hybrid upsampling block and hybrid loss is implemented in public benchmark dataset and achieves the best performance against state-of-the-art methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A., Dean, J., Devin, M., Ghemawat, S., Irving, G., Isard, M., et al.: Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: 12th \(\{\)USENIX\(\}\) Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (\(\{\)OSDI\(\}\) 16), pp. 265–283 (2016)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR 2009, pp. 1597–1604 (2009)
Borji, A., Sihite, D.N., Itti, L.: Salient Object Detection: A Benchmark. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Chen, H., Li, Y.: Three-stream attention-aware network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2891104
Chen, H., Li, Y., Su, D.: Multi-modal fusion network with multi-scale multi-path and cross-modal interactions for RGB-D salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 86, 376–385 (2019)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2018)
Cheng, M.M., Zhang, G.X., Mitra, N.J., Huang, X., Hu, S.M.: Global contrast based salient region detection. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 409–416 (2011)
Cong, R., Lei, J., Fu, H., Huang, Q., Cao, X., Hou, C.: Co-saliency detection for RBGD images based on multi-constraint feature matching and cross label propagation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. PP(99), 1–1 (2018)
Fan, D.P., Cheng, M.M., Liu, Y., Li, T., Borji, A.: Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4548–4557 (2017)
Fan, D.P., Cheng, M.M., Liu, J.J., Gao, S.H., Hou, Q., Borji, A.: Salient objects in clutter: bringing salient object detection to the foreground. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 196–212. Springer (2018)
Ilg, E., Mayer, N., Saikia, T., Keuper, M., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T.: Flownet 2.0: evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Jiang, P., Ling, H., Yu, J., Peng, J.: Salient region detection by UFO: uniqueness, focusness and objectness. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1976–1983 (2013)
Krähenbühl, P., Koltun, V.: Efficient inference in fully connected CRFs with Gaussian edge potentials. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 109–117 (2011)
Lee, G., Tai, Y.W., Kim, J.: Deep saliency with encoded low level distance map and high level features. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 660–668 (2016)
Li, G., Yu, Y.: Visual saliency based on multiscale deep features. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5455–5463 (2015)
Li, G., Yu, Y.: Deep contrast learning for salient object detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 478–487 (2016)
Li, X., Zhao, L., Wei, L., Yang, M.H., Wu, F., Zhuang, Y., Ling, H., Wang, J.: Deepsaliency: multi-task deep neural network model for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 25(8), 3919 (2016)
Liu, T., Sun, J., Zheng, N.N., Tang, X., Shum, H.Y.: Learning to detect a salient object. In: 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR ’07, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Luo, Z., Mishra, A., Achkar, A., Eichel, J., Li, S., Jodoin, P.M.: Non-local deep features for salient object detection. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6593–6601 (2017)
Mochizuki, I., Toyoura, M., Mao, X.: Visual attention prediction for images with leading line structure. Vis. Comput. 34(6–8), 1031–1041 (2018)
Pan, J., Canton, C., Mcguinness, K., O’Connor, N.E., Torres, J., Sayrol, E., Giro-I-Nieto, X.: Salgan: visual saliency prediction with generative adversarial networks. (2017) arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.01081
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Comput. Sci. (2014) arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556
e Souza, M.R., Pedrini, H.: Motion energy image for evaluation of video stabilization. Vis. Comput. pp. 1–13 (2017)
Wang, H., Dai, L., Cai, Y., Sun, X., Chen, L.: Salient object detection based on multi-scale contrast. Neural Netw 101, 47–56 (2018a)
Wang, L., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.H.: Deep networks for saliency detection via local estimation and global search. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3183–3192 (2015)
Wang, T., Zhang, L., Lu, H., Sun, C., Qi, J.: Kernelized subspace ranking for saliency detection. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 450–466 (2016a)
Wang, W., Shen, J.: Deep visual attention prediction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. PP(99), 1–1 (2018)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Shao, L., Porikli, F.: Correspondence driven saliency transfer. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(11), 5025–5034 (2016b)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Video salient object detection via fully convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(1), 38–49 (2018b)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Sun, H., Shao, L.: Video co-saliency guided co-segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 28(8), 1727–1736 (2018c)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Yang, R., Porikli, F.: Saliency-aware video object segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(1), 20–33 (2018d)
Wei, Y., Wen, F., Zhu, W., Sun, J.: Geodesic saliency using background priors. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 29–42. Springer (2012)
Wenguan, W., Jianbing, S., Ling, S.: Consistent video saliency using local gradient flow optimization and global refinement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 24(11), 4185 (2015)
Yan, B., Wang, H., Wang, X., Zhang, Y.: An accurate saliency prediction method based on generative adversarial networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2339–2343. IEEE (2017)
Yan, Q., Xu, L., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Hierarchical saliency detection. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1155–1162 (2013)
Yang, C., Zhang, L., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.H.: Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3166–3173 (2013)
Zhang, D., Meng, D., Han, J.: Co-saliency detection via a self-paced multiple-instance learning framework. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(5), 865–878 (2016)
Zhang, P., Wang, D., Lu, H., Wang, H., Xiang, R.: Amulet: Aggregating multi-level convolutional features for salient object detection. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 202–211 (2017a)
Zhang, P., Wang, D., Lu, H., Wang, H., Yin, B.: Learning uncertain convolutional features for accurate saliency detection. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 212–221 (2017b)
Zhu, W., Liang, S., Wei, Y., Sun, J.: Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2814–2821 (2014)
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Ming-ming Cheng from Nankai University for providing the codes of all evaluation metrics and result saliency maps. We further thank all anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. This research is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61602004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Tang, J. & Zhao, P. Salient object detection via hybrid upsampling and hybrid loss computing. Vis Comput 36, 843–853 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01659-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01659-w