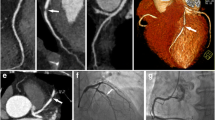
Abstract
Objective
To explore the image quality (IQ) and diagnostic value of 70 kVp turbo high-pitch coronary CT angiography (THP-CCTA) using automated tube voltage selection (ATVS) and 30 mL of low-concentration contrast agent.
Methods
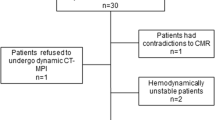
Patients who underwent 70 kVp THP-CCTA using ATVS with 30 mL of contrast agent (group A) were prospectively enrolled, and those who underwent conventional CCTA (100/120 kVp, prospective sequential mode with 65–75 mL of contrast agent) (group B) were retrospectively selected for study. IQ was assessed subjectively on a 5-point scale, and diagnostic value was assessed based on invasive coronary angiography as the gold standard. Heart rate (HR), HR fluctuation (HRF), body mass index (BMI), effective radiation dose (ED), and iodine uptake (IU) were recorded.
Results
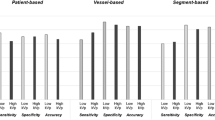
A total of 796 patients (398/398 in groups A/B) were included. Between-group differences in age, gender, BMI, HR, HRF, and IQ values were not significant. The ED/IU values were 0.3 ± 0.1 mSv/9.0 ± 0.0 g and 5.8 ± 1.8 mSv/22.9 ± 1.0 g in groups A and B, respectively (p < 0.01). The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy of THP-CCTA for the diagnosis of ≥ 50% stenosis were 94.8%, 97.5%, 92.0%, 98.4%, and 96.9% respectively. The mean HR and coronary calcium score were independent predictors of diagnostic image quality, and the best cutoff values were 71.5 bpm and 444.1 respectively.
Conclusion
This third-generation dual-source CT imaging modality, a 70-kVp THP-CCTA system using ATVS with 30 mL of low-concentration contrast agent, produces high-quality images with high diagnostic accuracy for significant stenosis, with ultra low ED and IU. This technique was most promising in individuals with an HR < 71.5 bpm and coronary calcium score < 444.1.
Key Points
• Turbo high-pitch CCTA using 70 kVp via automated tube voltage selection and 30 mL of low-concentration contrast agent is feasible.
• This protocol provides high diagnostic accuracy for significant coronary stenosis and reduces radiation doses and iodine uptake significantly.
• This protocol was most promising in individuals with an HR < 71.5 bpm and coronary calcium score < 444.1.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATVS:
-
Automated tube voltage selection
- AUCs:
-
Areas under curves
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DLP:
-
Dose length product
- DSCT:
-
Dual-source CT
- ED:
-
Effective radiation dose
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- HRF:
-
HR fluctuation
- ICA:
-
Invasive coronary angiography
- IQ:
-
Image quality
- IU:
-
Iodine uptake
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- THP-CCTA:
-
Turbo high-pitch coronary CT angiography
References
St Noble V, Douraghi-Zadeh D, Padley SPG et al (2014) Maximizing the clinical benefit of high-pitch, single-heartbeat CT coronary angiography in clinical practice. Clin Radiol 69:674–677
Achenbach S, Marwan M, Ropers D et al (2010) Coronary computed tomography angiography with a consistent dose below 1 mSv using prospectively electrocardiogram-triggered high-pitch spiral acquisition. Eur Heart J 31:340–346
Koplay M, Erdogan H, Avci A et al (2016) Radiation dose and diagnostic accuracy of high-pitch dual-source coronary angiography in the evaluation of coronary artery stenoses. Diagn Interv Imaging 97:461–469
Hell MM, Bittner D, Schuhbaeck A et al (2014) Prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch coronary angiography with third-generation dual-source CT at 70 kVp tube voltage: feasibility, image quality, radiation dose, and effect of iterative reconstruction. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 8:418–425
Gordic S, Desbiolles L, Sedlmair M et al (2016) Optimizing radiation dose by using advanced modelled iterative reconstruction in high-pitch coronary CT angiography. Eur Radiol 26:459–468
Slovis TL (2002) The ALARA concept in pediatric CT: myth or reality? Radiology 223:5–6
Zhang LJ, Wang Y, Schoepf UJ et al (2016) Image quality, radiation dose, and diagnostic accuracy of prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch coronary CT angiography at 70 kVp in a clinical setting: comparison with invasive coronary angiography. Eur Radiol 26:797–806
Higashigaito K, Schmid T, Puippe G et al (2016) CT angiography of the aorta: prospective evaluation of individualized low-volume contrast media protocols. Radiology 280:960–968
Kosmala A, Petritsch B, Weng AM et al (2018) Radiation dose of coronary CT angiography with a third-generation dual-source CT in a “real-world” patient population. Eur Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5856-6
Pontone G, Muscogiuri G, Baggiano A et al (2018) Image quality, overall evaluability, and effective radiation dose of coronary computed tomography angiography with prospective electrocardiographic triggering plus intracycle motion correction algorithm in patients with a heart rate over 65 beats per minute. J Thorac Imaging 33:225–231
Apfaltrer G, Albrecht MH, Schoepf UJ et al (2018) High-pitch low-voltage CT coronary artery calcium scoring with tin filtration: accuracy and radiation dose reduction. Eur Radiol 28:3097–3104
Li Y, Yu M, Li W et al (2018) Third generation dual-source CT enables accurate diagnosis of coronary restenosis in all size stents with low radiation dose and preserved image quality. Eur Radiol 28:2647–2654
Nakaura T, Kidoh M, Sakaino N et al (2013) Low contrast- and low radiation dose protocol for cardiac CT of thin adults at 256-row CT: usefulness of low tube voltage scans and the hybrid iterative reconstruction algorithm. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29:913–923
Lembcke A, Schwenke C, Hein PA et al (2014) High-pitch dual-source CT coronary angiography with low volumes of contrast medium. Eur Radiol 24:120–127
Zhang C, Yu Y, Zhang Z et al (2015) Imaging quality evaluation of low tube voltage coronary CT angiography using low concentration contrast medium. PLoS One 10:e120539
Yin WH, Lu B, Gao JB et al (2015) Effect of reduced x-ray tube voltage, low iodine concentration contrast medium, and sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction on image quality and radiation dose at coronary CT angiography: results of the prospective multicenter REALISE trial. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 9:215–224
Zheng M, Wu Y, Wei M et al (2015) Low-concentration contrast medium for 128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography at a very low radiation dose using prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch spiral acquisition. Acad Radiol 22:195–202
Meyer M, Haubenreisser H, Schoepf UJ et al (2014) Closing in on the K edge: coronary CT angiography at 100, 80, and 70 kV-initial comparison of a second- versus a third-generation dual-source CT system. Radiology 273:373–382
Meyer M, Haubenreisser H, Schoepf UJ et al (2017) Radiation dose levels of retrospectively ECG-gated coronary CT angiography using 70-kVp tube voltage in patients with high or irregular heart rates. Acad Radiol 24:30–37
Ochs MM, Andre F, Korosoglou G et al (2017) Strengths and limitations of coronary angiography with turbo high-pitch third-generation dual-source CT. Clin Radiol 72:739–744
Zhang LJ, Qi L, De Cecco CN et al (2014) High-pitch coronary CT angiography at 70 kVp with low contrast medium volume: comparison of 80 and 100 kVp high-pitch protocols. Medicine (Baltimore) 93:e92
Wang W, Zhao YE, Qi L et al (2017) Prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch coronary CT angiography at 70 kVp with 30mL contrast agent: an intraindividual comparison with sequential scanning at 120 kVp with 60 mL contrast agent. Eur J Radiol 90:97–105
Ghoshhajra BB, Engel LC, Karolyi M et al (2013) Cardiac computed tomography angiography with automatic tube potential selection: effects on radiation dose and image quality. J Thorac Imaging 28:40–48
Albrecht MH, Nance JW, Schoepf UJ et al (2018) Diagnostic accuracy of low and high tube voltage coronary CT angiography using an X-ray tube potential-tailored contrast medium injection protocol. Eur Radiol 28:2134–2142
Sun K, Han R, Ma L et al (2012) Prospectively electrocardiogram-gated high-pitch spiral acquisition mode dual-source CT coronary angiography in patients with high heart rates: comparison with retrospective electrocardiogram-gated spiral acquisition mode. Korean J Radiol 13:684
Feng R, Mao J, Liu X et al (2018) High-pitch coronary computed tomographic angiography using the third-generation dual-source computed tomography: initial experience in patients with high heart rate. J Comput Assist Tomogr 42:248–255
Acknowledgements
Thanks to BioMed Proofreading LLC for polishing this article.
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Zhao-qian Wang.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• prospective
• case-control study
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Cf., Zhong, J., Meng, Xy. et al. Image quality and diagnostic value of ultra low-voltage, ultra low-contrast coronary CT angiography. Eur Radiol 29, 3678–3685 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06111-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06111-0