Abstract
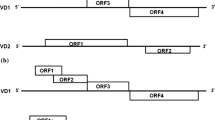
Bombyx mori bidensovirus (BmBDV) VD1-ORF4 (open reading frame 4, ORF4) consists of 3,318 nucleotides, which codes for a predicted 1,105-amino acid protein containing a conserved DNA polymerase motif. However, its functions in viral propagation remain unknown. In the current study, the transcription of VD1-ORF4 was examined from 6 to 96 h postinfection (p.i.) by RT-PCR, 5′-RACE revealed the transcription initiation site of BmBDV ORF4 to be −16 nucleotides upstream from the start codon, and 3′-RACE revealed the transcription termination site of VD1-ORF4 to be +7 nucleotides downstream from termination codon. Three different proteins were examined in the extracts of BmBDV-infected silkworms midguts by Western blot using raised antibodies against VD1-ORF4 deduced amino acid, and a specific protein band about 53 kDa was further detected in purified virions using the same antibodies. Taken together, BmBDV VD1-ORF4 codes for three or more proteins during the viral life cycle, one of which is a 53 kDa protein and confirmed to be a component of BmBDV virion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MJ, Carstens EB (2012) Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2012). Arch Virol 157:1411–1422
Blanco L, Salas M (1996) Relating structure to function in phi29 DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem 271:8509–8512
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Hu Z, Yuan M, Wu W et al (2010) Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus ac76 is involved in intranuclear microvesicle formation. J Virol 84:7437–7447
Hayakawa T, Kojima K, Nonaka K et al (2000) Analysis of proteins encoded in the bipartite genome of a new type of parvo-like virus isolated from silkworm–structural protein with DNA polymerase motif. Virus Res 66:101–108
Kong J, Hu Z, He Y et al (2011) Expression analysis of Bombyx mori parvo-like virus VD2-ORF1 gene encoding a minor structural protein. Biologia 66:684–689
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2006) Self-synthesizing DNA transposons in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4540–4545
Katsuma S, Kang W, Shin-i T et al (2011) Mass identification of transcriptional units expressed from the Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus genome. J Gen Virol 92:200–203
Li G, Sun C, Zhang J et al (2009) Characterization of Bombyx mori parvo-like virus non-structural protein NS1. Virus Genes 39:396–402
Lv M, Yao Q, Wang Y et al (2011) Identification of structural proteins of Bombyx mori parvo-like virus (China Zhenjiang isolate). Intervirology 54:37–43
Pan L, Li Z, Gong Y et al (2005) Characterization of gp41 gene of Spodoptera litura multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virus Res 110:73–79
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NewYork
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wang YJ, Yao Q, Chen KP et al (2007) Characterization of the genome structure of Bombyx mori densovirus (China isolate). Virus Genes 35:103–108
Zhang J, Li G, Chen H et al (2010) Molecular cloning and expression of key gene encoding hypothetical DNA polymerase from B. mori parvo-like virus. Genet Mol Biol 33:739–744
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31000080, 31270192 and 31272507), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2011M500855), National basic Research Program of China under Grant No. 2012CB114604, and starting fund projects for senior professionals (09JDG057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Hu, Z., Guo, X. et al. Identification of Bombyx mori Bidensovirus VD1-ORF4 Reveals a Novel Protein Associated with Viral Structural Component. Curr Microbiol 66, 527–534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0306-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0306-9