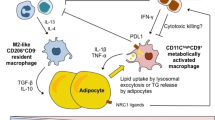
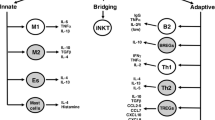
Abstract
Throughout evolution, effective nutrient sensing and control of systemic energy homeostasis have relied on a close physical and functional interaction between immune and metabolically active cells. However, in today's obesogenic environment, this fine-tuned immunometabolic interface is perturbed. As a consequence, chronic inflammatory conditions and aberrant activation of immune cells have emerged as key features of obesity-related metabolic disorders, including insulin resistance, cardiovascular complications, and type 2 diabetes, whereas a major research focus has been placed on the adipocyte–macrophage interaction in the context of metabolic dysfunction; recent studies have not only expanded the scope of relevant immune cells in this setting but also highlight the impact of distinct metabolic organs, including the liver, on immunometabolic control, metabolic disease development, and potential anti-inflammatory therapeutic options in obesity-driven pathologies. This review will thus summarize recent progress in this emerging area of metabolic research.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, Farzadfar F, Riley LM, Ezzati M (2011) National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet 377(9765):557–567. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414(6865):813–820
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Investig 112(12):1796–1808
Hotamisligil GS, Budavari A, Murray D, Spiegelman BM (1994) Reduced tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in obesity-diabetes, central role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Clin Investig 94(4):1543–1549
Chiang SH, Bazuine M, Lumeng CN, Geletka LM, Mowers J, White NM, Ma JT, Zhou J, Qi N, Westcott D, Delproposto JB, Blackwell TS, Yull FE, Saltiel AR (2009) The protein kinase IKKepsilon regulates energy balance in obese mice. Cell 138(5):961–975. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.046
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Gorgun CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS (2002) A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420(6913):333–336. doi:10.1038/nature01137 nature01137
Yuan M, Konstantopoulos N, Lee J, Hansen L, Li ZW, Karin M, Shoelson SE (2001) Reversal of obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of Ikkbeta. Science 293(5535):1673–1677
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444(7121):860–867
Farooqi IS (2011) Genetic, molecular and physiological insights into human obesity. Eur J Clin Investig 41(4):451–455. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02468.x
Rohm M, Sommerfeld A, Strzoda D, Jones A, Sijmonsma TP, Rudofsky G, Wolfrum C, Sticht C, Gretz N, Zeyda M, Leitner L, Nawroth PP, Stulnig TM, Diaz MB, Vegiopoulos A, Herzig S (2013) Transcriptional cofactor TBLR1 controls lipid mobilization in white adipose tissue. Cell metabolism 17(4):575–585. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.02.010
Casteels K, Mathieu C (2003) Diabetic ketoacidosis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 4(2):159–166
Sommerfeld A, Krones-Herzig A, Herzig S (2011) Transcriptional co-factors and hepatic energy metabolism. Mol Cell Endocrinol 332(1–2):21–31. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2010.11.020
Kulozik P, Jones A, Mattijssen F, Rose AJ, Reimann A, Strzoda D, Kleinsorg S, Raupp C, Kleinschmidt J, Muller-Decker K, Wahli W, Sticht C, Gretz N, von Loeffelholz C, Stockmann M, Pfeiffer A, Stohr S, Dallinga-Thie GM, Nawroth PP, Berriel Diaz M, Herzig S (2011) Hepatic deficiency in transcriptional cofactor TBL1 promotes liver steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia. Cell metabolism 13(4):389–400. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.011
Kim JK, Gavrilova O, Chen Y, Reitman ML, Shulman GI (2000) Mechanism of insulin resistance in A-ZIP/F-1 fatless mice. J Biol Chem 275(12):8456–8460
Michael MD, Kulkarni RN, Postic C, Previs SF, Shulman GI, Magnuson MA, Kahn CR (2000) Loss of insulin signaling in hepatocytes leads to severe insulin resistance and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Mol Cell 6(1):87–97
Du K, Herzig S, Kulkarni RN, Montminy M (2003) TRB3: a tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by insulin in liver. Science 300(5625):1574–1577
Odegaard JI, Chawla A (2013) Pleiotropic actions of insulin resistance and inflammation in metabolic homeostasis. Science 339(6116):172–177. doi:10.1126/science.1230721
Sell H, Habich C, Eckel J (2012) Adaptive immunity in obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8(12):709–716. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2012.114
Shu CJ, Benoist C, Mathis D (2012) The immune system's involvement in obesity-driven type 2 diabetes. Semin Immunol 24(6):436–442. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2012.12.001
Biswas SK, Mantovani A (2012) Orchestration of metabolism by macrophages. Cell Metab 15(4):432–437. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.11.013
Dalmas E, Clement K, Guerre-Millo M (2011) Defining macrophage phenotype and function in adipose tissue. Trends Immunol 32(7):307–314. doi:10.1016/j.it.2011.04.008
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C, Jaillon S (2011) Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 11(8):519–531. doi:10.1038/nri3024
Elgazar-Carmon V, Rudich A, Hadad N, Levy R (2008) Neutrophils transiently infiltrate intra-abdominal fat early in the course of high-fat feeding. J Lipid Res 49(9):1894–1903. doi:10.1194/jlr.M800132-JLR200
Talukdar S, da Oh Y, Bandyopadhyay G, Li D, Xu J, McNelis J, Lu M, Li P, Yan Q, Zhu Y, Ofrecio J, Lin M, Brenner MB, Olefsky JM (2012) Neutrophils mediate insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet through secreted elastase. Nat Med 18(9):1407–1412. doi:10.1038/nm.2885
Pham CT (2006) Neutrophil serine proteases: specific regulators of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 6(7):541–550. doi:10.1038/nri1841
Nijhuis J, Rensen SS, Slaats Y, van Dielen FM, Buurman WA, Greve JW (2009) Neutrophil activation in morbid obesity, chronic activation of acute inflammation. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17(11):2014–2018. doi:10.1038/oby.2009.113
Herishanu Y, Rogowski O, Polliack A, Marilus R (2006) Leukocytosis in obese individuals: possible link in patients with unexplained persistent neutrophilia. Eur J Haematol 76(6):516–520. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0609.2006.00658.x
Zaldivar F, McMurray RG, Nemet D, Galassetti P, Mills PJ, Cooper DM (2006) Body fat and circulating leukocytes in children. Int J Obes (Lond) 30(6):906–911. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0803227
Suzukawa M, Nagase H, Ogahara I, Han K, Tashimo H, Shibui A, Koketsu R, Nakae S, Yamaguchi M, Ohta K (2011) Leptin enhances survival and induces migration, degranulation, and cytokine synthesis of human basophils. J Immunol 186(9):5254–5260. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1004054
Laurson KR, McCann DA, Senchina DS (2011) Age, sex, and ethnicity may modify the influence of obesity on inflammation. Journal of investigative medicine : the official publication of the American Federation for Clinical Research 59 (1): 27–31. doi:10.231/JIM.0b013e318200151a
Johannsen NM, Priest EL, Dixit VD, Earnest CP, Blair SN, Church TS (2010) Association of white blood cell subfraction concentration with fitness and fatness. Br J Sports Med 44(8):588–593. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2008.050682
Vasudevan AR, Wu H, Xydakis AM, Jones PH, Smith EO, Sweeney JF, Corry DB, Ballantyne CM (2006) Eotaxin and obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(1):256–261. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-1280
Wu D, Molofsky AB, Liang HE, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Jouihan HA, Bando JK, Chawla A, Locksley RM (2011) Eosinophils sustain adipose alternatively activated macrophages associated with glucose homeostasis. Science 332(6026):243–247. doi:10.1126/science.1201475
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA, Piliponsky AM, Williams CM, Tsai M (2005) Mast cells as “tunable” effector and immunoregulatory cells: recent advances. Annu Rev Immunol 23:749–786. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141025
Poglio S, De Toni-Costes F, Arnaud E, Laharrague P, Espinosa E, Casteilla L, Cousin B (2010) Adipose tissue as a dedicated reservoir of functional mast cell progenitors. Stem Cells 28(11):2065–2072. doi:10.1002/stem.523
Liu J, Divoux A, Sun J, Zhang J, Clement K, Glickman JN, Sukhova GK, Wolters PJ, Du J, Gorgun CZ, Doria A, Libby P, Blumberg RS, Kahn BB, Hotamisligil GS, Shi GP (2009) Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat Med 15(8):940–945. doi:10.1038/nm.1994
Altintas MM, Azad A, Nayer B, Contreras G, Zaias J, Faul C, Reiser J, Nayer A (2011) Mast cells, macrophages, and crown-like structures distinguish subcutaneous from visceral fat in mice. J lipid Res 52(3):480–488. doi:10.1194/jlr.M011338
Tanaka A, Nomura Y, Matsuda A, Ohmori K, Matsuda H (2011) Mast cells function as an alternative modulator of adipogenesis through 15-deoxy-delta-12, 14-prostaglandin J2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301(6):C1360–1367. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00514.2010
Murakami M, Tada K, Nakajima K, Kudo I (1997) Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent delayed prostaglandin D2 generation is initiated by nerve growth factor in rat peritoneal mast cells: its augmentation by extracellular type II secretory phospholipase A2. J Immunol 159(1):439–446
Kliewer SA, Lenhard JM, Willson TM, Patel I, Morris DC, Lehmann JM (1995) A prostaglandin J2 metabolite binds peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Cell 83(5):813–819
Herlong JL, Scott TR (2006) Positioning prostanoids of the D and J series in the immunopathogenic scheme. Immunol lett 102(2):121–131. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2005.10.004
Sinha D, Addya S, Murer E, Boden G (1999) 15-Deoxy-delta(12,14) prostaglandin J2: a putative endogenous promoter of adipogenesis suppresses the ob gene. Metab: Clin Exp 48(6):786–791
Zhang J, Shi GP (2012) Mast cells and metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(1):14–20. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.12.012
Caspar-Bauguil S, Cousin B, Galinier A, Segafredo C, Nibbelink M, Andre M, Casteilla L, Penicaud L (2005) Adipose tissues as an ancestral immune organ: site-specific change in obesity. FEBS lett 579(17):3487–3492. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.05.031
Barra NG, Chew MV, Reid S, Ashkar AA (2012) Interleukin-15 treatment induces weight loss independent of lymphocytes. PloS One 7(6):e39553. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039553
Lynch LA, O'Connell JM, Kwasnik AK, Cawood TJ, O'Farrelly C, O'Shea DB (2009) Are natural killer cells protecting the metabolically healthy obese patient? Obesity (Silver Spring) 17(3):601–605. doi:10.1038/oby.2008.565
Duffaut C, Galitzky J, Lafontan M, Bouloumie A (2009) Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384(4):482–485. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.002
O'Rourke RW, White AE, Metcalf MD, Olivas AS, Mitra P, Larison WG, Cheang EC, Varlamov O, Corless CL, Roberts CT Jr, Marks DL (2011) Hypoxia-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion in human adipose tissue stromovascular cells. Diabetologia 54(6):1480–1490. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2103-y
Barra NG, Reid S, MacKenzie R, Werstuck G, Trigatti BL, Richards C, Holloway AC, Ashkar AA (2010) Interleukin-15 contributes to the regulation of murine adipose tissue and human adipocytes. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18(8):1601–1607. doi:10.1038/oby.2009.445
Ahima RS, Flier JS (2000) Leptin. Annu Rev Physiol 62:413–437. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.62.1.413
La Cava A, Matarese G (2004) The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4(5):371–379. doi:10.1038/nri1350
Faggioni R, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C (2001) Leptin regulation of the immune response and the immunodeficiency of malnutrition. FASEB J : Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 15(14):2565–2571. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0431rev
Gainsford T, Willson TA, Metcalf D, Handman E, McFarlane C, Ng A, Nicola NA, Alexander WS, Hilton DJ (1996) Leptin can induce proliferation, differentiation, and functional activation of hemapoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(25):14564–14568
Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, Klein AS, Bulkley GB, Bao C, Noble PW, Lane MD, Diehl AM (1998) Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J : Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 12(1):57–65
Lee FY, Li Y, Yang EK, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Trush MA, Dannenberg AJ, Diehl AM (1999) Phenotypic abnormalities in macrophages from leptin-deficient, obese mice. Am J Physiol 276(2 Pt 1):C386–394
Mattioli B, Giordani L, Quaranta MG, Viora M (2009) Leptin exerts an anti-apoptotic effect on human dendritic cells via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. FEBS lett 583(7):1102–1106. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.02.029
Smith AG, Sheridan PA, Harp JB, Beck MA (2007) Diet-induced obese mice have increased mortality and altered immune responses when infected with influenza virus. J Nutr 137(5):1236–1243
Tian Z, Sun R, Wei H, Gao B (2002) Impaired natural killer (NK) cell activity in leptin receptor deficient mice: leptin as a critical regulator in NK cell development and activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298(3):297–302
Wrann CD, Laue T, Hubner L, Kuhlmann S, Jacobs R, Goudeva L, Nave H (2012) Short-term and long-term leptin exposure differentially affect human natural killer cell immune functions. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 302(1):E108–116. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00057.2011
Beckman EM, Porcelli SA, Morita CT, Behar SM, Furlong ST, Brenner MB (1994) Recognition of a lipid antigen by CD1-restricted alpha beta + T cells. Nature 372(6507):691–694. doi:10.1038/372691a0
Lynch L, Nowak M, Varghese B, Clark J, Hogan AE, Toxavidis V, Balk SP, O'Shea D, O'Farrelly C, Exley MA (2012) Adipose tissue invariant NKT cells protect against diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorder through regulatory cytokine production. Immunity 37(3):574–587. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.06.016
Ohmura K, Ishimori N, Ohmura Y, Tokuhara S, Nozawa A, Horii S, Andoh Y, Fujii S, Iwabuchi K, Onoe K, Tsutsui H (2010) Natural killer T cells are involved in adipose tissues inflammation and glucose intolerance in diet-induced obese mice. Arterioscler, Thromb, Vasc Biol 30(2):193–199. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.198614
Mantell BS, Stefanovic-Racic M, Yang X, Dedousis N, Sipula IJ, O'Doherty RM (2011) Mice lacking NKT cells but with a complete complement of CD8+ T-cells are not protected against the metabolic abnormalities of diet-induced obesity. PloS One 6(6):e19831. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019831
Schipper HS, Rakhshandehroo M, van de Graaf SF, Venken K, Koppen A, Stienstra R, Prop S, Meerding J, Hamers N, Besra G, Boon L, Nieuwenhuis EE, Elewaut D, Prakken B, Kersten S, Boes M, Kalkhoven E (2012) Natural killer T cells in adipose tissue prevent insulin resistance. J Clin Investig 122(9):3343–3354. doi:10.1172/JCI62739
Ji Y, Sun S, Xu A, Bhargava P, Yang L, Lam KS, Gao B, Lee CH, Kersten S, Qi L (2012) Activation of natural killer T cells promotes M2 macrophage polarization in adipose tissue and improves systemic glucose tolerance via interleukin-4 (IL-4)/STAT6 protein signaling axis in obesity. J Biol Chem 287(17):13561–13571. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.350066
Ji Y, Sun S, Xia S, Yang L, Li X, Qi L (2012) Short-term high-fat-diet challenge promotes alternative macrophage polarization in adipose tissue via natural killer T cells and interleukin-4. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.371807
Wu L, Parekh VV, Gabriel CL, Bracy DP, Marks-Shulman PA, Tamboli RA, Kim S, Mendez-Fernandez YV, Besra GS, Lomenick JP, Williams B, Wasserman DH, Van Kaer L (2012) Activation of invariant natural killer T cells by lipid excess promotes tissue inflammation, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obese mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(19):E1143–1152. doi:10.1073/pnas.1200498109
Lynch L, O'Shea D, Winter DC, Geoghegan J, Doherty DG, O'Farrelly C (2009) Invariant NKT cells and CD1d(+) cells amass in human omentum and are depleted in patients with cancer and obesity. Eur J Immunol 39(7):1893–1901. doi:10.1002/eji.200939349
Kenna T, Golden-Mason L, Porcelli SA, Koezuka Y, Hegarty JE, O'Farrelly C, Doherty DG (2003) NKT cells from normal and tumor-bearing human livers are phenotypically and functionally distinct from murine NKT cells. J Immunol 171(4):1775–1779
Banchereau J, Steinman RM (1998) Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392(6673):245–252. doi:10.1038/32588
Dominguez PM, Ardavin C (2010) Differentiation and function of mouse monocyte-derived dendritic cells in steady state and inflammation. Immunol Rev 234(1):90–104. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00876.x
Joffre O, Nolte MA, Sporri R, Reis e Sousa C (2009) Inflammatory signals in dendritic cell activation and the induction of adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 227(1):234–247. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065×.2008.00718.x
Bedford PA, Todorovic V, Westcott ED, Windsor AC, English NR, Al-Hassi HO, Raju KS, Mills S, Knight SC (2006) Adipose tissue of human omentum is a major source of dendritic cells, which lose MHC Class II and stimulatory function in Crohn's disease. J Leukoc Biol 80(3):546–554. doi:10.1189/jlb.0905501
Bertola A, Ciucci T, Rousseau D, Bourlier V, Duffaut C, Bonnafous S, Blin-Wakkach C, Anty R, Iannelli A, Gugenheim J, Tran A, Bouloumie A, Gual P, Wakkach A (2012) Identification of adipose tissue dendritic cells correlated with obesity-associated insulin-resistance and inducing Th17 responses in mice and patients. Diabetes 61(9):2238–2247. doi:10.2337/db11-1274
Stefanovic-Racic M, Yang X, Turner MS, Mantell BS, Stolz DB, Sumpter TL, Sipula IJ, Dedousis N, Scott DK, Morel PA, Thomson AW, O'Doherty RM (2012) Dendritic cells promote macrophage infiltration and comprise a substantial proportion of obesity-associated increases in CD11c + cells in adipose tissue and liver. Diabetes 61(9):2330–2339. doi:10.2337/db11-1523
Winer S, Paltser G, Chan Y, Tsui H, Engleman E, Winer D, Dosch HM (2009) Obesity predisposes to Th17 bias. Eur J Immunol 39(9):2629–2635. doi:10.1002/eji.200838893
Gao B, Jeong WI, Tian Z (2008) Liver: an organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology 47(2):729–736. doi:10.1002/hep.22034
Bjorkstrom NK, Kekalainen E, Mjosberg J (2013) Tissue-specific effector functions of innate lymphoid cells. Immunology. doi:10.1111/imm.12098
Sakaguchi S, Takahashi S, Sasaki T, Kumagai T, Nagata K (2011) Progression of alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: common metabolic aspects of innate immune system and oxidative stress. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 26(1):30–46
Williams KH, Shackel NA, Gorrell MD, McLennan SV, Twigg SM (2013) Diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a pathogenic duo. Endocr Rev 34(1):84–129. doi:10.1210/er.2012-1009
Larrain S, Rinella ME (2012) A myriad of pathways to NASH. Clin liver Dis 16(3):525–548. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2012.05.009
Bohinc BN, Diehl AM (2012) Mechanisms of disease progression in NASH: new paradigms. Clin liver Dis 16(3):549–565. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2012.05.002
Zhan YT, An W (2010) Roles of liver innate immune cells in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol : WJG 16(37):4652–4660
Bilzer M, Roggel F, Gerbes AL (2006) Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int : Off J Int Assoc Study of the Liver 26(10):1175–1186. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01342.x
Szabo G, Petrasek J, Bala S (2012) Innate immunity and alcoholic liver disease. Dig Dis 30(Suppl 1):55–60. doi:10.1159/000341126
Cubero FJ, Nieto N (2012) Arachidonic acid stimulates TNFalpha production in Kupffer cells via a reactive oxygen species-pERK1/2-Egr1-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303(2):G228–239. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00465.2011
Mandrekar P, Ambade A, Lim A, Szabo G, Catalano D (2011) An essential role for monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in alcoholic liver injury: regulation of proinflammatory cytokines and hepatic steatosis in mice. Hepatology 54(6):2185–2197. doi:10.1002/hep.24599
Miura K, Kodama Y, Inokuchi S, Schnabl B, Aoyama T, Ohnishi H, Olefsky JM, Brenner DA, Seki E (2010) Toll-like receptor 9 promotes steatohepatitis by induction of interleukin-1beta in mice. Gastroenterology 139(1):323–334. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.03.052, e327
Yang YY, Huang YT, Tsai TH, Hou MC, Lee FY, Lee SD, Lin HC (2012) Kupffer cell depletion attenuates leptin-mediated methoxamine-stimulated portal perfusion pressure and thromboxane A2 release in a rodent model of NASH-cirrhosis. Clin Sci 123(12):669–680. doi:10.1042/CS20110572
Tosello-Trampont AC, Landes SG, Nguyen V, Novobrantseva TI, Hahn YS (2012) Kuppfer cells trigger nonalcoholic steatohepatitis development in diet-induced mouse model through tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. J Biol Chem 287(48):40161–40172. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.417014
Seki E, Schnabl B (2012) Role of innate immunity and the microbiota in liver fibrosis: crosstalk between the liver and gut. J Physiol 590(Pt 3):447–458. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.219691
Leroux A, Ferrere G, Godie V, Cailleux F, Renoud ML, Gaudin F, Naveau S, Prevot S, Makhzami S, Perlemuter G, Cassard-Doulcier AM (2012) Toxic lipids stored by Kupffer cells correlates with their pro-inflammatory phenotype at an early stage of steatohepatitis. J Hepatol 57(1):141–149. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.02.028
Odegaard JI, Chawla A (2008) Mechanisms of macrophage activation in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4(11):619–626. doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0976
Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Red Eagle A, Vats D, Morel CR, Goforth MH, Subramanian V, Mukundan L, Ferrante AW, Chawla A (2008) Alternative M2 activation of Kupffer cells by PPARdelta ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab 7(6):496–507. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2008.04.003
de las Casas-Engel M, Dominguez-Soto A, E S-F, Bragado R, Nieto C, Puig-Kroger A, Samaniego R, Loza M, Corcuera MT, Gomez-Aguado F, Bustos M, Sanchez-Mateos P, Corbi AL (2013) Serotonin skews human macrophage polarization through HTR2B and HTR7. J Immunol 190(5):2301–2310. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1201133
Muldoon MF, Mackey RH, Korytkowski MT, Flory JD, Pollock BG, Manuck SB (2006) The metabolic syndrome is associated with reduced central serotonergic responsivity in healthy community volunteers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(2):718–721. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-1654
Gao B, Radaeva S (2012) Natural killer and natural killer T cells in liver fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.09.008
Kahraman A, Fingas CD, Syn WK, Gerken G, Canbay A (2012) Role of stress-induced NKG2D ligands in liver diseases. Liver Int : Off J Int Assoc Study Liver 32(3):370–382. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02608.x
Mondelli MU (2012) NKG2D and its ligands: key to immunotherapy of liver cancer? J Hepatol 56(2):308–310. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.07.008
Zou Y, Chen T, Han M, Wang H, Yan W, Song G, Wu Z, Wang X, Zhu C, Luo X, Ning Q (2010) Increased killing of liver NK cells by Fas/Fas ligand and NKG2D/NKG2D ligand contributes to hepatocyte necrosis in virus-induced liver failure. J Immunol 184(1):466–475. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900687
Tian Z, Chen Y, Gao B (2012) Natural killer cells in liver disease. Hepatology. doi:10.1002/hep.26115
Kahraman A, Schlattjan M, Kocabayoglu P, Yildiz-Meziletoglu S, Schlensak M, Fingas CD, Wedemeyer I, Marquitan G, Gieseler RK, Baba HA, Gerken G, Canbay A (2010) Major histocompatibility complex class I-related chains A and B (MIC A/B): a novel role in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 51(1):92–102. doi:10.1002/hep.23253
O'Shea D, Cawood TJ, O'Farrelly C, Lynch L (2010) Natural killer cells in obesity: impaired function and increased susceptibility to the effects of cigarette smoke. PloS One 5(1):e8660. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008660
Glassner A, Eisenhardt M, Kramer B, Korner C, Coenen M, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U, Nattermann J (2012) NK cells from HCV-infected patients effectively induce apoptosis of activated primary human hepatic stellate cells in a TRAIL-, FasL- and NKG2D-dependent manner. Lab Investig; J Tech Methods Pathol 92(7):967–977. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2012.54
Gomez-Santos L, Luka Z, Wagner C, Fernandez-Alvarez S, Lu SC, Mato JM, Martinez-Chantar ML, Beraza N (2012) Inhibition of natural killer cells protects the liver against acute injury in the absence of glycine N-methyltransferase. Hepatology 56(2):747–759. doi:10.1002/hep.25694
Liaskou E, Wilson DV, Oo YH (2012) Innate immune cells in liver inflammation. Mediat Inflamm 2012:949157. doi:10.1155/2012/949157
Rahman AH, Aloman C (2013) Dendritic cells and liver fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.01.005
Ibrahim J, Nguyen AH, Rehman A, Ochi A, Jamal M, Graffeo CS, Henning JR, Zambirinis CP, Fallon NC, Barilla R, Badar S, Mitchell A, Rao RS, Acehan D, Frey AB, Miller G (2012) Dendritic cell populations with different concentrations of lipid regulate tolerance and immunity in mouse and human liver. Gastroenterology 143(4):1061–1072. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.003
Henning JR, Graffeo CS, Rehman A, Fallon NC, Zambirinis CP, Ochi A, Barilla R, Jamal M, Deutsch M, Greco S, Ego-Osuala M, Saeed UB, Rao RS, Badar S, Quesada JP, Acehan D, Miller G (2013) Dendritic cells limit fibro-inflammatory injury in NASH. Hepatology. doi:10.1002/hep.26267
Satoh M, Andoh Y, Clingan CS, Ogura H, Fujii S, Eshima K, Nakayama T, Taniguchi M, Hirata N, Ishimori N, Tsutsui H, Onoe K, Iwabuchi K (2012) Type II NKT cells stimulate diet-induced obesity by mediating adipose tissue inflammation, steatohepatitis and insulin resistance. PloS One 7(2):e30568. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030568
Tajiri K, Shimizu Y, Tsuneyama K, Sugiyama T (2009) Role of liver-infiltrating CD3 + CD56+ natural killer T cells in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21(6):673–680. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e32831bc3d6
Xu CF, Yu CH, Li YM, Xu L, Du J, Shen Z (2007) Association of the frequency of peripheral natural killer T cells with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol : WJG 13(33):4504–4508
Johnson AR, Milner JJ, Makowski L (2012) The inflammation highway: metabolism accelerates inflammatory traffic in obesity. Immunol Rev 249(1):218–238. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065×.2012.01151.x
Syn WK, Agboola KM, Swiderska M, Michelotti GA, Liaskou E, Pang H, Xie G, Philips G, Chan IS, Karaca GF, Pereira Tde A, Chen Y, Mi Z, Kuo PC, Choi SS, Guy CD, Abdelmalek MF, Diehl AM (2012) NKT-associated hedgehog and osteopontin drive fibrogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 61(9):1323–1329. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301857
Locatelli I, Sutti S, Vacchiano M, Bozzola C, Albano E (2013) NF-kappaB1 deficiency stimulates the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in mice by promoting NKT-cell-mediated responses. Clin Sci 124(4):279–287. doi:10.1042/CS20120289
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259(5091):87–91
Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, Volund A, Ehses JA, Seifert B, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Donath MY (2007) Interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 356(15):1517–1526. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa065213
Sauter NS, Schulthess FT, Galasso R, Castellani LW, Maedler K (2008) The antiinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protects from high-fat diet-induced hyperglycemia. Endocrinology 149(5):2208–2218. doi:10.1210/en.2007-1059
Rizos CV, Elisaf MS, Mikhailidis DP, Liberopoulos EN (2009) How safe is the use of thiazolidinediones in clinical practice? Expert Opin Drug Saf 8(1):15–32. doi:10.1517/14740330802597821
De Vito R, Alisi A, Masotti A, Ceccarelli S, Panera N, Citti A, Salata M, Valenti L, Feldstein AE, Nobili V (2012) Markers of activated inflammatory cells correlate with severity of liver damage in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Med 30(1):49–56. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2012.965
Inzaugarat ME, Ferreyra Solari NE, Billordo LA, Abecasis R, Gadano AC, Chernavsky AC (2011) Altered phenotype and functionality of circulating immune cells characterize adult patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin Immunol 31(6):1120–1130. doi:10.1007/s10875-011-9571-1
Acknowledgments
We apologize to our colleagues whose contributions could not be cited due to space limitations. We thank Tatiana Golea for the support with the figure design. Our work is supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the FP7 EU Project “DIABAT”, the German Cancer Aid, the Helmholtz cross program topic “Metabolic Dysfunction”, and the Helmholtz Alliance “ICEMED.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the special issue on Metabolic Syndrome - Guest Editor: T. Miyazaki
Ashley Eheim and Dasa Medrikova contributed equally to the manuscript preparation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eheim, A., Medrikova, D. & Herzig, S. Immune cells and metabolic dysfunction. Semin Immunopathol 36, 13–25 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-013-0403-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-013-0403-7