Abstract
Purpose
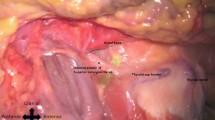
In this study, we aimed to reveal the detailed anatomy of mental nerve branches to the inferior labial glands.
Methods
Embalmed cadaveric heads were used in this study and the mental nerve branches to the inferior labial glands were dissected. Branches to the glands were then excised for histological observation.
Results
On all sides, the inferior labial glands were innervated by small branches arising from mental nerve branches that innervated the lower lip. No nerve branches to the inferior labial gland crossed the midline. Histological observation found that the tissue to the inferior labial gland were composed primarily of nerve fibers with a small number of surrounding vessels. Histological findings in examined specimens were consistent.
Conclusion
The inferior labial glands were innervated by small branches of the mental nerve to the lower lip.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartling R, Freeman K, Kraut RA (1999) The incidence of altered sensation of the mental nerve after mandibular implant placement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:1408–1410
Chisholm DM, Mason DK (1968) Labial salivary gland biopsy in Sjögren’s disease. J Clin Pathol 21:656–660
Emmelin N (1972) Control of salivary glands. In: Emmelin N, Zotterman Y (eds) Oral physiology. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 1–16
Hu KS, Yun HS, Hur MS, Kwon HJ, Abe S, Kim HJ (2007) Branching patterns and intraosseous course of the mental nerve. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:2288–2294
Hur Y, Bui MN, Griffin TJ, Ogata Y (2015) Modified periosteal releasing incision for flap advancement: a practical technique for tensionless closure. Clin Adv Periodontics 5:229–234
Hwang K, Lee WJ, Song YB, Chung IH (2005) Vulnerability of the inferior alveolar nerve and mental nerve during genioplasty: an anatomic study. J Craniofacial Surg 16:10–14
Iwanaga J, Saga T, Tabira Y, Nakamura M, Kitashima S, Watanabe K, Kusukawa J, Yamaki K (2015) The clinical anatomy of accessory mental nerves and foramina. Clin Anat 28:848–856
Iwanaga J, Watanabe K, Saga T, Tabira Y, Kitashima S, Kusukawa J, Yamaki KI (2016) Accessory mental foramina and nerves: application to periodontal, periapical, and implant surgery. Clin Anat 29:493–501
Iwanaga J, Nakamura K, Alonso F, Kirkpatrick C, Oskouian RJ, Watanabe K, Tubbs RS (2018) Anatomical study of the so-called “retromolar gland”: distinguishing normal anatomy from oral cavity pathology. Clin Anat 31:462–465
Iwanaga J, Singh V, Ohtsuka A, Hwang Y, Kim HJ, Moryś J, Ravi KS, Ribatti D, Trainor PA, Sañudo JR, Apaydin N, Şengül G, Albertine KH, Walocha JA, Loukas M, Duparc F, Paulsen F, Del Sol M, Adds P, Hegazy A, Tubbs RS (2021) Acknowledging the use of human cadaveric tissues in research papers: recommendations from anatomical journal editors. Clin Anat 34:2–4
Kalladka M, Proter N, Benoliel R, Czerninski R, Eliav E (2008) Mental nerve neuropathy: patient characteristics and neurosensory changes. Oral Sur Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol 106:364–370
Kamijo Y (1967) Oral anatomy, 1st edn. Anatom Co., Tokyo
Matthews B, Robinson PP (1980) The course of post-ganglionic sympathetic fibres distributed with the trigeminal nerve in the cat. J Physiol 303:391–401
Moiseiwitsch JR (1995) Avoiding the mental foramen during periapical surgery. J Endod 21:340–342
Ousterhout DK (1996) Sliding genioplasty, avoiding mental nerve injuries. J Craniofacial Surg 7:297–298
Proctor GB, Carpenter GH (2007) Regulation of salivary gland function by autonomic nerves. Auton Neurosci 133:3–18
Segal K, Lisnyansky I, Nageris B, Feinmesser R (1996) Parasympathetic innervation of the salivary glands. Oper Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 7:333–338
Standring S (2020) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Elsevier Health Sciences, London
Umemura Y, Tadokoro O, Utsuno H (2009) Immunocytochemical localization of autonomic nerve fibers in the human labial glands. Matsumoto Shigaku 35:8–16
Won SY, Yang HM, Woo HS, Chang KY, Youn KH, Kim HJ, Hu KS (2014) Neuroanastomosis and the innervation territory of the mental nerve. Clin Anat 27:598–602
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank those who donated their bodies to science so that anatomical research could be performed. Results from such research can potentially increase mankind’s overall knowledge that can then improve patient care. Therefore, these donors and their families deserve our highest gratitude [10].
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JI: data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing. YH: data analysis, and manuscript writing. KN: data analysis and manuscript editing. JK: data analysis and manuscript editing. KW: protocol/project development and manuscript editing. RST: protocol/project development and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwanaga, J., Haikata, Y., Nakamura, K. et al. An anatomical and histological study of mental nerve branches to the inferior labial glands. Surg Radiol Anat 43, 1801–1804 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02795-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02795-6