Abstract
Background
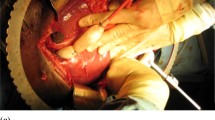
Severe lesions in the liver are associated with a high mortality rate. Alternative surgical techniques such as the use of an intrahepatic balloon may be effective and reduce mortality in severe hepatic lesions. This study aimed to demonstrate the experience of a university hospital in the use of the Sengstaken-Blakemore balloon in patients with transfixing penetrating hepatic injury as an alternative way to treat these challenging injuries.
Methods
A retrospective study based on the trauma registry of a university hospital was performed. All patients admitted with hepatic penetrating injuries and treated with the Sengstaken-Blakemore balloon within the period 1990–2010 were reviewed.
Results
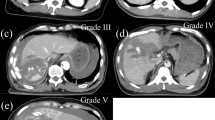
Forty-six patients with transfixing hepatic injuries were treated with the Sengstaken-Blakemore balloon in the study period. The most frequent cause of injury was gunshot wound (87 % of the patients). The mean trauma scores on admission were Revised Trauma Score (RTS) = 7.12 ± 1.46, Injury Severity Score (ISS) = 22.4 ± 9.7, and Abdominal Trauma Index (ATI) = 19.5 ± 11. According to the severity of the hepatic trauma, 71.8 % of patients had grade III, 23.9 % grade IV, and 4.3 % grade V injuries. Associated abdominal injuries were found in 89.1 % of the patients. The most frequent liver-related complications were hepatic abscess postoperative bleeding (8.6 %), biliary fistula (8.6 %), (4.3 %), and biliary peritonitis (2.1 %). Surgical reintervention was necessary in 14 patients (31.1 %). From those 14, only 3 had the balloon removed. The overall morbidity and mortality rates were 56.5 % and 23.9 % (11 patients), respectively.
Conclusion
The knowledge of alternative surgical techniques is essential in improving survival in patients with severe penetrating hepatic injuries. The use of intrahepatic balloon is a viable surgical strategy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asensio JA, Demetriades D, Chahwan S, Gomez H, Hanpeter D, Velmahos G, Murray J, Shoemaker W, Berne TV (2000) Approach to the management of complex hepatic injuries. J Trauma 48(1):66–69
Cogbill TH, Moore EE, Jurkovich GJ, Feliciano DV, Morris JA, Mucha P (1988) Severe hepatic trauma: a multi-center experience with 1,335 liver injuries. J Trauma 28(10):1433–1438
Sriussadaporn S, Pak-art R, Tharavej C, Sirichindakul B, Chiamananthapong S (2002) A multidisciplinary approach in the management of hepatic injuries. Injury 33(4):309–315
Seligman JY, Egan M (1997) Balloon tamponade: an alternative in the treatment of liver trauma. Am Surg 63(11):1022–1023
Morimoto RY, Birolini D, Junqueira AR Jr, Poggetti R, Horita LT (1987) Balloon tamponade for transfixing lesions of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 164(1):87–88
Ozdogan M, Ozdogan H (2006) Balloon tamponade with Sengstaken-Blakemore tube for penetrating liver injury: case report. J Trauma 60(5):1122–1123
Smaniotto B, Bahten LC, Nogueira Filho DC, Tano AL, Thomaz Junior L, Fayad O (2009) Hepatic trauma: analysis of the treatment with intrahepatic balloon in a university hospital of Curitiba. Rev Col Bras Cir 36(3):217–222
Branco PD, Poggetti RS, Bernini Cde O, Birolini D (1988) Balloon tamponade in transfixing wounds of the liver: immediate results. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo 43(1):20–25
Pellegrino A, Taronna I, Vento G, Mathison L, Del Medico P, Smitter J, Carretta M (1999) Balloon tamponade in penetrating liver lesions. Technical note. Minerva Chir 54(5):363–366
Demetriades D (1998) Balloon tamponade for bleeding control in penetrating liver injuries. J Trauma 44(3):538–539
Ball CG, Wyrzykowski AD, Nicholas JM, Rozycki GS, Feliciano DV (2011) A decade’s experience with balloon catheter tamponade for the emergency control of hemorrhage. J Trauma 70(2):330–333
Champion HR, Sacco WJ, Copes WS, Gann DS, Gennarelli TA, Flanagan ME (1989) A revision of the Trauma Score. J Trauma 29(5):623–629
Baker SP, O’Neill B, Haddon W Jr, Long WB (1974) The Injury Severity Score: a method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care. J Trauma 14(3):187–196
Schluter PJ, Nathens A, Neal ML, Goble S, Cameron CM, Davey TM et al (2010) Trauma and Injury Severity Score (TRISS) coefficients 2009 revision. J Trauma 68(4):761–770
Borlase BC, Moore EE, Moore FA (1990) The abdominal trauma index–a critical reassessment and validation. J Trauma 30(11):1340–1344
Moore EE, Cogbill TH, Jurkovich GJ, Shackford SR, Malangoni MA, Champion HR (1995) Organ injury scaling: spleen and liver (1994 revision). J Trauma 38(3):323–324
Kozar RA, Moore JB, Niles SE, Holcomb JB, Moore EE, Cothren CC et al (2005) Complications of nonoperative management of high-grade blunt hepatic injuries. J Trauma 59(5):1066–1071
Sikhondze WL, Madiba TE, Naidoo NM, Muckart DJ (2007) Predictors of outcome in patients requiring surgery for liver trauma. Injury 38(1):65–70
Fávero SS, Corsi PR, Coimbra RS, Rasslan S (1994) Treatment of transfixing hepatic lesions with a hydrostatic balloon. Sao Paulo Med J 112(4):629–634
Poggetti RS, Moore EE, Moore FA, Mitchell MB, Read RA (1992) Balloon tamponade for bilobar transfixing hepatic gunshot wounds. J Trauma 33(5):694–697
Denton JR, Moore EE, Coldwell DM (1997) Multimodality treatment for grade V hepatic injuries: perihepatic packing, arterial embolization, and venous stenting. J Trauma 42(5):964–967
Benckert C, Thelen A, Gaebelein G, Hepp P, Josten C, Bartels M et al (2010) Balanced management of hepatic trauma is associated with low liver-related mortality. Langenbecks Arch Surg 395(4):381–386
Asensio JA, Petrone P, García-Núñez L, Kimbrell B, Kuncir E (2007) Multidisciplinary approach for the management of complex hepatic injuries AAST-OIS grades IV–V: a prospective study. Scand J Surg 96(3):214–220
Asensio JA, Roldán G, Petrone P, Rojo E, Tillou A, Kuncir E et al (2003) Operative management and outcomes in 103 AAST-OIS grades IV and V complex hepatic injuries: trauma surgeons still need to operate, but angioembolization helps. J Trauma 54(4):647–653
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fraga, G.P., Zago, T.M., Pereira, B.M. et al. Use of Sengstaken-Blakemore Intrahepatic Balloon: An Alternative for Liver-Penetrating Injuries. World J Surg 36, 2119–2124 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1625-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1625-x