Abstract
Background
There are few studies that evaluate the differences in the perception of beauty and attractiveness of different races or ethnicities. The purpose of this study was to determine whether there are any actual differences in the configuration of beautiful eyes among different races.
Methods
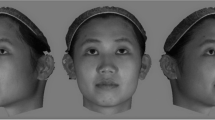
Using seven composite faces of different races or ethnicities, photogrammetric measurements were performed to determine the relative differences in the average and attractive configuration of the eyes. Fourteen distance measurements and five angular measurements were performed for analyzing the morphological differences in the configuration of attractive and average faces.
Results
The results of our study found that attractive Korean faces have relatively wide-set eyes and that the medial and lateral eye fissure height is greater than that in average Korean faces. Attractive Korean faces have larger but not ptotic eyes than those in average Korean faces and they have a narrow double fold line; however, attractive Asian faces have a slightly higher double fold line. Attractive Korean or Asian faces do not have an epicanthus and there is a lot of exposure of white in the medial and lateral area of the eyes. Attractive Caucasian and African faces have an acute or keen shape to the eyes like the jaguar’s eye. Attractive Asian faces have a less steep slant of the palpebral fissure compared to that of the average Asian face, but attractive Caucasian and African faces have a steeper palpebral slant than that of average Caucasian and African faces. Attractive Caucasian and African faces have a relatively narrower palpebral fissure height and width than average Caucasian and African faces. Regardless of race, attractive faces have wide-set eyes and a lower brow position than average faces.
Conclusions
“Beautiful eyes” can be defined as youthful, brilliant, vivid, and attractive. We found that there are some common and some different characteristics in the configuration of beautiful eyes according to racial background.
Level of Evidence I
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heart SF (2012) Quotes on beauty. http://www.sfheart.com/beauty_quotes.html. Accessed February 21, 2012
Romm S (1989) The changing face of beauty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 13:91–98
Iglesias-Linares A, Yáñez-Vico RM, Moreno-Manteca B, Moreno-Fernández AM, Mendoza–Mendoza A, Solano-Reina E (2011) Common standards in facial esthetics: craniofacial analysis of most attractive black and white subjects according to People magazine during previous 10 years. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69(6):e216–e224
Perrett DI, May KA, Yoshikawa S (1994) Facial shape and judgements of female attractiveness. Nature 368(6468):239–242
McCurdy JA Jr (2006) Beautiful eyes: characteristics and application to aesthetic surgery. Facial Plast Surg 22(3):204–214
Michiels G, Sather AH (1994) Determinants of facial attractiveness in a sample of white women. Int J Adult Orthognath Surg 9:95–103
Liu D, Hsu WM (1986) Oriental eyelids. Anatomic difference and surgical consideration. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2(2):59–64
Heir JS, Sandhu BS, Barber HD (2000) Considerations for esthetic facial surgery in the African-American patient. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 8(2):113–125
Rhee SC, Koo SH (2007) An objective system for measuring facial attractiveness. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(6):1952–1953
Rhee SC, Lee SH (2010) Attractive composite faces of different races. Aesthetic Plast Surg 34(6):800–801
Rhee SC, Kang SR, Park HS (2004) Balanced angular profile analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(2):535–544
Rhee SC (2006) The average Korean attractive face. Aesthetic Plast Surg 30(6):729–730
Cho YJ (2007) Me-In. Hainaim, Seoul
Kim HK (2002) Structural attributes and affective conceptual components of facial beauty. Department of Psychology, Graduate School, Yonsei University, Seoul
Little AC, Jones BC, Waitt C, Tiddeman BP, Feinberg DR, Perrett DI, Apicella CL, Marlowe FW (2008) Symmetry is related to sexual dimorphism in faces: data across culture and species. PLoS One 3(5):e2106
Dodgson NA (2004) Variation and extrema of human interpupillary distance. In: Woods AJ, Merritt JO, Benton SA, Bolas MT (eds), Stereoscopic displays and virtual reality systems, XIth proceedings of the SPIE, San Jose CA, 18–22 January 2004
Kim CJ, Ham KS (1988) A facial anthropometric study on the Korean youths. Arch Plast Surg 5:427
Barretto RL, Mathog RH (1999) Orbital measurement in black and white populations. Laryngoscope 109:1051–1054
Murphy WK, Laskin DM (1990) Intercanthal and interpupillary distance in the black population. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 69(6):676–680
Lee HB, Lee SH, Kim JS, Rhee SC (2010) Evaluation of influence of individual facial aesthetic subunits on the cognition of facial attractiveness in public. Arch Plast Surg 37(4):361–368
Nunes TP, Oliveira TF, Matayoshi S (2005) A comparative study of the manual and digital measurements of the palpebral fissure. Arq Bras Oftalmol 68(6):785–787
The Psychology of Beauty (2009) Standardizing facial photographs via IPD may introduce error, February 1, 2009. http://psychologyofbeauty.wordpress.com/2009/02/01/standardizing-facial-photographs-via-ipd-may-introduce-error/. Accessed February 22, 2012
Woods JO (2004) In: Woods AJ, Merritt JO, Benton SA, Bolas MT (eds), Stereoscopic displays and virtual reality systems, XIth proceedings of the SPIE, San Jose CA, 18–22 January 2004
Park DH, Choi WS, Yoon SH, Song CH (1993) Anthropometry of Asian eyelids by age. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:1405–1413
Park DM, Song Han KW, Kang JS (1990) Anthropometry of Korean eyelids. Korean Soc Aesthetic Plast Surg 17:822
Hwang K, Ough M, Baik SH (1996) Morphometrical study of interocular distances in Korean adults. Arch Plast Surg 23:9
Cho DH, Ham KS, Cho YJ (1989) An anthropometric analysis on the beautiful and ugly faces of the young Koreans. Arch Plast Surg 16:926
Baek SW, Kom H, Park SH, Band YH (1995) Anthropometric analysis of palpebral fissure. Korean Soc Aesthetic Plast Surg 1:221
Cho JH, Han KH, Kang JS (1993) Normal anthropometric values and standardized templates of Korean face and head. Korean Soc Aesthetic Plast Surg 20:995
Bae TH, Kim JC, Kim WS, Kim HK, Kim SH (2007) A photogrammetric study of the eyes in Korean youths. Arch Plast Surg 34:37–43
Lee JS, Kim HK, Kim YW (2004) Anthropometric analysis of the attractive and normal faces in Korean female. Arch Plast Surg 31:526
Lee DJ, Kim WK, Kim SS (1989) Photogrammetric study on the face of adult Korean female. Arch Plast Surg 16(3):423
Wee SS, Ham KS, Lee JU (1981) Anthropometrical studies on the standard beauty of Korean adult female. Arch Plast Surg 8:283
Song WS, KimYH LeeSJ (2001) Morphologic study of upper eyelid contour and functional evaluation of levator palpebrae superioris muscle in adult and young people. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 42:1523–1529
Wu XS, Jian XC, He ZJ, Gao X, Li Y, Zhong X (2010) Investigation of anthropometric measurements of anatomic structures of orbital soft tissue in 102 young Han Chinese adults. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 26:339–343
Patil SB, Kale SM, Math M, Khare N, Sumeet J (2011) Anthropometry of the eyelid and palpebral fissure in an Indian population. Aesthet Surg J 31:290–294
Farkas LG, Sohm P, Kolar JC, Katie MJ, Munro R (1985) Inclination of the facial profile: art versus reality. Plast Reconstr Surg 75:509–519
Price KM, Gupta PK, Woodward JA, Stinnett SS, Murchison AP (2009) Eyebrow and eyelid dimensions: an anthropometric analysis of African Americans and Caucasians. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:615–623
Kunjur J, Sabesan T, Ilankovan V (2006) Anthropometric analysis of eyebrows and eyelids: an inter-racial study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:89–93
Porter JP, Olson KL (2001) Anthropometric facial analysis of the African American woman. Arch Facial Plast Surg 3:191–197
Farkas LG (1994) Anthropometry of the Head and Face. Raven Press, New York
Duke-Elder S (1916) System of ophthalmology. Mosby, St Louis, p 205
Song CH, Ahn KY, Hand DC, Park DH (1999) The age-related anthropometric analysis of eyelids and orbits in Koreans. Arch Plast Surg 26:1131–1137
Kim YH, Kim YS, Lee SI (1985) A statistical study of upper eyelids of Korean young women. Arch Plast Surg 12:325
Hwang K, Seo MS (2002) Double fold found in portraits of Korean women. Arch Plast Surg 8(1):13–15
Chen W, Li S, Li Y, Wang YJ (2009) Medial epicanthoplasty using the palpebral margin incision method. Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62(12):1621–1626
Oh YW, Seul CH, Yoo WM (2007) Medial epicanthoplasty using the skin redraping method. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(2):703–710
Lee YJ, Baek RM, Song YT, Chung WJ, Lee JH (2006) Periciliary Y-V epicanthoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 56(3):274
Shin YH, Hwang K (2004) Cosmetic lateral canthoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 28(5):317–320
Bartsich S, Swartz KA, Spinelli HM (2012) Lateral canthoplasty using the Mitek anchor system. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36(1):3–7
Taban M, Nakra T, Hwang C, Hoenig JA, Douglas RS, Shorr N, Goldberg RA (2010) Aesthetic lateral canthoplasty. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 26(3):190–194
Hirohi T, Yoshimura K (2011) Vertical enlargement of the palpebral aperture by static shortening of the anterior and posterior lamellae of the lower eyelid: a cosmetic option for Asian eyelids. Plast Reconstr Surg 127(1):396–406
Park DH, Baik BS (2008) Advancement of the Müller muscle-levator aponeurosis composite flap for correction of blepharoptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 122(1):140–142
Maheshwari R, Maheshwari S (2011) Muller’s muscle resection for ptosis and relationship with levator and Muller’s muscle function. Orbit 30(3):150–153
Park JW, Shin HS, Park ES, Kim YB (2006) Balanced tucking of the levator muscle and Muller’s muscle in blepharoptosis. Arch Plast Surg 33(2):149–154
Welling LL, Jones BC, DeBruine LM, Smith FG, Feinberg DR, Little AC, Al-Dujaili EA (2008) Men report stronger attraction to femininity in women’s faces when their testosterone levels are high. Horm Behav 54:703–708
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products or devices mentioned in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhee, S.C., Woo, KS. & Kwon, B. Biometric Study of Eyelid Shape and Dimensions of Different Races with References to Beauty. Aesth Plast Surg 36, 1236–1245 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9937-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9937-7