Abstract
Background
The current study was designed to assess the effect of magnesium sulphate infusion on hemodynamic parameters, neuromuscular blocking, propofol consumption, serum concentration of magnesium ions, and recovery from anesthesia during total intravenous anesthesia.
Methods
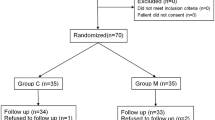
For this study, 60 patients undergoing septorhinoplasty operations were randomly allocated to receive magnesium sulphate (group M) or saline (group C) intravenously. The patients in group M received 15% magnesium sulphate 50 mg/kg in 100 ml of saline, and those in group C received an equal volume of saline before induction of anesthesia followed by 8 mg/kg/h infusion of either magnesium sulphate (group M) or an equal volume of saline (group C) until the end of surgery. Anesthesia was induced and maintained with propofol, remifentanil infusions, and vecuronium in both groups.
Results
Propofol requirements were significantly lower in group M than in group C (p < 0.05). The hemodynamic variables were similar in the two groups. The neuromuscular potency of vecuronium was greater in group M than in group C (p < 0.05). The verbal numeric scale values for pain were found to be significantly lower in group M than in group C (p < 0.05). Whereas the serum magnesium was in the normal range at the induction of anesthesia in the both groups, it was significantly lower in group C than in group M postoperatively (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Magnesium sulphate can be used safely as an adjuvant to total intravenous anesthesia for day case surgeries, with the effect from potentialization of neuromuscular blockade taken into consideration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrete JA, Barnes DR, Aikawa JK: Does magnesium produce anesthesia? Anesth Analg 47:428–433, 1968
Altan A, Turgut N, Yıldız F, Türkmen A, Üstün T: Effects of magnesium sulphate and clonidine on propofol consumption, haemodynamics, and postoperative recovery. Br J Anaesth 94:438–441, 2005
Apan A, Buyukkocak U, Ozcan S, Sari F, Basar H: Postoperative magnesium sulphate infusion reduces analgesic requirements in spinal anaesthesia. Eur J Anaesthesiol 21:766–769, 2004
Bahar M, Cohen ML, Grinshpun Y, et al. Serum electrolyte and blood gas changes after intrathecal and intravenous bolus injections of magnesium sulphate. Anaesthesia 52:1065–1069, 1997
Bhatia A, Kashyap L, Pawar DK, Trikha A: Effect of intraoperative magnesium infusion on perioperative analgesia in open cholecystectomy. J Clin Anesth 16:262–265, 2004
Choi JC, Yoon KB, Um DJ, Kim C, Kim JSK, Lee SG: Intravenous magnesium sulphate administration reduces propofol infusion requirements during maintenance of propofol–N2O anesthesia. Anesthesiology 97:1137–1141, 2002
Dube L, Granry JC: The therapeutic use of magnesium in anesthesiology, intensive care, and emergency medicine: A review. Can J Anaesth 50:732–746, 2003
Fawcett WJ, Haxby EJ, Male DA: Magnesium: physiology and pharmacology. Br J Anaesth 83:302–320, 1999
Fuchs-Buder T, Wilder-Smith HG, Borgeat A, Tassonyi E: Interaction of magnesium sulphate with vecuronium-induced neuromusculer block. Br J Anaesth 74:404–409, 1995
Hodgson RE, Rout CC, Rocke DA, Louw NJ: Mivacurium for caesarean section in hypertensive parturients receiving magnesium sulphate therapy. Int J Obstet Anesth 7:12–17, 1996
Hollman MW, Liu HT, Hoenemann CW, Liu WH, Durieux ME: Modulation of NMDA receptor function by ketamine and magnesium: Part II. Interactions with volatile anesthetics. Anesth Analg 92:1182–1191, 2001
James MF, Manson ED: The use of magnesium sulphate infusions in the management of very severe tetanus. Intensive Care Med 11:5–12, 1985
James MF, Schenk PA, van der Veen BW: Priming of pancuronium with magnesium. Br J Anaesth 66:247–249, 1991
Koinig H, Wallner T, Marhofer P, Andel H, Horauf K, Mayer N: Magnesium sulphate reduces intra- and postoperative analgesic requirements. Anesth Analg 87:206–210, 1998
Levaux CH, Bonhomme V, Dewandre PY, Brichant JF, Hans P: Effect of intraoperative magnesium sulphate on pain relief and patient comfort after lumbar orthopaedic surgery. Anaesthesia 58:131–135, 2003
Noronha JL, Matuschak GM: Magnesium in critical illness: Metabolism, assessment, and treatment. Intensive Care Med 28:667–679, 2002
Olivieri L, Plourde G: Prolonged (more than ten hours) neuromuscular blockade after cardiac surgery: Report of two cases. Can J Anaesth 52:88–93, 2005
Pinard AM, Donati F, Martineau R, Denault AY, Taillefer J, Carrier M: Magnesium potentiates neuromuscular blockade with cisatracurium during cardiac surgery. Can J Anaesth 50:172–178, 2003
Sasaki R, Hirota K, Roth SH, Yamazaki M: Extracelluler magnesium ion modifies the actions of volatile anesthetics in area CA1 of rat hippocampus in vitro. Anesthesiology 96:681–687, 2002
Schulz-Stubner S, Wettmann G, Reyle-Hahn SM, Rossaint R: Magnesium as part of balanced general anaesthesia with propofol, remifentanil, and mivacurium: A double-blind, randomized prospective study in 50 patients. Eur J Anaesthesiol 18:723–729, 2001
Sinatra RS, Philip BK, Naulty S, Ostheimer GW: Prolonged neuromuscular blockade with vecuronium in a patient treated with magnesium sulphate. Anesth Analg 64:1220–1222, 1985
Sirvinskas E, Rokas L: Use of magnesium sulphate in anesthesiology. Medicina 38:147–150, 2002
Telci L, Esen F, Akcora D, Erden T, Canpolat T, Akpir K: Evaluation of effects of magnesium sulphate in reducing intraoperative anesthetic requirements. Br J Anaesth 89:594–598, 2002
Thompson SW, Moscicki JC, Difazio CA: The anesthetic contribution of magnesium sulphate and ritodrine hydrochloride in rats. Anesth Analg 67:31–34, 1998
Tramer MR, Schneider J, Marti RA, Rifat K: Role of magnesium sulphate in postoperative analgesia. Anesthesiology 84:340–347, 1996
Zarauza R, Saez-Fernandez AN, Iribarren MJ: A comparable study with oral nimodipine and magnesium sulphate in postoperative analgesia. Anesth Analg 91:938–943, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented in part as an abstract at the Annual Congress of the Turkish Anaesthesiology and Reanimation Society, Antalya, Turkey, December 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cizmeci, P., Ozkose, Z. Magnesium Sulphate as an Adjuvant to Total Intravenous Anesthesia in Septorhinoplasty: A Randomized Controlled Study. Aesth Plast Surg 31, 167–173 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0194-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0194-5