Abstract
Purpose
The lateral compartment of the knee is biomechanically and anatomically different from the medial compartment. Most commercially available unicompartmental implants are not designed specifically for the lateral compartment. Patient-specific custom-made unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) are designed to provide optimal fit on both femoral and tibial surfaces. This study aimed to determine if the use of patient-specific lateral unicompartmental implants provide better bone coverage than standard, off-the-shelf commercially available unicompartmental implants in lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasties. As a secondary question, we wished to determine if patient-specific unicompartmental implants provide good clinical outcomes in surgical treatment of lateral unicompartmental osteoarthritis.
Methods
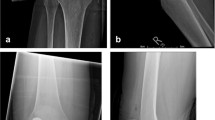
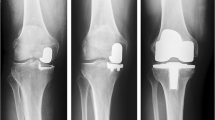
We prospectively evaluated 33 patients who underwent lateral unicompartmental arthroplasty using patient-specific implants and instrumentation with a minimum of 24 months of follow-up. We analysed bone coverage observed in plain radiographs in 33 patient-specific lateral unicompartmental arthroplasties and compared to 20 lateral unicompartmental arthroplasties performed with commercially-available, standard off-the-shelf unicondylar implants.
Results
The mean tibial implant lateral coverage mismatch in the patient-specific implant group was 1.0 mm (S.D. 1.2, range 0–5.7 mm ) versus 3.3 mm (S.D. 2.43, range 0.4–7.8 mm) in the conventional implant group (p < 0.01). In the patient specific cohort, pre-operative limb alignment was 3.3 (valgus) and post-operative limb alignment was −0.9 (varus). The Knee Society score improved from 48 (S.D. 16.2) to 95 (S.D. 7.6). Survivorship in the patient-specific implant group was 97% at an average follow up of 37 months, versus 85% at a follow-up period of 32 months for the standard implant group.
Conclusions
Patient-specific lateral unicompartmental knee replacements demonstrated better tibial coverage and provide excellent short-term clinical and radiological results as compared to a standard lateral UKA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ledingham J, Regan M, Jones A, Doherty M (1993) Radiographic patterns and associations of osteoarthritis of the knee in patients referred to hospital. Ann Rheum Dis 52:520–526
Sah AP, Scott RD (2008) Lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty through a medial approach. Surg Techn J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Suppl 2 Pt 2):195–205. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00257
Schindler OS, Scott WN, Scuderi GR (2010) The practice of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in the United Kingdom. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 18:312–319
Pennington DW, Swienckowski JJ, Lutes WB, Drake GN (2006) Lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: survivorship and technical considerations at an average follow-up of 12.4 years. J Arthroplasty 21:13–17. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2004.11.021
Heyse TJ, Tibesku CO (2010) Lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:1539–1548. doi:10.1007/s00402-010-1137-9
Berend KR, Kolczun MC 2nd, George JW Jr, Lombardi AV Jr (2012) Lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty through a lateral parapatellar approach has high early survivorship. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:77–83. doi:10.1007/s11999-011-2005-9
Lustig S, Parratte S, Magnussen RA, Argenson JN, Neyret P (2012) Lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty relieves pain and improves function in posttraumatic osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:69–76. doi:10.1007/s11999-011-1963-2
Fitzpatrick C, FitzPatrick D, Lee J, Auger D (2007) Statistical design of unicompartmental tibial implants and comparison with current devices. Knee 14:138–144. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2006.11.005
Gulati A, Chau R, Beard DJ, Price AJ, Gill HS, Murray DW (2009) Localization of the full-thickness cartilage lesions in medial and lateral unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res 27:1339–1346. doi:10.1002/jor.20880
Scott RD (2005) Lateral unicompartmental replacement: a road less traveled. Orthopedics 28:983–984
Fitz W (2009) Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with use of novel patient-specific resurfacing implants and personalized jigs. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(Suppl 1):69–76. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01448
Servien E, Fary C, Lustig S, Demey G, Saffarini M, Chomel S, Neyret P (2011) Tibial component rotation assessment using CT scan in medial and lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97:272–275. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2010.11.002
Mahoney OM, Kinsey T (2010) Overhang of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty: risk factors and clinical consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92:1115–1121. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00434
Chau R, Gulati A, Pandit H, Beard DJ, Price AJ, Dodd CA, Gill HS, Murray DW (2009) Tibial component overhang following unicompartmental knee replacement—does it matter? Knee 16:310–313. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2008.12.017
Gudena R, Pilambaraei MA, Werle J, Shrive NG, Frank CB (2013) A safe overhang limit for unicompartmental knee arthroplasties based on medial collateral ligament strains: an in vitro study. J Arthroplasty 28:227–233. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2012.05.019
Fitz W (2009) Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with use of novel patient-specific resurfacing implants and personalized jigs. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(Suppl 1):69–76. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01448
Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Mahfouz M (2003) In vivo fluoroscopic analysis of the normal human knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 410:69–81. DOI 10.1097/01.blo.0000062384.79828.3b
Mensch JS, Amstutz HC (1975) Knee morphology as a guide to knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 112:231–241
Hofmann AA, Bachus KN, Wyatt RW (1991) Effect of the tibial cut on subsidence following total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 269:63–69
Bloebaum RD, Bachus KN, Mitchell W, Hoffman G, Hofmann AA (1994) Analysis of the bone surface area in resected tibia. Implications in tibial component subsidence and fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 309:2–10
Koeck FX, Beckmann J, Luring C, Rath B, Grifka J, Basad E (2011) Evaluation of implant position and knee alignment after patient-specific unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee 18:294–299. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2010.06.008
Funding
No funding was received for the research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demange, M.K., Von Keudell, A., Probst, C. et al. Patient-specific implants for lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 39, 1519–1526 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2678-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2678-x