Abstract
Purpose
In various cancer types, an abundance of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Treg) has been associated with an unfavorable outcome. Yet, the role of Treg on cancer immunity has been shown to be complex. In single cell marker technique, other tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) such as cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (CTL) also influenced prognosis. This study for the first time investigates the concurrent spatial distribution pattern of CD8+ and FoxP3+ TILs and their prognostic impact in human gastric cancer.
Materials and methods
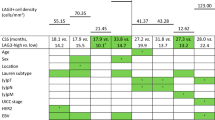
Tumor tissue microarrays of 50 patients with surgically treated adenocarcinoma of the cardia were studied. An immunohistochemical double staining of CD8+ and FoxP3+ TILs was performed. Cell counts and cell-to-cell distances in tumor epithelium and stroma were evaluated with image-processing software. Metastasis-free survival, no-evidence-of-disease survival, and overall survival were investigated (mean follow-up time 6.9 years).
Results
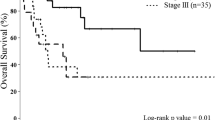
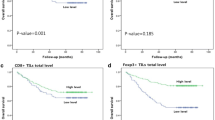
High intraepithelial infiltration of CD8+ and FoxP3+ TIL was associated with the improved 10-year metastasis-free survival (83 vs. 54 %, p = 0.04 and 85 vs. 59 %, p = 0.09, respectively). Considering cell-to-cell distance and comparing patients with functional (30–110 μm) versus nonfunctional distances of CD8+ and FoxP3+ TILs, 10-year survival rates differed between 89 and 55 % (p = 0.009), respectively.
Conclusion
Prognostic influence of tumor-infiltrating immune cells in gastric cancer critically depends on their cell-to-cell distance. FoxP3+ TILs must be located within a distance between 30 and 110 μm of CD8+ T cells to positively impact on prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piccirillo CA, Thornton AM (2004) Cornerstone of peripheral tolerance: naturally occurring CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. Trends Immunol 25:374–380. doi:10.1016/j.it.2004.04.009
Mathai AM, Kapadia MJ, Alexander J, Kernochan LE, Swanson PE, Yeh MM (2012) Role of Foxp3-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in the histologic features and clinical outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 36:980–986. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31824e9b7c
Perrone G, Ruffini PA, Catalano V et al (2008) Intratumoural FOXP3-positive regulatory T cells are associated with adverse prognosis in radically resected gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer 44:1875–1882. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.05.017
Yuan XL, Chen L, Li MX et al (2010) Elevated expression of Foxp3 in tumor-infiltrating Treg cells suppresses T-cell proliferation and contributes to gastric cancer progression in a COX-2-dependent manner. Clin Immunol 134:277–288. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2009.10.005
Distel L, Buttner M (2012) Radiochemotherapy fosters a favorable pattern of inflammatory cells in head and neck tumors. Oncoimmunology 1:982–983. doi:10.4161/onci.20200
Wang B, Xu D, Yu X, Ding T, Rao H, Zhan Y, Zheng L, Li L (2011) Association of intra-tumoral infiltrating macrophages and regulatory T cells is an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer after radical resection. Ann Surg Oncol 18:2585–2593. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-1609-3
Mizukami Y, Kono K, Kawaguchi Y, Akaike H, Kamimura K, Sugai H, Fujii H (2008) Localisation pattern of Foxp3 + regulatory T cells is associated with clinical behaviour in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 98:148–153. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604149
Powell J, McConkey CC (1990) Increasing incidence of adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia and adjacent sites. Br J Cancer 62:440–443
Giordano A, Cito L (2012) Advances in gastric cancer prevention. World J Clin Oncol 3:128–136. doi:10.5306/wjco.v3.i9.128
Ohno S, Tachibana M, Fujii T, Ueda S, Kubota H, Nagasue N (2002) Role of stromal collagen in immunomodulation and prognosis of advanced gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 97:770–774
Jung AC, Guihard S, Krugell S et al (2012) CD8-alpha T-cell infiltration in human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal carcinoma correlates with improved patient prognosis. Int J Cancer. doi:10.1002/ijc.27776
Okuyama T, Higashi T, Edagawa A et al (2012) Ten-year survival of curability B gastric cancer patients treated by tegafur-uracil as postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy in a common public hospital: univariate and multivariate analyses. Fukuoka Acta Med 103:138–144
Haas M, Buttner M, Rau TT, Fietkau R, Grabenbauer GG, Distel LV (2011) Inflammation in gastric adenocarcinoma of the cardia: how do EBV infection, Her2 amplification and cancer progression influence tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes? Virchows Arch 458:403–411. doi:10.1007/s00428-011-1058-1
Haas M, Dimmler A, Hohenberger W, Grabenbauer GG, Niedobitek G, Distel LV (2009) Stromal regulatory T-cells are associated with a favourable prognosis in gastric cancer of the cardia. BMC Gastroenterol 9:65. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-9-65
Ishigami S, Arigami T, Uenosono Y et al (2012) Cancerous HLA class I expression and regulatory T cell infiltration in gastric cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:1663–1669. doi:10.1007/s00262-012-1225-5
Kono K, Kawaida H, Takahashi A, Sugai H, Mimura K, Miyagawa N, Omata H, Fujii H (2006) CD4(+)CD25high regulatory T cells increase with tumor stage in patients with gastric and esophageal cancers. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55:1064–1071
Lee HE, Park DJ, Kim WH, Kim HH, Lee HS (2011) High FOXP3 + regulatory T-cell density in the sentinel lymph node is associated with downstream non-sentinel lymph-node metastasis in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 105:413–419. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.248
Peng LS, Zhuang Y, Shi Y et al (2012) Increased tumor-infiltrating CD8(+)Foxp3(+) T lymphocytes are associated with tumor progression in human gastric cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:2183–2192. doi:10.1007/s00262-012-1277-6
Shen Z, Zhou S, Wang Y, Li RL, Zhong C, Liang C, Sun Y (2010) Higher intratumoral infiltrated Foxp3+ Treg numbers and Foxp3+/CD8+ ratio are associated with adverse prognosis in resectable gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:1585–1595. doi:10.1007/s00432-010-0816-9
Chew A, Salama P, Robbshaw A, Klopcic B, Zeps N, Platell C, Lawrance IC (2011) SPARC, FOXP3, CD8 and CD45 correlation with disease recurrence and long-term disease-free survival in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 6:e22047. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022047
Salama P, Phillips M, Grieu F, Morris M, Zeps N, Joseph D, Platell C, Iacopetta B (2009) Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:186–192. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.18.7229
Whiteside TL, Schuler P, Schilling B (2012) Induced and natural regulatory T cells in human cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther 12:1383–1397. doi:10.1517/14712598.2012.707184
Wang LH, Su L, Wang JT (2010) Correlation between elevated FOXP3 expression and increased lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. Chin Med J 123:3545–3549
Heckman KL, Schenk EL, Radhakrishnan S, Pavelko KD, Hansen MJ, Pease LR (2007) Fast-tracked CTL: rapid induction of potent anti-tumor killer T cells in situ. Eur J Immunol 37:1827–1835. doi:10.1002/eji.200637002
Kawaida H, Kono K, Takahashi A, Sugai H, Mimura K, Miyagawa N, Omata H, Ooi A, Fujii H (2005) Distribution of CD4+ CD25high regulatory T-cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes in patients with gastric cancer. J Surg Res 124:151–157
Acknowledgments
We thank Christa Winkelmann for excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Anita Feichtenbeiner and Matthias Haas have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feichtenbeiner, A., Haas, M., Büttner, M. et al. Critical role of spatial interaction between CD8+ and Foxp3+ cells in human gastric cancer: the distance matters. Cancer Immunol Immunother 63, 111–119 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1491-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1491-x