Abstract
Purpose
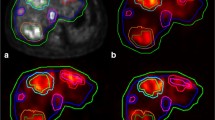
90Y microspheres are used for intra-arterial treatment of liver tumours. In the patient preparation, a hepatic angiogram is performed and all arteries that could transport microspheres from the targeted liver vasculature to extrahepatic organs are blocked. 99mTc-labelled macroaggregated albumin (MAA) is injected intra-arterially to simulate the treatment and whole-body scintigraphy and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) of the abdomen are performed.
Methods
Various aspects of lung shunt fraction (LSF) estimation were studied: interobserver and intrapatient variability, influence of scan quality and underlying disease. Secondly, the interobserver variability in reading the MAA SPECT of the abdomen was investigated. We reviewed 90 whole-body scans and 20 SPECT scans performed at our institution. Readers were blinded to each other’s findings. Scoring the scan quality was based on the visualization of tracer degradation.
Results
The mean difference in LSF between the readers was 1%. In 1 of 23 patients who underwent repeated MAA injections a marked change in LSF was observed. No significant differences in LSF were recorded for primary versus secondary liver tumours. There was a correlation between scan quality and LSF, suggesting that low scan quality leads to overestimation of the LSF. Concordant results in ruling out the presence of extrahepatic tracer deposition were reached in 17 of 20 scans (85%).
Conclusion
Interobserver and intrapatient variability in LSF calculation was limited. LSF was clearly dependent on scan quality. The underlying disease had no significant impact on the LSF. Interobserver variability for reading the MAA SPECT scans was acceptable.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin MD, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2005;55:74–108.
Ahmadzadehfar H, Biersack HJ, Ezziddin S. Radioembolization of liver tumors with yttrium-90 microspheres. Semin Nucl Med 2010;40:105–21.
Annals of the ICRP. Publication 38: radionuclide transformations: energy and intensity of emissions. Oxford: Pergamon; 1983.
ICRU. Stopping powers for electrons and positrons report 37. Bethesda: International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements; 1984
Ho S, Lau WY, Leung TW, Chan M, Johnson PJ, Li AK. Clinical evaluation of the partition model for estimating radiation doses from yttrium-90 microspheres in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Eur J Nucl Med 1997;24:293–8.
Kennedy A, Nag S, Salem R, Murthy R, McEwan AJ, Nutting C, et al. Recommendations for radioembolization of hepatic malignancies using yttrium-90 microsphere brachytherapy: a consensus panel report from the radioembolization brachytherapy oncology consortium. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;68:13–23.
Flamen P, Vanderlinden B, Delatte P, Ghanem G, Ameye L, Van Den Eynde M, et al. Multimodality imaging can predict the metabolic response of unresectable colorectal liver metastases to radioembolization therapy with yttrium-90 labeled resin microspheres. Phys Med Biol 2008;53:6591–603.
Sangro B, Bilbao JI, Boan J, Martinez-Cuesta A, Benito A, Rodriguez J, et al. Radioembolization using 90Y-resin microspheres for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;66:792–800.
Hamami ME, Poeppel TD, Müller S, Heusner T, Bockisch A, Hilgard P, et al. SPECT/CT with 99mTc-MAA in radioembolization with 90Y microspheres in patients with hepatocellular cancer. J Nucl Med 2009;50:688–92.
Garin E, Rolland Y, Boucher E, Ardisson V, Laffont S, Boudjema K, et al. First experience of hepatic radioembolization using microspheres labelled with yttrium-90 (TheraSphere): practical aspects concerning its implementation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:453–61.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambert, B., Mertens, J., Sturm, E.J. et al. 99mTc-labelled macroaggregated albumin (MAA) scintigraphy for planning treatment with 90Y microspheres. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37, 2328–2333 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1566-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1566-2