Abstract
Purpose
There is growing interest in the human sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) gene both as a molecular imaging reporter gene and as a therapeutic gene. Here, we show the feasibility of radioisotope therapy of neuroendocrine tumors. As a separate application of NIS gene transfer, we image NIS-expressing tumors with pinhole SPECT in living subjects.
Methods
Biodistribution studies and in vivo therapy experiments were performed in nude mice carrying stably NIS-expressing neuroendocrine tumor xenografts following i.v. injection of 131I and 99mTc pertechnetate. To show the usefulness of NIS as an imaging reporter gene, 99mTc pertechnetate uptake was imaged in vivo using a clinical gamma camera in combination with a custom-made single pinhole collimator, followed by SPECT/small animal MRI data coregistration.
Results
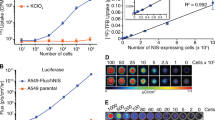
NIS-expressing neuroendocrine tumors strongly accumulated 131I and 99mTc pertechnetate, as did thyroid, stomach, and salivary gland. The volume of NIS-expressing neuroendocrine tumors decreased significantly after therapeutic administration of 131I or 99mTc pertechnetate, whereas control tumors continued to grow. NIS-mediated uptake of 99mTc pertechnetate could be imaged in vivo at high resolution with a clinical gamma camera equipped with a custom-made single pinhole collimator. High-resolution functional and morphologic information could be combined in a single three-dimensional data set by coregistration of SPECT and small animal MRI data. Lastly, we demonstrated a therapeutic effect of 99mTc pertechnetate on NIS-expressing neuroendocrine tumors in cell culture and, for the first time, in vivo, thought to be due to emitted Auger and conversion electrons.
Conclusions
NIS-expressing neuroendocrine tumors efficiently concentrate radioisotopes, allowing for in vivo high-resolution small animal SPECT imaging as well as rendering possible successful radioisotope therapy of neuroendocrine tumors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai G, Levy O, Carrasco N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature 1996;379:458–60.
Heufelder AE, Morgenthaler N, Schipper ML, Joba W. Sodium iodide symporter-based strategies for diagnosis and treatment of thyroidal and nonthyroidal malignancies. Thyroid 2001;11:839–47.
Dohan O, De la Vieja A, Paroder V, Riedel C, Artani M, Reed M, et al. The sodium/iodide symporter (NIS): characterization, regulation, and medical significance. Endocr Rev 2003;24:48–77.
Chow SM, Law SC, Mendenhall WM, Au SK, Chan PT, Leung TW, et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: prognostic factors and the role of radioiodine and external radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;52:784–95.
Boland A, Ricard M, Opolon P, Bidart JM, Yeh P, Filetti S, et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of the thyroid sodium/iodide symporter gene into tumors for a targeted radiotherapy. Cancer Res 2000;60:3484–92.
Carlin S, Cunningham SH, Boyd M, McCluskey AG, Mairs RJ. Experimental targeted radioiodide therapy following transfection of the sodium iodide symporter gene: effect on clonogenicity in both two-and three-dimensional models. Cancer Gene Ther 2000;7:1529–36.
Cho JY, Shen DH, Yang W, Williams B, Buckwalter TL, La Perle KM, et al. In vivo imaging and radioiodine therapy following sodium iodide symporter gene transfer in animal model of intracerebral gliomas. Gene Ther 2002;9:1139–45.
Dadachova E, Bouzahzah B, Zuckier LS, Pestell RG. Rhenium-188 as an alternative to iodine-131 for treatment of breast tumors expressing the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS). Nucl Med Biol 2002;29:13–8.
Dingli D, Diaz RM, Bergert ER, O’Connor MK, Morris JC, Russell SJ. Genetically targeted radiotherapy for multiple myeloma. Blood 2003;102:489–96.
Haberkorn U. Gene therapy with sodium/iodide symporter in hepatocarcinoma. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2001;109:60–2.
La Perle KM, Blomme EA, Capen CC, Jhiang SM. Effect of exogenous human sodium iodide symporter expression on growth of MATLyLu cells. Thyroid 2003;13:133–40.
Mandell RB, Mandell LZ, Link CJ Jr. Radioisotope concentrator gene therapy using the sodium/iodide symporter gene. Cancer Res 1999;59:661–8.
Min JJ, Chung JK, Jin Lee Y, Hoon Shin J, Seok Yeo J, Min Jeong J, et al. In vitro and in vivo characteristics of a human colon cancer cell line, SNU-C5N, expressing sodium-iodide symporter. Nucl Med Biol 2002;29:537–45.
Nakamoto Y, Saga T, Misaki T, Kobayashi H, Sato N, Ishimori T, et al. Establishment and characterization of a breast cancer cell line expressing Na+/I− symporters for radioiodide concentrator gene therapy. J Nucl Med 2000;41:1898–904.
Petrich T, Helmeke HJ, Meyer GJ, Knapp WH, Potter E. Establishment of radioactive astatine and iodine uptake in cancer cell lines expressing the human sodium/iodide symporter. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:842–54.
Sieger S, Jiang S, Schonsiegel F, Eskerski H, Kubler W, Altmann A, et al. Tumour-specific activation of the sodium/iodide symporter gene under control of the glucose transporter gene 1 promoter (GTI-1.3). Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:748–56.
Smit JW, Schroder-van der Elst JP, Karperien M, Que I, Stokkel M, van der Heide D, et al. Iodide kinetics and experimental 131I therapy in a xenotransplanted human sodium-iodide symporter-transfected human follicular thyroid carcinoma cell line. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:1247–53.
Spitzweg C, Dietz AB, O’Connor MK, Bergert ER, Tindall DJ, Young CY, et al. In vivo sodium iodide symporter gene therapy of prostate cancer. Gene Ther 2001;8:1524–31.
Schipper ML, Weber A, Behe M, Goke R, Joba W, Schmidt H, et al. Radioiodide treatment after sodium iodide symporter gene transfer is a highly effective therapy in neuroendocrine tumor cells. Cancer Res 2003;63:1333–8.
Barton KN, Tyson D, Stricker H, Lew YS, Heisey G, Koul S, et al. GENIS: gene expression of sodium iodide symporter for noninvasive imaging of gene therapy vectors and quantification of gene expression in vivo. Mol Ther 2003;8:508–18.
Cho JY. A transporter gene (sodium iodide symporter) for dual purposes in gene therapy: imaging and therapy. Curr Gene Ther 2002;2:393–402.
Dingli D, Peng KW, Harvey ME, Greipp PR, O’Connor MK, Cattaneo R, et al. Image-guided radiovirotherapy for multiple myeloma using a recombinant measles virus expressing the thyroidal sodium iodide symporter. Blood 2004;103:1641–6.
Groot-Wassink T, Aboagye EO, Glaser M, Lemoine NR, Vassaux G. Adenovirus biodistribution and noninvasive imaging of gene expression in vivo by positron emission tomography using human sodium/iodide symporter as reporter gene. Hum Gene Ther 2002;13:1723–35.
Massoud TF, Gambhir SS. Molecular imaging in living subjects: seeing fundamental biological processes in a new light. Genes Dev 2003;17:545–80.
Behr M, Schmitt TL, Espinoza CR, Loos U. Cloning of a functional promoter of the human sodium/iodide-symporter gene. Biochem J 1998;331 (Pt 2):359–63.
Carlin S, Akabani G, Zalutsky MR. In vitro cytotoxicity of 211At-astatide and 131I-iodide to glioma tumor cells expressing the sodium/iodide symporter. J Nucl Med 2003;44:1827–38.
Carlin S, Mairs RJ, Welsh P, Zalutsky MR. Sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)-mediated accumulation of [211At]astatide in NIS-transfected human cancer cells. Nucl Med Biol 2002;29:729–39.
Amaral A, Colas-Linhart N, Stabin M, Petiet A, Guiraud-Vitaux F, Jacquet N. In vitro irradiation of blood with 99mTc: evaluation of dose and chromosome aberrations in irradiated lymphocytes. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2001;47:545–8.
Griffiths GL, Govindan SV, Sgouros G, Ong GL, Goldenberg DM, Mattes MJ. Cytotoxicity with Auger electron-emitting radionuclides delivered by antibodies. Int J Cancer 1999;81:985–92.
Narra VR, Sastry KS, Goddu SM, Howell RW, Strand SE, Rao DV. Relative biological effectiveness of 99mTc radiopharmaceuticals. Med Phys 1994;21:1921–6.
Nettleton JS, Lawson RS. Cellular dosimetry of diagnostic radionuclides for spherical and ellipsoidal geometry. Phys Med Biol 1996;41:1845–54.
Schurrat T, Alfke H, Behe M, Maina T, Nock B, Macke H, et al. Molecular gastrin receptor localisation in mice using high-resolution SPET-MRI image fusion. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:800.
Schramm N, Ebel G, Engeland U, Schurrat T, Behe M, Behr TM. High-resolution SPECT using multipinhole collimation. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 2003;50:315–20.
Schurrat T. Ein hochauflösender hochsensitiver Multipinhole-Einzelphotonen-Emissionscomputertomograph für Kleintier-Bildgebung. Department of Nuclear Medicine/Physics, Philipps University Marburg, Germany; 2004.
Alfke H, Stoppler H, Nocken F, Heverhagen JT, Kleb B, Czubayko F, et al. In vitro MR imaging of regulated gene expression. Radiology 2003;228:488–92.
Heverhagen JT, Hahn HK, Wegmann M, Herz U, Whitaker CD, Matschl V, et al. Volumetric analysis of mice lungs in a clinical magnetic resonance imaging scanner. MAGMA 2004;17:80–5.
Wells WM 3rd, Viola P, Atsumi H, Nakajima S, Kikinis R. Multi-modal volume registration by maximization of mutual information. Med Image Anal 1996;1:35–51.
Boland A, Magnon C, Filetti S, Bidart JM, Schlumberger M, Yeh P, et al. Transposition of the thyroid iodide uptake and organification system in nonthyroid tumor cells by adenoviral vector-mediated gene transfers. Thyroid 2002;12:19–26.
Huang M, Batra RK, Kogai T, Lin YQ, Hershman JM, Lichtenstein A, et al. Ectopic expression of the thyroperoxidase gene augments radioiodide uptake and retention mediated by the sodium iodide symporter in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2001;8:612–8.
Zhang L, Sharma S, Zhu LX, Kogai T, Hershman JM, Brent GA, et al. Nonradioactive iodide effectively induces apoptosis in genetically modified lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2003;63:5065–72.
Haberkorn U, Beuter P, Kubler W, Eskerski H, Eisenhut M, Kinscherf R, et al. Iodide kinetics and dosimetry in vivo after transfer of the human sodium iodide symporter gene in rat thyroid carcinoma cells. J Nucl Med 2004;45:827–33.
Haberkorn U, Henze M, Altmann A, Jiang S, Morr I, Mahmut M, et al. Transfer of the human NaI symporter gene enhances iodide uptake in hepatoma cells. J Nucl Med 2001;42:317–25.
Shimura H, Haraguchi K, Miyazaki A, Endo T, Onaya. Iodide uptake and experimental 131I therapy in transplanted undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells expressing the Na+/I− symporter gene. Endocrinology 1997;138:4493–6.
Dingli D, Bergert ER, Bajzer Z, O’Connor MK, Russell SJ, Morris JC. Dynamic iodide trapping by tumor cells expressing the thyroidal sodium iodide symporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004;325:157–66.
Tazebay UH, Wapnir IL, Levy O, Dohan O, Zuckier LS, Zhao QH, et al. The mammary gland iodide transporter is expressed during lactation and in breast cancer. Nat Med 2000;6:871–8.
Munzenrider JE. Recent advances in radiotherapy. Rev Interam Radiol 1977;2:123–33.
Iyer M, Salazar FB, Lewis X, Zhang L, Wu L, Carey M, et al. Non-invasive imaging of a transgenic mouse model using a prostate-specific two-step transcriptional amplification strategy. Transgenic Res 2005;14:47–55.
Iyer M, Salazar FB, Lewis X, Zhang L, Carey M, Wu L, et al. Noninvasive imaging of enhanced prostate-specific gene expression using a two-step transcriptional amplification-based lentivirus vector. Mol Ther 2004;10:545–52.
Sato M, Johnson M, Zhang L, Gambhir SS, Carey M, Wu L, et al. Functionality of androgen receptor-based gene expression imaging in hormone refractory prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:3743–9.
Furuya F, Shimura H, Miyazaki A, Taki K, Ohta K, Haraguchi K, et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of thyroid transcription factor-1 induces radioiodide organification and retention in thyroid cancer cells. Endocrinology 2004;145:5397–405.
Wenzel A, Upadhyay G, Schmitt TL, Loos U. Iodination of proteins in TPO transfected thyroid cancer cells is independent of NIS. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2003;213:99–108.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a research scholarship No. SCHI 644/1-1 (M.L.S.) from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Society, DFG), and by grants No. 12/2000 (M.L.S.) from the Stiftung P.E. Kempkes (Kempkes Foundation), Marburg, and No. 10-1600-Be2 (T.M.B.) and No. 10-01193 (A.E.H.), both from the Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid). We thank Birgit Herbst (Department of Nuclear Medicine, Philipps University Marburg) for expert technical assistance and Claudia Cyborn (Institute for Anatomy and Cell Biology, Philipps University Marburg) for outstanding help with animal experiments. All experiments performed in this study comply with current German laws and regulations, including ethics approval.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schipper, M.L., Riese, C.G.U., Seitz, S. et al. Efficacy of 99mTc pertechnetate and 131I radioisotope therapy in sodium/iodide symporter (NIS)-expressing neuroendocrine tumors in vivo. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34, 638–650 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0254-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0254-8