Abstract
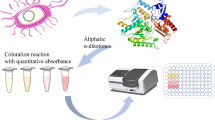
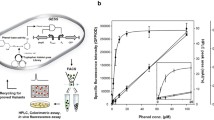
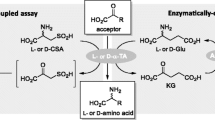
ω-Transaminase (ω-TA) is an attractive alternative to metal catalysts for the stereoselective amination of prochiral ketones. The narrow substrate scope of an R-ω-transaminase from Mycobacterium vanbaalenii (MvTA) limits its application in R-amine synthesis. A fluorescence-based TA activity screening system was developed to extend its substrate scope. The reactions were conducted in microtiter plates (MTPs) and displayed low background interference, high sensitivity (μM magnitude), and a wide dynamic range (ɀ-factor > 0.9). A KnowVolution campaign was performed on this enzyme, and screening ~ 8000 clones with this fluorescence-based screening system resulted in two beneficial substitutions (G68Y and F129A) and three improved variants (M3, M4, and M5). The best variant, MvTA M5 (WT+G68Y+F129A), achieved the highest catalytic efficiency (toward fluorogenic substrate NMA) which was 3.2-fold higher than that of the WT enzyme. MvTA M5 exhibited significantly enhanced activity toward six different prochiral ketones with e.e. > 99% (R). The specific activity of MvTA M5 was more than 100 times higher than that of the WT enzyme toward acetonaphthone (M5: 8.1 U/mg, WT: ~ 0.07 U/mg), and it showed the highest activity on acetonaphthone, p-ethylacetophenone, and phenylacetone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmeyer HU, Beutler HO (1985) Ammonia. In: Bergmeyer HU, Bergmeyer J, Graβl M (eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 8. Academic Press, New York, pp 454–461
Buss O, Buchholz PCF, Graff M, Klausmann P, Rudat J, Pleiss J (2018) The ω-transaminase engineering database (oTAED): a navigation tool in protein sequence and structure space. Proteins 86(6):566–580. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.25477
Baud D, Ladkau N, Moody TS, Ward JM, Hailes HC (2015) A rapid, sensitive colorimetric assay for the highthroughput screening of transaminases in liquid or solid-phase. Chem Commun 2015(51):17225–17228. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc06817g
Cheng F, Tang XL, Kardashliev T (2018) Transcription factor-based biosensors in high-throughput screening. Biotechnol J 13(7):1700648. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700648
Cheng F, Xu JM, Xiang C, Liu ZQ, Zhao LQ, Zheng YG (2017) Simple-MSSM: a simple and efficient method for simultaneous multi-site saturation mutagenesis. Biotechnol Lett 39(4):567–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2278-x
Cheng F, Zhu LL, Lue HQ, Bernahagen J, Schwaneberg U (2015a) Directed arginine deiminase evolution for efficient inhibition of arginine-auxotrophic melanomas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(3):1237–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5985-z
Cheng F, Zhu LL, Schwaneberg U (2015b) Directed evolution 2.0: improving and deciphering enzyme properties. Chem Commun 51(48):9760–9772. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.201530319
Duan Y, Wu C, Chowdhury S, Lee MC, Xiong GM, Zhang W, Yang R, Cieplak P, Luo R, Lee T, Caldwell J, Wang J, Kollman P (2003) A point-charge force field for molecular mechanics simulations of proteins based on condensed-phase quantum mechanical calculations. J Comput Chem 24(16):1999–2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.10349
Galman JL, Slabu I, Weise NJ, Iglesias C, Parmeggiani F, Lloyd RC, Turner NJ (2017) Biocatalytic transamination with near-stoichiometric inexpensive amine donors mediated by bifunctional mono- and di-amine transaminases. Green Chem 2017(19):361–366. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC02102F
Ghislieri D, Turner NJ (2014) Biocatalytic approaches to the synthesis of enantiomerically pure chiral amines. Top Catal 57(5):284–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-013-0184-1
Green AP, Turner NJ, O'Reilly E (2014) Chiral amine synthesis using ω-transaminases: an amine donor that displaces equilibria and enables high-throughput screening. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(40):10714–10717. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201406571
Gomm A, Lewis W, Green AP, O’Reilly E (2016) A new generation of smart amine donors for transaminase-mediated biotransformations. Chemistry. 22(36):12692–126925. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201603188
Guan LJ, Ohtsuka J, Okai M, Miyakawa T, Mase T, Zhi YH, Hou F, Ito N, Iwasaki A, Yasohara Y, Tanokura M (2015) A new target region for changing the substrate specificity of amine transaminases. Sci Rep 5:10753–10711. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10753
Guo F, Berglund P (2017) Transaminase biocatalysis: optimization and application. Green Chem 19(2):333–360. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC02328B
Höhne M, Schätzle S, Jochens H, Robins K, Bornscheuer UT (2010) Rational assignment of key motifs for function guides in silico enzyme identification. Nat Chem Biol 6(11):807–813. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.447
Hopwood J, Truppo MD, Turner NJ, Lloyd RC (2011) A fast and sensitive assay for measuring the activity and enantioselectivity of transaminases. Chem Commun 47(2):773–775. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02919J
Hwang BY, Kim BG (2004) High-throughput screening method for the identification of active and enantioselective omega-transaminases. Enzym Microb Technol 34(5):429–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2003.11.019
Iglesias C, Panizza P, Giordano SR (2017) Identification, expression and characterization of an R-ω-transaminase from Capronia semiimmersa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(14):5677–5687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8309-2
Islam S, Laaf D, Infanzon B, Pelantova H, Davari MD, Jakob F, Křen V, Elling L, Schwaneberg U (2018) KnowVolution Campaign of an Aryl Sulfotransferase Increases Activity toward Cellobiose. Chemistry 24(64):17117–17124. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201803729
Kim J, Kyung D, Yun H, Cho BK, Seo JH, Cha M, Kim BG (2007) Cloning and characterization of a novel beta-transaminase from Mesorhizobium sp Strain LUK: a new biocatalyst for the synthesis of enantiomerically pure beta-amino acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(6):1772–1782. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02119-06
Koszelewski D, Tauber K, Faber K, Kroutil W (2010) ω-Transaminases for the synthesis of non-racemic α-chiral primary amines. Trends Biotechnol 28(6):324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.03.003
Liu ZQ, Lu MM, Zhang XH, Cheng F, Xu JM, Xue YP, Jin LQ, Wang YS, Zheng YG (2018) Significant improvement of the nitrilase activity by semi-rational protein engineering and its application in the production of iminodiacetic acid. Int J Biol Macromol 116:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.045
Martin AR, DiSanto R, Plotnikov I, Kamat S, Shonnard D, Pannuri S (2007) Improved activity and thermostability of (S)-aminotransferase by error-prone polymerase chain reaction for the production of a chiral amine. Biochem. Eng. J. 37:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2007.05.001
Mathew S, Shin G, Shon M, Yun H (2013) High throughput screening methods for ω-transaminases. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 18(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0544-x
Miyazaki K, Takenouchi M (2002) Creating random mutagenesis libraries using megaprimer PCR of whole plasmid. Biotechniques 33(5):1033–1034. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-395-X:23
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256
Padrosa DR, Alaux R, Smith P, Dreveny I, López-Gallego F, Francesca Paradisi F (2019) Enhancing PLP-binding capacity of class-III ω-transaminase by single residue substitution front. Bioeng Biotechnol 7:282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00282
Pavlidis IV, Weiss MS, Genz M, Spurr P, Hanlon SP, Wirz B, Iding H, Bornscheuer UT (2016) Identification of (S)-selective transaminases for the asymmetric synthesis of bulky chiral amines. Nat Chem 8(11):1076–1082. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2578
Rubsam K, Davari MD, Jakob F, Schwaneberg U (2018) KnowVolution of the polymer-binding peptide LCI for improved polypropylene binding. Polymers 10(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040423
Savile CK, Janey JM, Mundorff EC, Moore JC, Tam S, Jarvis WR, Colbeck JC, Krebber A, Fleitz FJ, Brands J, Devine PN, Huisman GW, Hughes GJ (2010) Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amines from ketones applied to sitagliptin manufacture. Science 329(5989):305–309. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1188934
Schätzle S, Höhne M, Redestad E, Robins K, Bornscheuer UT (2009) Rapid and sensitive kinetic assay for characterization of ω-transaminases. Anal Chem 81(19):8244–8248. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac901640q
Schätzle S, Höhne M, Robins K, Bornscheuer UT (2010) Conductometric method for the rapid characterization of the substrate specificity of amine-transaminases. Anal Chem 82(5):2082–2086. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9028483
Scheidt T, Land H, Anderson M, Chen YJ, Berglund P, Yi D, Fessner WD (2015) Fluorescence-based kinetic assay for high-throughput discovery and engineering of stereoselective ω-transaminases. Adv Synth Catal 357(8):1721–1731. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201500215
Schymkowitz J, Borg J, Stricher F, Nys R, Rousseau F, Serrano L (2005) The FoldX web server: an online force field. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W382–W388. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki387
Shin JS, Kim BG (1997) Kinetic resolution of alpha-methylbenzylamine with omega-transaminase screened from soil microorganisms: application of a biphasic system to overcome product inhibition. Biotechnol Bioeng 55(2):348–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19970720)55:2<348::AID-BIT12>3.0.CO;2-D
Soding J, Biegert A, Lupas AN (2005) The HHpred interactive server for protein homology detection and structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W244–W248. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki408
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) Software news and update AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Truppo MD, Turner NJ (2010) Micro-scale process development of transaminase catalysed reactions. Org Biomol Chem 8(6):1280–1283. https://doi.org/10.1039/B924209K
Wang G, Lu X, Zhu Y, Zhang W, Liu J, Wu Y, Yu L, Sun D, Cheng F (2018) A light-controlled cell lysis system in bacteria. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45(6):429–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2034-4
Weiss MS, Pavlidis IV, Spurr P, Hanlon SP, Wirz B, Iding H, Bornscheuer UT (2017) Amine transaminase engineering for spatially bulky substrate acceptance. Chembiochem 18(11):1022–1026. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700033
Wilding M, Walsh E, Dorrian SJ, Scott C (2015) Identification of novel transaminases from a 12-aminododecanoic acid-metabolizing Pseudomonas strain. Microb Biotechnol 8(4):665–672. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12278
Zhang JH, Chung TDY, Oldenburg KR (1999) A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J Biomol Screen 4(2):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/108705719900400206
Zhu L, Cheng F, Piatkowski V, Schwaneberg U (2014) Protein engineering of the antitumor enzyme PpADI for improved thermal resistance. Chembiochem 15(2):276–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201300433
Zhu L, Tee KL, Roccatano D, Sonmez B, Ni Y, Sun ZH, Schwaneberg U (2010a) Directed evolution of an antitumor drug (arginine Deiminase PpADI) for increased activity at physiological pH. Chembiochem 11(5):691–697. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200900717
Zhu L, Verma R, Roccatano D, Ni Y, Sun ZH, Schwaneberg U (2010b) A potential antitumor drug (arginine deiminase) reengineered for efficient operation under physiological conditions. Chembiochem 11(16):2294–2301. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201000458
Zimmermann L, Stephens A, Nam SZ, Rau D, Kubler J, Lozajic M, Gabler F, Söding J, Lupas AN. Alva V (2018) A completely reimplemented MPI bioinformatics toolkit with a new HHpred server at its core. J Mol Biol 430(15):2237–2243. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.007
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31700693, 31970046, and 21878274) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M612030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 948 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, F., Chen, XL., Xiang, C. et al. Fluorescence-based high-throughput screening system for R-ω-transaminase engineering and its substrate scope extension. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 2999–3009 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10444-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10444-y