Abstract
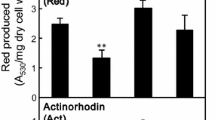
Mutations in rrn encoding ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and rRNA modification often confer resistance to ribosome-targeting antibiotics by altering the site of their interaction with the small (30S) and large (50S) subunits of the bacterial ribosome. The highly conserved central loop of domain V of 23S rRNA (nucleotides 2042–2628 in Escherichia coli; the exact position varies by species) of the 50S subunit, which is implicated in peptidyl transferase activity, is known to be important in macrolide interactions and resistance. In this study, we identified an A2302T mutation in the rrnA-23S rRNA gene and an A2281G mutation in the rrnC-23S rRNA gene that were responsible for resistance to erythromycin in the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and its close relative Streptomyces lividans 66, respectively. Interestingly, genetic and phenotypic characterization of the erythromycin-resistant mutants indicated a possibility that under coexistence of the 23S rRNA mutation and mutations in other genes, S. coelicolor A3(2) and S. lividans 66 can produce abundant amounts of the pigmented antibiotics actinorhodin and undecylprodigiosin depending on the combinations of mutations. Herein, we report the unique phenomenon occurring by unexpected characteristics of the 23S rRNA mutations that can affect the emergence of additional mutations probably with an upswing in spontaneous mutations and enrichment in their variations in Streptomyces strains. Further, we discuss a putative mechanism underlying secondary metabolite overproduction by Streptomyces strains with a 23S rRNA mutation conferring erythromycin resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltz RH (2014) Spontaneous and induced mutations to rifampicin, streptomycin and spectinomycin resistances in actinomycetes: mutagenic mechanisms and applications for strain improvement. J Antibiot 67:619–624
Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA (2000) The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 289:905–920
Barnard AM, Simpson NJ, Lilley KS, Salmond GP (2010) Mutation in rpsL that confer streptomycin resistance show pleiotropic effects on virulence and the production of a carbapenem antibiotic in Erwinia carotovora. Microbiology 156:1030–1039
Bentley S, Chater K, Cerdeño-Tárraga AM, Challis G, Thomson N, James K, Harris D, Quail M, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen C, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell B, Parkhill J, Hopwood D (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Crowe-McAuliffe C, Graf M, Huter P, Takada H, Abdelshahid M, Nováček J, Murina V, Atkinson GC, Hauryliuk V, Wilson DN (2018) Structural basis for antibiotic resistance mediated by the Bacillus subtilis ABCF ATPase VmlR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:8978–8983
Davis JR, Sello JK (2010) Regulation of genes in Streptomyces bacteria required for catabolism of lignin-derived aromatic compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:921–929
Davis JH, Williamson JR (2017) Structure and dynamics of bacterial ribosome biogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc B 372:20160181
Davis JH, Tan YZ, Carragher B, Potter CS, Lyumkis D, Williamson JR (2016) Modular assembly of the bacterial large ribosomal subunit. Cell 167:1610–1622
Dinos GP (2017) The macrolide antibiotic renaissance. Br J Pharmacol 174:2967–2983
Dohra H, Miyake Y, Kodani S (2017) Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces olivochromogenes NBRC 3561, a bioactive peptide-producing Actinobacterium. Genome Announc 5:e01048–e01017
Fyfe C, Grossman TH, Kerstein K, Sutcliffe J (2016) Resistance to macrolide antibiotics in public health pathogens. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6:a025395
Gosse JT, Ghosh S, Sproule A, Overy D, Cheeptham N, Boddy CN (2019) Whole genome sequencing and metabolomic study of cave Streptomyces isolates ICC1 and ICC4. Front Microbiol 10:1020
Hojati Z, Milne C, Harvey B, Gordon L, Borg M, Flett F, Wilkinson B, Sidebottom PJ, Rudd BAM, Hayes MA, Smith CP, Micklefield J (2002) Structure, biosynthetic origin, and engineered biosynthesis of calcium-dependent antibiotics from Streptomyces coelicolor. Chem Biol 9:1175–1187
Hosaka T, Xu J, Ochi K (2006) Increased expression of ribosome recycling factor is responsible for the enhanced protein synthesis during the late growth phase in an antibiotic-overproducing Streptomyces coelicolor ribosomal rpsL mutant. Mol Microbiol 61:883–897
Hosaka T, Ohnishi-Kameyama M, Muramatsu H, Murakami K, Tsurumi Y, Kodani S, Yoshida M, Fujie A, Ochi K (2009) Antibacterial discovery in actinomycetes strains with mutations in RNA polymerase or ribosomal protein S12. Nat Biotechnol 27:462–464
Hu H, Zhang Q, Ochi K (2002) Activation of antibiotic biosynthesis by specified mutations in the rpoB gene (encoding the RNA polymerase beta subunit) of Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol 184:3984–3991
Hutchings MI, Hoskisson PA, Chandra G, Buttner J (2004) Sensing and responding to diverse extracellular signals? Analysis of the sensor kinases and response regulators of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 150:2795–2806
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21:526–531
Imai Y, Fujiwara T, Ochi K, Hosaka T (2012) Development of the ability to produce secondary metabolites in Streptomyces through the acquisition of erythromycin resistance. J Antibiot 65:323–326
Ishizuka M, Imai Y, Mukai K, Shimono K, Hamauzu R, Ochi K, Hosaka T (2018) A possible mechanism for lincomycin induction of secondary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:705–716
Jelic D, Antolivic R (2016) From erythromycin to azithromycin and new potential ribosome-binding antimicrobials. Antibiotics 5:29
Kaweewan I, Komaki H, Hemmi H, Hoshino K, Hosaka T, Isokawa G, Oyoshi T, Kodani S (2019) Isolation and structure determination of a new cytotoxic peptide curacozole from Streptomyces curacoi based on genome mining. J Antibiot 72:1–7
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kodani S, Hudson ME, Durrant MC, Buttner MJ, Nodwell JR, Willey JM (2004) The SapB morphogen is a lantibiotic-like peptide derived from the product of the developmental gene ramS in Streptomyces coelicolor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:11448–11453
Kreider G, Brownstein BL (1974) Pleiotropic effects resulting from mutations in genes for ribosomal proteins: analysis of revertants from streptomycin dependence. J Mol Biol 84:159–171
Lambert T (2012) Antibiotics that affect the ribosome. Rev Sci Tech 31:57–64
Li W, Ying X, Guo Y, Yu Z, Zhou X, Deng Z, Kieser H, Chater KF, Tao M (2006) Identification of a gene negatively affecting antibiotic production and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 188:8368–8375
McCoy LS, Xie Y, Tor Y (2011) Antibiotics that target protein synthesis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2:209–232
Ochi K (2017) Insights into microbial cryptic gene activation and strain improvement: principle, application and technical aspects. J Antibiot 70:25–40
Ochi K, Hosaka T (2013) New strategies for drug discovery: activation of silent or weakly expressed microbial gene clusters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:87–98
Ochi K, Okamoto S, Tozawa Y, Inaoka T, Hosaka T, Xu J, Kurosawa K (2004) Ribosome engineering and secondary metabolite production. Adv Appl Microbiol 56:155–184
Ohnishi Y, Ishikawa J, Hara H, Suzuki H, Ikenoya M, Ikeda H, Yamashita A, Hattori M, Horinouchi S (2008) Genome sequence of the streptomycin-producing microorganism Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J Bacteriol 190:4050–4060
Okamoto-Hosoya Y, Hosaka T, Ochi K (2003) An aberrant protein synthesis activity is linked with antibiotic overproduction in rpsL mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 149:3299–3309
Opron K, Burton ZF (2019) Ribosome structure, function, and early evolution. Int J Mol Sci 20:40
Pakula KK, Hansen LH, Vester B (2017) Combined effect of the Cfr methyltransferase and ribosomal protein L3 mutations on resistance to ribosome-targeting antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e00862–e00817
Pawlik K, Kotowska M, Chater KF, Kuczek K, Takano E (2007) A cryptic type I polyketide synthase (cpk) gene cluster in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Arch Microbiol 187:87–99
Ramakrishnan V (2002) Ribosome structure and the mechanism of translation. Cell 108:557–572
Robinson LJ, Cameron AD, Stavrinides J (2015) Spontaneous and on point: do spontaneous mutations used for laboratory experiments cause pleiotropic effects that might confound bacterial infection and evolution assays? FEMS Microbiol Lett 362:fnv177
Scaiola A, Leibundgut M, Boehringer D, Caspers P, Bur D, Locher HH, Rueedi G, Ritz D (2019) Structural basis of translation inhibition by cadazolid, a novel quinoxolidinone antibiotic. Sci Rep 9:5634
Schwarz S, Shen J, Kadlec K, Wang Y, Michael GB, Febler AT, Vester B (2019) Lincosamides, streptogramins, penicols, and pleuromutilins: mode of action and mechanisms of resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6:a027037
Subramani R, Aalbersberg W (2012) Marine Actinomycetes: an ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites. Microbiol Res 167:571–580
Thoduka SG, Zaleski PA, Dąbrowska Z, Równicki M, Stróżecka J, Górska A, Olejniczak M, Trylska J (2016) Analysis of ribosomal inter-subunit sites as targets for complementary oligonucleotide. Biopolymers 107:23004
Vester B, Douthwaite S (2001) Macrolide resistance conferred by base substitutions in 23S rRNA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:1–12
Wang G, Hosaka T, Ochi K (2008) Dramatic activation of antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor by cumulative drug resistance mutations. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2834–2840
Xu J, Tozawa Y, Lai C, Hayashi H, Ochi K (2002) A rifampicin resistance mutation in the rpoB gene confers ppGpp-independent antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Gen Genomics 268:179–189
Funding
This work was financially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (A) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Grant No. 25712008) and by the Hokuto Bio-science Promotion Foundation (Japan) to T. H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1179 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoshino, K., Imai, Y., Mukai, K. et al. A putative mechanism underlying secondary metabolite overproduction by Streptomyces strains with a 23S rRNA mutation conferring erythromycin resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 2193–2203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10288-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10288-1