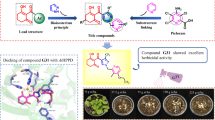
Abstract
Aurovertins are the structurally diverse polyketides that distribute widely in different fungal species. They feature a 2,6-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]-octane ring in structure and exhibit the potential antitumor activity against breast cancer as F1-ATPase β subunit inhibitor. In this study, we constructed the biosynthetic pathway of aurovertin in an Aspergillus nidulans host and obtained seven aurovertin-type compounds. Surprisingly, three new aurovertin geometric isomers were characterized. By introducing an inducible promoter xylP(p) in the pathway gene acyltransferase aurG, we can control the product ratios among different aurovertin compounds by adding glucose and/or inducer xylose. The yields of aurovertins could be increased up to about 20 times by adding a constitutive promoter gpdA(p) to transcription factor AurF, which indicates AurF’s positive role in the biosynthesis of aurovertin. Taken together, our results provided not only an efficient way to generate bioactive fungal natural products but also realized the rational controlling their yields with designed promoters.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi H, Doi H, Kasahara Y, Sawa R, Nakajima K, Kubota Y, Hosokawa N, Tateishi K, Nomoto A (2015) Asteltoxins from the entomopathogenic fungus Pochonia bulbillosa 8-H-28. J Nat Prod 78:1730–1734
Azumi M, Ishidoh K, Kinoshita H, Nihira T, Ihara F, Fujita T, Igarashi Y (2008) Aurovertins F-H from the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. J Nat Prod 71:278–280
Baldwin CL, Nash HA, Osborne CE, Brooker RM, Weaver LC, Jacobsen TN (1964) Biological and chemical properties of aurovertin, a metabolic product of Calcarisporium abuscula. Lloyd 27:88–95
Colot HV, Park G, Turner GE, Ringelberg C, Crew CM, Litvinkova L, Weiss RL, Borkovich KA, Dunlap JC (2006) A high-throughput gene knockout procedure for Neurospora reveals functions for multiple transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:10352–10357
Franck B, Gehrken HP (1980) Citreoviridins from Aspergillus terreus. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 19:461–462
Guo H, Feng T, Li Z-H, Liu JK (2013) Ten new aurovertins from cultures of the basidiomycete Albatrellus confluens. Nat Prod Bioprospect 3:8–13
Haas H, Friedlin E, Stoffler G, Redl B (1993) Cloning and structural organization of a xylanase-encoding gene from Penicillium chrysogenum. Gene 126:237–242
Huang TC, Chang HY, Hsu CH, Kuo WH, Chang KJ, Juan HF (2008) Targeting therapy for breast carcinoma by ATP synthase inhibitor aurovertin B. J Proteome Res 7:1433–1444
Lin TS, Chiang YM, Wang CC (2016) Biosynthetic pathway of the reduced polyketide product citreoviridin in Aspergillus terreus var. aureus revealed by heterologous expression in Aspergillus nidulans. Org Lett 18:1366–1369
Liu N, Hung YS, Gao SS, Hang L, Zou Y, Chooi YH, Tang Y (2017) Identification and heterologous production of a benzoyl-primed tricarboxylic acid polyketide intermediate from the zaragozic acid a biosynthetic pathway. Org Lett 19:3560–3563
Mao XM, Xu W, Li D, Yin WB, Chooi YH, Li YQ, Tang Y, Hu Y (2015) Epigenetic genome mining of an endophytic fungus leads to the pleiotropic biosynthesis of natural products. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54:7592–7596
Mao XM, Zhan ZJ, Grayson MN, Tang MC, Xu W, Li YQ, Yin WB, Lin HC, Chooi YH, Houk KN, Tang Y (2015) Efficient biosynthesis of fungal polyketides containing the dioxabicyclo-octane ring system. J Am Chem Soc 137:11904–11907
Mulheirn LJ, Beechey RB, Leworthy DP, Osselton MD (1974) Aurovertin B, a metabolite of Calcarisporium arbuscula. J Chem Soc Chem Comm 21:874–876
Nishiyama S, Toshima H, Kanai H, Yamamura S (1986) Total synthesis and the absolute-configuration of aurovertin B. Tetrahedron Lett 27:3643–3646
Niu XM, Wang YL, Chu YS, Xue HX, Li N, Wei LX, Mo MH, Zhang KQ (2010) Nematodetoxic aurovertin-type metabolites from a root-knot nematode parasitic fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia. J Agric Food Chem 58:828–834
Palmer JM, Mallaredy S, Perry DW, Sanchez JF, Theisen JM, Szewczyk E, Oakley BR, Wang CC, Keller NP, Mirabito PM (2010) Telomere position effect is regulated by heterochromatin-associated proteins and NkuA in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiology 156(Pt 12):3522–3531
Pauline W (1965) Further observations on Calcarisporium arbuscula. Trans Brit mycol Soc 48(I):9–17
van Raaij MJ, Abrahams JP, Leslie AG, Walker JE (1996) The structure of bovine F1-ATPase complexed with the antibiotic inhibitor aurovertin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6913–6917
Silber J, Ohlendorf B, Labes A, Nather C, Imhoff JF (2013) Calcaripeptides A-C, cyclodepsipeptides from a Calcarisporium strain. J Nat Prod 76:1461–1467
Steyn PS, Vleggaar R, Wessels PL (1981) Biosynthesis of the aurovertins B and D. The role of methionine and propionate in the simultaneous operation of two independent biosynthetic pathways. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:1298–1308
Wang YL, Li LF, Li DX, Wang BL, Zhang KQ, Niu XM (2015) Yellow pigment aurovertins mediate interactions between the pathogenic fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia and its nematode host. J Agric Food Chem 63:6577–6587
Wang F, Luo DQ, Liu JK (2005) Aurovertin E, a new polyene pyrone from the basidiomycete Albatrellus confluens. J Antibiot 58:412–415
Wang M, Sun M, Hao H, Lu C (2015) Avertoxins A−D, prenyl asteltoxin derivatives from Aspergillus versicolor Y10, an endophytic fungus of Huperzia serrata. J Nat Prod 78:3067–3070
Yin WB, Amaike S, Wohlbach DJ, Gasch AP, Chiang YM, Wang CCC, Bok JW, Rohlfs M, Keller NP (2012) An Aspergillus nidulans bZIP response pathway hardwired for defensive secondary metabolism operates through aflR. Mol Microbiol 83:1024–1034
Yin WB, Chooi YH, Smith AR, Cacho RA, Hu YC, White TC, Tang Y (2013) Discovery of cryptic polyketide metabolites from dermatophytes using heterologous expression in Aspergillus nidulans. ACS Synth Biol 2:629–634
Zadra I, Abt B, Parson W, Haas H (2000) xylP promoter-based expression system and its use for antisense downregulation of the Penicillium chrysogenum nitrogen regulator NRE. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4810–4816
Zaki MA, Balachandran P, Khan S, Wang M, Mohammed R, Hetta MH, Pasco DS, Muhammad I (2013) Cytotoxicity and modulation of cancer-related signaling by (Z)- and (E)-3,4,3′,5′-tetramethoxystilbene isolated from Eugenia rigida. J Nat Prod 76:679–684
Zhang P, Wang X, Fan A, Zheng Y, Liu X, Wang S, Zou H, Oakley BR, Keller NP, Yin WB (2017) A cryptic pigment biosynthetic pathway uncovered by heterologous expression is essential for conidial development in Pestalotiopsis fici. Mol Microbiol 105:469–483
Zhao H, Wu R, Ma LF, Wo LK, Hu YY, Chen C, Zhan ZJ (2016) Aurovertin-type polyketides from Calcarisporium arbuscula with potent cytotoxic activities against triple-negative breast cancer. Helv Chim Acta 99:543–546
Zhou ZY, Liu R, Jiang MY, Zhang L, Niu Y, Zhu YC, Dong ZJ, Liu JK (2009) Two new cleistanthane diterpenes and a new isocoumarine from cultures of the basidiomycete Albatrellus confluens. Chem Pharm Bull 57:975–978
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yi Tang (University of California, in Los Angeles) for providing Calcarisporium arbuscular strain. We thank Drs. Jinwei Ren and Wenzhao Wang (Institute of Microbiology, CAS) for NMR and MS data collection. We thank Dr. Aili Fan for the helpful discussion for NMR spectra. W.B.Y. is a scholar of “the 100 Talents Project” of CAS.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470178) and CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2182 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Li, W., Zhang, P. et al. Rational design for heterologous production of aurovertin-type compounds in Aspergillus nidulans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 297–304 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8606-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8606-9