Abstract
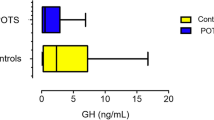
This study was designed to analyse the serum resistin level in children with postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and its clinical significance. Twenty-one children with POTS and 31 healthy children as controls participated in the study. Clinical characteristics, heart rate and blood pressure in the supine and upright positions were monitored and collected during an upright test, and the symptom scoring of POTS patients was recorded. The serum resistin levels of patients in both groups were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The change in serum resistin levels in the POTS group before and after standing, as well as its correlation with symptom scores and change in heart rate after standing, was analysed. Compared with the control group, the serum resistin levels in the POTS group were significantly increased (P < 0.01). The serum resistin levels in the POTS group before and after standing did not differ (P > 0.05). There was a negative correlation between the serum resistin levels and a change in heart rate from the supine to upright position (correlation coefficient = −0.615, P < 0.01). Moreover, serum resistin levels were negatively correlated with symptom scores (correlation coefficient = −0.493, P < 0.05). Serum resistin levels in children with POTS were significantly higher than those in healthy children and negatively correlated with a change in heart rate from the supine to upright position and symptom scores. These results suggest a protective role of increased resistin in the pathogenesis of POTS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin J, Han Z, Li X, Ochs T, Zhao J, Zhang X et al (2014) Risk factors for postural tachycardia syndrome in children and adolescents. PLoS ONE 9:e113625–e113625
Fu Q, VanGundy TB, Galbreath MM, Shibata S, Jain M, Hastings JL et al (2010) Cardiac origins of the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2858–2868
Elsayed H (1996) Salt supplement increases plasma volume and orthostatic tolerance in patients with unexplained syncope. Heart 75:134–140
Low PA, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Textor SC, Benarroch EE, Shen WK (2009) Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 20:352–358
Zhang Q, Liao Y, Tang C, Du J, Jin H (2012) Twenty-four-hour urinary sodium excretion and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Pediatr 161:281–284
Jordan J, Shannon JR, Diedrich A, Black BK, Robertson D (2002) Increased sympathetic activation in idiopathic orthostatic intolerance: role of systemic adrenoreceptor sensitivity. Hypertension 39:173–178
Zhang Q, Xia C, Li J, Du J (2014) Orthostatic plasma norepinephrine level as a predictor for therapeutic response to metoprolol in children with postural tachycardia syndrome. J Translat Med 12:1–6
Wang XL, Chai Q, Charlesworth MC, Figueroa JJ, Low P, Shen WK et al (2012) Autoimmunoreactive IgGs from patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Proteom Clin Appl 6:615–625
Yu X, Stavrakis S, Hill MA, Huang S, Reim S, Li H et al (2012) Autoantibody activation of beta-adrenergic and muscarinic receptors contributes to an “autoimmune” orthostatic hypotension. J Am Soc Hypertens 6:40–47
Wang XL, Ling TY, Charlesworth MC, Figueroa JJ, Low P, Shen WK et al (2013) Autoimmunoreactive IgGs against cardiac lipid raft-associated proteins in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Trans Res 162:34–44
Thieben MJ, Sandroni P, Sletten DM, Benrud-Larson LM, Fealey RD, Vernino S et al (2007) Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: the Mayo clinic experience. Mayo Clin Proc 82:308–313
Liao Y, Chen S, Liu X, Zhang Q, Ai Y, Wang Y et al (2010) Flow-Mediated vasodilation and endothelium function in children with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Am J Cardiol 106:378–382
Zhang F, Li X, Ochs T, Chen L, Liao Y, Tang C et al (2012) Midregional pro-adrenomedullin as a predictor for therapeutic response to midodrine hydrochloride in children with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:315–320
Zhang F, Li X, Chen S, Chen L, Liao Y, Tang C et al (2012) Plasma hydrogen sulfide in differential diagnosis between vasovagal syncope and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in children. J Pediatr 160:227–231
Medow MS, Minson CT, Stewart JM (2005) Decreased microvascular nitric oxide–dependent vasodilation in postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 112:2611–2618
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ et al (2001) The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 409:307–312
Jamaluddin MS, Weakley SM, Yao Q, Chen C (2012) Resistin: functional roles and therapeutic considerations for cardiovascular disease. Br J Pharmacol 165:622–632
Hs J, Kh P, Ym C, Ss C, Hj C, Sy C et al (2006) Resistin is secreted from macrophages in atheromas and promotes atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 69:76–85
Norata GD, Ongari M, Garlaschelli K, Raselli S, Grigore L, Catapano AL (2007) Plasma resistin levels correlate with determinants of the metabolic syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol 156:279
Gamboa A, Okamoto LE, Raj SR, Diedrich A, Shibao CA, Robertson D et al (2013) Nitric oxide and regulation of heart rate in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome and healthy subjects. Hypertension 61:376–381
Yang J, Zhao J, Du S, Liu D, Fu C, Li X et al (2013) Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome with increased erythrocytic hydrogen sulfide and response to midodrine hydrochloride. J Pediatr 163(1169–1173):e1162
Reilly MP, Lehrke M, Wolfe ML, Rohatgi A, Lazar MA, Rader DJ (2005) Resistin is an inflammatory marker of atherosclerosis in humans. Circulation 111:932–939
Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L, Smith U, Tarkowski A (2005) Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory properties. J Immunol 174:5789–5795
Calabro P, Samudio I, Willerson JT, Yeh ET (2004) Resistin promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways. Circulation 110:3335–3340
Verma S, Li SH, Wang CH, Fedak PW, Li RK, Weisel RD et al (2003) Resistin promotes endothelial cell activation: further evidence of adipokine-endothelial interaction. Circulation 108:736–740
Kawanami D, Maemura K, Takeda N, Harada T, Nojiri T, Imai Y et al (2004) Direct reciprocal effects of resistin and adiponectin on vascular endothelial cells: a new insight into adipocytokine–endothelial cell interactions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:415–419
Sun Y, Tang CS, Jb DU, Jin HF (2011) Hydrogen sulfide and vascular relaxation. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:3816–3819
Li H, Liao Y, Han Z, Wang Y, Liu P, Zhang Q et al (2015) Changes of plasma intermedin during head-up tilt test in children with postural tachycardia syndrome and its significance. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 53:375–378
Fang C, Lei J, Zhou SX, Zhang YL, Yuan GY, Wang JF (2013) Association of higher resistin levels with inflammatory activation and endothelial dysfunction in patients with essential hypertension. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 126:646–649
Takata Y, Osawa H, Kurata M, Kurokawa M, Yamauchi J, Ochi M et al (2008) Hyperresistinemia is associated with coexistence of hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Hypertension 51:534–539
Zhang L, Curhan GC, Forman JP (2010) Plasma resistin levels associate with risk for hypertension among nondiabetic women. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1185–1191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants in this study in the form of written consent from parents and written assent from children.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, W., Han, Z., Chen, S. et al. Serum Resistin Negatively Correlates with Clinical Severity of Postural Tachycardia Syndrome in Children. Pediatr Cardiol 38, 1639–1644 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1708-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1708-4