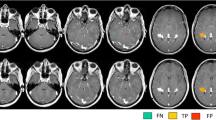
Abstract
Purpose
Repeated use of Gadolinium (Gd) contrast for multiple sclerosis (MS) imaging leads to Gd deposition in brain. We aimed to study the utility of phase values by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) to assess the iron content in MS lesions to differentiate active and inactive lesions.
Methods
MS persons who underwent MRI were grouped into group 1 with active lesions and group 2 with inactive lesions based on the presence or absence of contrast enhancing lesions. Phase values of lesions (PL) and contralateral normal white matter (PN) were calculated using the SPIN software by drawing ROI. Subtracted phase values (PS = PL − PN) and iron content (PS/3) of the lesions were calculated in both groups.
Results
We analyzed 69 enhancing lesions from 22 patients (group 1) and 84 non-enhancing lesions from 29 patients (group 2). Mean-subtracted phase values and iron content corrected for voxels in ROI were significantly lower in enhancing lesions compared to non-enhancing lesions (p < 0.001). A cut-off value 2.8 μg/g for iron content showed area under the curve of 0.909 with good sensitivity.
Conclusion
Quantification of iron content using SWI phase values holds promise as a biomarker to differentiate active from inactive lesions of MS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Filippi M, Rocca MA, Barkhof F, Brück W, Chen JT, Comi G, DeLuca G, de Stefano N, Erickson BJ, Evangelou N, Fazekas F, Geurts JJ, Lucchinetti C, Miller DH, Pelletier D, Popescu BF, Lassmann H, Attendees of the Correlation between Pathological MRI findings in MS workshop (2012) Association between pathological and MRI findings in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 11(4):349–360
Tjoa CW, Benedict RH, Weinstock-Guttman B, Fabiano AJ, Bakshi R (2005) MRI T2 hypointensity of the dentate nucleus is related to ambulatory impairment in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 234:17–24
MacKay A, Laule C, Vavasour I, Bjarnason T, Kolind S, Mädler B (2006) Insights into brain microstructure from the T2 distribution. Magn Reson Imaging 24:515–525
Schenck JF, Zimmerman EA (2004) High-field magnetic resonance imaging of brain iron: birth of a biomarker? NMR Biomed 17:433–445
Vellinga MM, Oude Engberink RD, Seewann A, Pouwels PJW, Wattjes MP, van der Pol SMA, Pering C, Polman CH, de Vries HE, Geurts JJG, Barkhof F (2008) Pluriformity of inflammation in multiple sclerosis shown by ultra-small iron oxide particle enhancement. Brain 131:800–807
Roccatagliata L, Vuolo L, Bonzano L, Pichiecchio A, Mancardi GL (2009) Multiple sclerosis: hyperintense dentate nucleus on unenhanced T1-weightedMRimages is associated with the secondary progressive subtype. Radiology 251:503–510
Radbruch A, Weberling LD, Kieslich PJ, Eidel O, Burth S, Kickingereder P, Heiland S, Wick W, Schlemmer HP, Bendszus M (2015) Gadolinium retention in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus is dependent on the class of contrast agent. Radiology 275:783–791
Kutzelnigg A, Lassmann H (2014) Pathology of multiple sclerosis and related inflammatory demyelinating diseases. Handb Clin Neurol 122:15–58
Cairo G, Recalcati S, Mantovani A, Locati M (2011) Iron trafficking and metabolism in macrophages: contribution to the polarized phenotype. Trends Immunol 32:241–247
Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC, Reichenbach JR (2004) Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med 52:612–618
Ge Y, Jensen JH, Lu H, Helpern JA, Miles L, Inglese M, Babb JS, Herbert J, Grossman RI (2007) Quantitative assessment of iron accumulation in the deep gray matter of multiple sclerosis by magnetic field correlation imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(9):1639–1644
Haacke EM, Makki M, Ge Y, Maheshwari M, Sehgal V, Hu J, Selvan M, Wu Z, Latif Z, Xuan Y, Khan O, Garbern J, Grossman RI (2009) Characterizing iron deposition in multiple sclerosis lesions using susceptibility weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:537–544
Thompson AJ, Banwell BL, Barkhof F, Carroll WM, Coetzee T, Comi G, Correale J, Fazekas F, Filippi M, Freedman MS, Fujihara K, Galetta SL, Hartung HP, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Marrie RA, Miller AE, Miller DH, Montalban X, Mowry EM, Sorensen PS, Tintoré M, Traboulsee AL, Trojano M, Uitdehaag BMJ, Vukusic S, Waubant E, Weinshenker BG, Reingold SC, Cohen JA (2018) Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol 17(2):162–173
Sheelakumari R, Madhusoodanan M, Radhakrishnan A, Ranjith G, Thomas B (2016) A potential biomarker in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: can assessment of brain iron deposition with SWI and corticospinal tract degeneration with DTI help? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37(2):252–258
Hametner S, Wimmer I, Haider L, Pfeifenbring S, Bruck W, Lassmann H (2013) Iron and neurodegeneration in the multiple sclerosis brain. Ann Neurol 74(6):848–861
Langkammer C, Liu T, Khalil M, Enzinger C, Jehna M, Fuchs S, Fazekas F, Wang Y, Ropele S (2013) Quantitative susceptibility mapping in multiple sclerosis. Radiology 267(2):551–559
Walsh AJ, Blevins G, Lebel RM, Seres P, Emery DJ, Wilman AH (2014) Longitudinal MR imaging of iron in multiple sclerosis: an imaging marker of disease. Radiology 270(1):186–196
Chen W, Gauthier SA, Gupta A, Comunale J, Liu T, Wang S, Pei M, Pitt D, Wang Y (2014) Quantitative susceptibility mapping of multiple sclerosis lesions at various ages. Radiology 271(1):183–192
Khalil M, Langkammer C, Pichler A, Pinter D, Gattringer T, Bachmaier G, Ropele S, Fuchs S, Enzinger C, Fazekas F (2015) Dynamics of brain iron levels in multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal 3 T MRI study. Neurology 84:2396–2402
Blystad I, Håkansson I, Tisell A, Ernerudh J, Smedby Ö, Lundberg P, Larsson EM (2016) Quantitative MRI for analysis of active multiple sclerosis lesions without gadolinium-based contrast agent. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:94–100
Zhang Y, Gauthier SA, Gupta A, Comunale J, Chia-Yi Chiang G, Zhou D, Chen W, Giambrone AE, Zhu W, Wang Y (2016) Longitudinal change in magnetic susceptibility of new enhanced multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions measured on serial quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM). J Magn Reson Imaging 44(2):426–432
Zhang Y, Gauthier SA, Gupta A et al (2016) Quantitative susceptibility mapping and R2* measured changes during white matter lesion development in multiple sclerosis: myelin breakdown, myelin debris degradation and removal, and iron accumulation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:1629–1635
Chen W, Zhang Y, Mu K, Pan C, Gauthier SA, Zhu W, Wang Y (2017) Quantifying the susceptibility variation of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis by quantitative susceptibility mapping. AJR Am J Roentgenol 209:889–894
Zhang Y, Gauthier SA, Gupta A, Tu L, Comunale J, Chiang GCY, Chen W, Salustri CA, Zhu W, Wang Y (2016) Magnetic susceptibility from quantitative susceptibility mapping can differentiate new enhancing from nonenhancing multiple sclerosis lesions without gadolinium injection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:1794–1799
Wang Y, Spincemaille P, Liu Z, Dimov A, Deh K, Li J, Zhang Y, Yao Y, Gillen KM, Wilman AH, Gupta A, Tsiouris AJ, Kovanlikaya I, Chiang GCY, Weinsaft JW, Tanenbaum L, Chen W, Zhu W, Chang S, Lou M, Kopell BH, Kaplitt MG, Devos D, Hirai T, Huang X, Korogi Y, Shtilbans A, Jahng GH, Pelletier D, Gauthier SA, Pitt D, Bush AI, Brittenham GM, Prince MR (2017) Clinical quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): biometal imaging and its emerging roles in patient care. J Magn Reson Imaging 46:951–971
Gupta A, Al-Dasuqi K, Xia F et al (2017) The use of noncontrast quantitative MRI to detect gadolinium-enhancing multiple sclerosis brain lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38:1317–1322
Zhang S, Nguyen TD, Zhao Y, Gauthier SA, Wang Y, Gupta A (2018) Diagnostic accuracy of semiautomatic lesion detection plus quantitative susceptibility mapping in the identification of new and enhancing multiple sclerosis lesions. Neuroimage Clin 18:143–148
Zhang S, Nguyen TD, Hurtado Rúa SM, Kaunzner UW, Pandya S, Kovanlikaya I, Spincemaille P, Wang Y, Gauthier SA (2019) Quantitative susceptibility mapping of time-dependent susceptibility changes in multiple sclerosis lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 40(6):987–993
Do Amaral LLF, Fragoso DC, Nunes RH et al (2019) Gadolinium-enhanced susceptibility-weighted imaging in multiple sclerosis: optimizing the recognition of active plaques for different MR imaging sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 40(4):614–619
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Mr Oommen P Mathew, MSc, PhD for his assistance with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Institutional Ethics Committee (IEC): SCT/IEC/1134. All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinayagamani, S., Sabarish, S., Nair, S.S. et al. Quantitative susceptibility-weighted imaging in predicting disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology 63, 1061–1069 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02605-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02605-7