Abstract
Background and purpose
The purpose of this randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study was to investigate the preventive effect of topical administration of atorvastatin (ATV) on the acute radiation-induced skin toxicity in patients with breast cancer.
Patients and methods
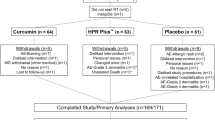
Seventy breast cancer patients were randomly assigned to use topical ATV 1% or placebo gels during radiotherapy twice daily. Radiation-induced dermatitis was classified according to the radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) criteria, as well as pain and itching were scored according to VAS (visual analogue scale) for 6 weeks of treatment.
Results
Topical administration of ATV gel during radiotherapy reduced significantly radiation-induced breast swelling, itching, and pain in breast cancer patients by factors of 1.8, 1.7, and 1.5, respectively. ATV reduced the redness caused by radiotherapy in patients as compared with placebo; however, this difference was statistically not significant.
Conclusion
ATV was able to reduce significantly itching, breast edema, and pain in patients during radiotherapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghoncheh M, Pournamdar Z, Salehiniya H (2016) Incidence and mortality and epidemiology of breast cancer in the world. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17(S3):43–46
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127(12):2893–2917. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25516
Overgaard M, Hansen PS, Overgaard J, Rose C, Andersson M, Bach F, Kjaer M, Gadeberg CC, Mouridsen HT, Jensen MB, Zedeler K (1997) Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk premenopausal women with breast cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Danish breast Cancer cooperative group 82b trial. N Engl J Med 337(14):949–955. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199710023371401
Whelan TJ, Levine M, Julian J, Kirkbride P, Skingley P, Group OCO (2000) The effects of radiation therapy on quality of life of women with breast carcinoma: results of a randomized trial. Cancer 88(10):2260–2266
Whelan TJ, Levine M, Julian J, Kirkbride P, Skingley P (2000) The effects of radiation therapy on quality of life of women with breast carcinoma: results of a randomized trial. Ontario Clinical Oncology Group. Cancer 88(10):2260–2266
Chan RJ, Keller J, Cheuk R, Blades R, Tripcony L, Keogh S (2012) A double-blind randomised controlled trial of a natural oil-based emulsion (Moogoo Udder Cream®) containing allantoin versus aqueous cream for managing radiation-induced skin reactions in patients with cancer. Radiat Oncol 7:121. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-7-121
Heggie S, Bryant GP, Tripcony L, Keller J, Rose P, Glendenning M, Heath J (2002) A phase III study on the efficacy of topical aloe vera gel on irradiated breast tissue. Cancer Nurs 25(6):442–451
Kang HC, Ahn SD, Choi DH, Kang MK, Chung WK, Wu HG (2014) The safety and efficacy of EGF-based cream for the prevention of radiotherapy-induced skin injury: results from a multicenter observational study. Radiat Oncol J 32(3):156–162. https://doi.org/10.3857/roj.2014.32.3.156
Shukla PN, Gairola M, Mohanti BK, Rath GK (2006) Prophylactic beclomethasone spray to the skin during postoperative radiotherapy of carcinoma breast: a prospective randomized study. Indian J Cancer 43(4):180–184
Fenig E, Brenner B, Katz A, Sulkes J, Lapidot M, Schachter J, Malik H, Sulkes A, Gutman H (2001) Topical Biafine and Lipiderm for the prevention of radiation dermatitis: a randomized prospective trial. Oncol Rep 8(2):305–309
Hosseinimehr SJ (2014) The use of angiotensin II receptor antagonists to increase the efficacy of radiotherapy in cancer treatment. Future Oncol 10(15):2381–2390. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.14.177
Salehifar E, Hosseinimehr SJ (2016) The use of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors for improvement of efficacy of radiotherapy in cancers. Drug Discov Today 21(4):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.02.019
Farsaei S, Khalili H, Farboud ES (2012) Potential role of statins on wound healing: review of the literature. Int Wound J 9(3):238–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-481X.2011.00888.x
Jowkar F, Namazi MR (2010) Statins in dermatology. Int J Dermatol 49(11):1235–1243. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04579.x
Tristano AG, Fuller K (2006) Immunomodulatory effects of statins and autoimmune rheumatic diseases: novel intracellular mechanism involved. Int Immunopharmacol 6(12):1833–1846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2006.08.006
Khattri S, Zandman-Goddard G (2013) Statins and autoimmunity. Immunol Res 56(2–3):348–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-013-8409-8
Asai J, Takenaka H, Hirakawa S, Sakabe J, Hagura A, Kishimoto S, Maruyama K, Kajiya K, Kinoshita S, Tokura Y, Katoh N (2012) Topical simvastatin accelerates wound healing in diabetes by enhancing angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Am J Pathol 181(6):2217–2224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.023
Bracht L, Caparroz-Assef SM, Magon TF, Ritter AM, Cuman RK, Bersani-Amado CA (2011) Topical anti-inflammatory effect of hypocholesterolaemic drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol 63(7):971–975. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01302.x
Suzuki-Banhesse VF, Azevedo FF, Araujo EP, do Amaral ME, Caricilli AM, Saad MJ, Lima MH (2015) Effect of atorvastatin on wound healing in rats. Biol Res Nurs 17(2):159–168. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099800414537348
Soehnlein O, Eskafi S, Schmeisser A, Kloos H, Daniel WG, Garlichs CD (2004) Atorvastatin induces tissue transglutaminase in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322(1):105–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.087
Lopez S, Peiretti F, Bonardo B, Juhan-Vague I, Nalbone G (2000) Effect of atorvastatin and fluvastatin on the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in cultured human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 152(2):359–366
Chang CZ, Wu SC, Lin CL, Hwang SL, Howng SL, Kwan AL (2010) Atorvastatin preconditioning attenuates the production of endothelin-1 and prevents experimental vasospasm in rats. Acta Neurochir 152(8):1399–1406; discussion 1405-1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0652-3
Pathak NN, Balaganur V, Lingaraju MC, More AS, Kant V, Kumar D, Kumar D, Tandan SK (2013) Antihyperalgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of atorvastatin in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Inflammation 36(6):1468–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9688-x
Ghaisas MM, Dandawate PR, Zawar SA, Ahire YS, Gandhi SP (2010) Antioxidant, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin in various experimental models. Inflammopharmacology 18(4):169–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-010-0044-6
Farsaei S, Khalili H, Farboud ES, Karimzadeh I, Beigmohammadi MT (2014) Efficacy of topical atorvastatin for the treatment of pressure ulcers: a randomized clinical trial. Pharmacotherapy 34(1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.1339
Toker S, Gulcan E, Cayc MK, Olgun EG, Erbilen E, Ozay Y (2009) Topical atorvastatin in the treatment of diabetic wounds. Am J Med Sci 338(3):201–204. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181aaf209
Jacobson G, Bhatia S, Smith BJ, Button AM, Bodeker K, Buatti J (2013) Randomized trial of pentoxifylline and vitamin E vs standard follow-up after breast irradiation to prevent breast fibrosis, evaluated by tissue compliance meter. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85(3):604–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.06.042
Rao S, Hegde SK, Baliga-Rao MP, Lobo J, Palatty PL, George T, Baliga MS (2017) Sandalwood oil and turmeric-based cream prevents ionizing radiation-induced dermatitis in breast cancer patients: clinical study. Medicines (Basel) 4(3) https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4030043
Cox JD, Stetz J, Pajak TF (1995) Toxicity criteria of the radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) and the European organization for research and treatment of cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31(5):1341–1346
Pezner RD, Patterson MP, Hill LR, Desai KR, Vora N, Lipsett JA (1985) Breast edema in patients treated conservatively for stage I and II breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 11(10):1765–1768
Harsolia A, Kestin L, Grills I, Wallace M, Jolly S, Jones C, Lala M, Martinez A, Schell S, Vicini FA (2007) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy results in significant decrease in clinical toxicities compared with conventional wedge-based breast radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68(5):1375–1380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.02.044
Berthelet E, Truong PT, Musso K, Grant V, Kwan W, Moravan V, Patterson K, Olivotto IA (2004) Preliminary reliability and validity testing of a new Skin Toxicity Assessment Tool (STAT) in breast cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol 27(6):626–631
Freedman GM, Li T, Nicolaou N, Chen Y, Ma CC, Anderson PR (2009) Breast intensity-modulated radiation therapy reduces time spent with acute dermatitis for women of all breast sizes during radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(3):689–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.08.071
Zygogianni A, Kouloulias V, Antypas C, Armpilia C, Kyrgias G, Kouvaris J (2014) The impact of intermediate time between chemotherapy and hypofractionated radiotherapy to the radiation induced skin toxicity for breast adjuvant treatment. Breast J 20(1):74–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbj.12206
James ML, Lehman M, Hider PN, Jeffery M, Francis DP, Hickey BE (2008) Fraction size in radiation treatment for breast conservation in early breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD003860. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003860.pub2
Harper JL, Franklin LE, Jenrette JM, Aguero EG (2004) Skin toxicity during breast irradiation: pathophysiology and management. South Med J 97(10):989–993. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.SMJ.0000140866.97278.87
Hosseinimehr SJ, Izakmehri M, Ghasemi A (2015) In vitro protective effect of atorvastatin against ionizing radiation induced genotoxicity in human lymphocytes. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 61(1):68–71
Hamzeh M, Talebpour Amiri F, Karimpour Malekshah A, Yaghubi Beklar S, Hosseinimehr J (2017) Protective effect of atorvastatin against cardiotoxicity and hematotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide in rat. J Mazand Univ Med Sci 27(151):1–11
Talebpour Amiri F, Hamzeh M, Naeimi RA, Ghasemi A, Hosseinimehr SJ (2018) Radioprotective effect of atorvastatin against ionizing radiation-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Int J Radiat Biol 94(2):106–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/09553002.2018.1420926
Naeimi RA, Talebpour Amiri F, Khalatbary AR, Ghasemi A, Zargari M, Ghesemi M, Hosseinimehr SJ (2017) Atorvastatin mitigates testicular injuries induced by ionizing radiation in mice. Reprod Toxicol 72:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2017.06.052
Barnett GC, Wilkinson JS, Moody AM, Wilson CB, Twyman N, Wishart GC, Burnet NG, Coles CE (2011) The Cambridge Breast Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy Trial: patient- and treatment-related factors that influence late toxicity. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 23(10):662–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2011.04.011
Verbelen H, Gebruers N, Beyers T, De Monie AC, Tjalma W (2014) Breast edema in breast cancer patients following breast-conserving surgery and radiotherapy: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 147(3):463–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3110-8
Adriaenssens N, Verbelen H, Lievens P, Lamote J (2012) Lymphedema of the operated and irradiated breast in breast cancer patients following breast conserving surgery and radiotherapy. Lymphology 45(4):154–164
Bani HA, Fasching PA, Lux MM, Rauh C, Willner M, Eder I, Loehberg C, Schrauder M, Beckmann MW, Bani MR (2007) Lymphedema in breast cancer survivors: assessment and information provision in a specialized breast unit. Patient Educ Couns 66(3):311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2007.01.004
Huang Z, Rose AH, Hoffmann PR (2012) The role of selenium in inflammation and immunity: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 16(7):705–743. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2011.4145
Pfister C, Dawzcynski H, Schingale FJ (2016) Sodium selenite and cancer related lymphedema: biological and pharmacological effects. J Trace Elem Med Biol 37:111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.05.005
Kulkarni NM, Muley MM, Jaji MS, Vijaykanth G, Raghul J, Reddy NK, Vishwakarma SL, Rajesh NB, Mookkan J, Krishnan UM, Narayanan S (2015) Topical atorvastatin ameliorates 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate induced skin inflammation by reducing cutaneous cytokine levels and NF-kappaB activation. Arch Pharm Res 38(6):1238–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0496-0
McGown CC, Brookes ZL, Hellewell PG, Ross JJ, Brown NJ (2015) Atorvastatin reduces endotoxin-induced microvascular inflammation via NOSII. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388(5):557–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1100-y
Kindgen-Milles D (1995) Effects of prostaglandin E2 on the intensity of bradykinin-evoked pain from skin and veins of humans. Eur J Pharmacol 294(2–3):491–496
Napimoga MH, Souza GR, Cunha TM, Ferrari LF, Clemente-Napimoga JT, Parada CA, Verri WA Jr, Cunha FQ, Ferreira SH (2008) 15d-prostaglandin J2 inhibits inflammatory hypernociception: involvement of peripheral opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324(1):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.107.126045
Acknowledgments
This research was the subject of a thesis of Zahra Ghashghaei as a Pharm D. student of Mazandaran University of Medical Science.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from Mazandaran University of Medical Science, Sari, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they had no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 16.3 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, A., Ghashghai, Z., Akbari, J. et al. Topical atorvastatin 1% for prevention of skin toxicity in patients receiving radiation therapy for breast cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 75, 171–178 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-018-2570-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-018-2570-x