Abstract
Background
Chronic migraine (CM) and medication-overuse headaches (MOH) are well-recognized disabling conditions affecting a significant portion of the headache population attending centers specialized in treating headaches. A dysfunctioning of the serotonergic system has been demonstrated in MOH and CM patients. Here we report on our assessment of the dysfunctioning of the endocannabinoid system as a potential underlying factor in pathogenic mechanisms involved in CM and MOH.
Method
To test the hypothesis of an impairment in the endocannabinoid system in patients with MOH and CM and to assess its relationship with any disruption of the serotonergic system, we determined the levels of the two main endogenous cannabinoids, anandamide (AEA) and 2-acylglycerol (2-AG), in platelets of 20 CM patients, 20 MOH patients and 20 control subjects and also measured the platelet serotonin levels in the same patients.
Results
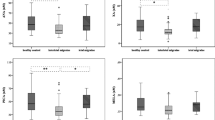
We found that 2-AG and AEA levels were significantly lower in MOH patients and CM patients than in the control subjects, without significant differences between the two patient groups. Serotonin levels were also strongly reduced in the two patient groups and were correlated with 2-AG levels, with higher values for MOH patients.
Conclusion
These data support the potential involvement of a dysfunctioning of the endocannabinoid and serotonergic systems in the pathology of CM and MOH. These systems appear to be mutually related and able to contribute to the chronification of both CM and MOH.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pascual J, Colas R, Castillo J (2001) Epidemiology of chronic daily headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep 5:529–536
Diener HC, Limmroth V (2004) Medication-overuse headache: a worldwide problem. Lancet Neurol 3:475–483
Boes CJ, Black DF, Dodick DW (2006) Pathophysiology and management of transformed migraine and medication overuse headache. Semin Neurol 26:232–241
Srikiatkhachorn A (2001) Pathophysiology of chronic daily headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep 5:537–544
Welch KM (2003) Concepts of migraine headache pathogenesis: insights into mechanisms of chronicity and new drug targets. Neurol Sci 24(Suppl 2):S149–S153
Cupini LM, Calabresi P (2005) Medication-overuse headache: pathophysiological insights. J Headache Pain 6:199–202
Calabresi P, Cupini LM (2005) Medication-overuse headache: similarities with drug addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:62–68
Fumal A, Laureys S, Di Clemente L, Boly M, Bohotin V, Vandenheede M, Coppola G, Salmon E, Kupers R, Schoenen J (2006) Orbitofrontal cortex involvement in chronic analgesic-overuse headache evolving from episodic migraine. Brain 129:543–550
D’Andrea G, Cananzi AR, Perini F, Hasselmark L (1995) Platelet models and their possibile usefulness in the study of migraine pathogenesis. Cephalagia 15:265–271
Gallai V, Floridi A, Mazzotta G, Codini M, Tognoloni M, Ambrosini P et al (1996) L-arginine/nitric oxide patway activation in platelets of migraine with and without aura patients. Acta Neurol Scand 94:151–160
Hering R, Glover V, Pattichis K, Catarci T, Steiner TJ (1993) 5HT in migraine patients with medication-induced headache. Cephalalgia 13:410–412
Srikiatkhachorn A, Govitrapong P, Limthavon C (1994) Up-regulation of 5-HT2 serotonin receptor: a possible mechanism of transformed migraine. Headache 34:8–11
Srikiatkhachorn A, Maneesri S, Govitrapong P, Kasantikul V (1998) Derangement of serotonin system in migrainous patients with analgesic abuse headache: clues from platelets. Headache 38:43–49
Sarchielli P, Alberti A, Russo S, Codini M, Panico R, Floridi A, Gallai V (1999) Nitric oxide pathway, Ca2+, and serotonin content in platelets from patients suffering from chronic daily headache. Cephalalgia 19:810–816
Calignano A, La Rana G, Giuffrida A, Piomelli D (1998) Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids. Nature 394:277–281
Walker JM, Hohmann AG (2005) Cannabinoid mechanisms of pain suppression. Handb Exp Pharmacol 168:509–554
Akerman S, Kaube H, Goadsby PJ (2004) Anandamide is able to inhibit trigeminal neurons using an in vivo model of trigeminovascular-mediated nociception. J Pharm Exp Ther 309:56–63
Quartilho A, Mata HP, Ibrahim MM, Vanderah TW, Porreca F, Makriyannis A, Malan TP Jr (2003) Inhibition of inflammatory hyperalgesia by activation of peripheral CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Anesthesiology 99:955–960
Kimura T, Ohta T, Watanabe K, Yoshimura H, Yamamoto I (1998) Anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, also interacts with 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptor. Biol Pharmacol Bull 21:224–226
Cheer JF, Cadogan AK, Marsden CA, Fone KC, Kendall DA (1999) Modification of 5-HT2 receptor mediated behaviour in the rat by oleamide and the role of cannabinoid receptors. Neuropharmacology 38:533–541
Maione S, Bisogno T, de Novellis V, Palazzo E, Cristino L, Valenti M, Petrosino S, Guglielmotti V, Rossi F, Di Marzo V (2006) Elevation of endocannabinoid levels in the ventrolateral periaqueductal grey through inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase affects descending nociceptive pathways via both cannabinoid receptor type 1 and transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:969–982
Parolaro D, Vigano D, Rubino T (2005) Endocannabinoids and drug dependence. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 4:643–655
Maccarrone M, Bari M, Battista N, Finazzi-Agro A (2002) Endocannabinoid degradation, endotoxic shock and inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 1:53–63
Macarrone M, Bari M, Menichelli A, Giuliani E, Del Principe D, Finazzi-Agro A (2001) Human platelets bind and degrade 2-arachidonoylglycerol, which activates these cells through a cannabinoid receptor. Eur J Biochem 268:819–825, Feb
Maccarrone M, Bari M, Principe DD, Finazzi-Agro A (2003) Activation of human platelets by 2-arachidonoylglycerol is enhanced by serotonin. Thromb Haemost 89:340–347
Braud S, Bon C, Touqui L, Mounier C (2000) Activation of rabbit blood platelets by anandamide through its cleavage into arachidonic acid. FEBS Lett 471:12–16
Berdyshev EV, Schmid PC, Krebsbach RJ, Schmid HH (2001) Activation of PAF receptors results in enhanced synthesis of 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) in immune cells. FASEB J 15:2171–2178
Cupini LM, Bari M, Battista N, Argiro G, Finazzi-Agro A, Calabresi P, Maccarrone M (2006) Biochemical changes in endocannabinoid system are expressed in platelets of female but not male migraineurs. Cephalalgia 26:277–281
Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (2004) The international classification of headache disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 24(Suppl 1):9–160
Silberstein SD, Olesen J, Bousser MG, Diener HC, Dodick D, First M, Goadsby PJ, Göbel H, Lainez MJA, Lance JW, Lipton RB, Nappi G, Sakai F, Schoenen J, Steiner TJ, on behalf of the International Headache Society (2005) The international classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd Edition (ICHD-II)-revision of criteria for 8.2 Medication-overuse headache. Cephalalgia 25:460–465
Headache Classification Committee, Olesen J, Bousser MG, Diener HC, Dodick D, First M, Goadsby PJ, Gobel H, Lainez MJ, Lance JW, Lipton RB, Nappi G, Sakai F, Schoenen J, Silberstein SD, Steiner TJ (2006) New appendix criteria open for a broader concept of chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 26:742–746
Lingjaerde O (1990) Blood platelets as a model system for studying serotonergic dysfunction and effects of antidepressants. Pharmacol Toxicol 66(Suppl 3):61–68
Uebelhack R, Franke L, Herold N, Plotkin M, Amthauer H, Felix R (2006) Brain and platelet serotonin transporter in humans-correlation between [123I]-ADAM SPECT and serotonergic measurements in platelets. Neurosci Lett 406:153–158, Epub 2006 Aug 24
Vogeser M, Hauer D, Christina Azad S, Huber E, Storr M, Schelling G (2006) Release of anandamide from blood cells. Clin Chem Lab Med 44:488–491
Sarchielli P, Pini LA, Coppola F, Rossi C, Baldi A, Mancini ML, Calabresi P (2007) Endocannabinoids in chronic migraine: CSF findings suggest a system failure. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1384–1390
Akerman S, Holland PR, Goadsby PJ (2007) Cannabinoid (CB1) receptor activation inhibits trigeminovascular neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:64–71
Maldonado R, Valverde O, Berrendero F (2006) Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Trends Neurosci 29:225–232
Fattore L, Spano MS, Deiana S, Melis V, Cossu G, Fadda P, Fratta W (2007) An endocannabinoid mechanism in relapse to drug seeking: a review of animal studies and clinical perspectives. Brain Res Rev 53:1–16
González S, Cascio MG, Fernández-Ruiz J, Fezza F, Di Marzo V, Ramos JA (2002) Changes in endocannabinoid contents in the brain of rats chronically exposed to nicotine, ethanol or cocaine. Brain Res 954:73–81
Ferrer B, Bermúdez-Silva FJ, Bilbao A, Alvarez-Jaimes L, Sanchez-Vera I, Giuffrida A, Serrano A, Baixeras E, Khaturia S, Navarro M, Parsons LH, Piomelli D, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (2007) Regulation of brain anandamide by acute administration of ethanol. Biochem J 404:97–104
Beardsley PM, Thomas BF (2005) Current evidence supporting a role of cannabinoid CB1 receptor (CB1R) antagonists as potential pharmacotherapies for drug abuse disorders. Behav Pharmacol 16:275–296
Tucci SA, Halford JC, Harrold JA, Kirkham TC (2006) Therapeutic potential of targeting the endocannabinoids: implications for the treatment of obesity, metabolic syndrome, drug abuse and smoking cessation. Curr Med Chem 13:2669–2680
Sipe JC, Chiang K, Gerber AL, Beutler E, Cravatt BF (2002) A missense mutation in human fatty acid amide hydrolase associated with problem drug use. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8394–8399
Parrish JC, Nichols DE (2006) Serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptor activation induces 2-arachidonoylglycerol release through a phospholipase c-dependent mechanism. J Neurochem 99:1164–1175
Gobbi G, Bambico FR, Mangieri R, Bortolato M, Campolongo P, Solinas M, Cassano T, Morgese MG, Debonnel G, Duranti A, Tontini A, Tarzia G, Mor M, Trezza V, Goldberg SR, Cuomo V, Piomelli D (2005) Antidepressant-like activity and modulation of brain monoaminergic transmission by blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(51):18620–18625, Erratum in: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2465, 2006
Vandevoorde S, Lambert DM (2005) Focus on the three key enzymes hydrolysing endocannabinoids as new drug targets. Curr Pharm Des 11:2647–2668
Bari M, Battista N, Fezza F, Gasperi V, Maccarrone M (2006) New insights into endocannabinoid degradation and its therapeutic potential. Mini Rev Med Chem 6:257–268
Acknowledgments
This study has been partially supported by the Lega Italiana Cefalalgici. The authors express their gratitude to John A. Toomey for editing the English and Marisa M. Morson for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi, C., Pini, L.A., Cupini, M.L. et al. Endocannabinoids in platelets of chronic migraine patients and medication-overuse headache patients: relation with serotonin levels. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64, 1–8 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0391-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0391-4