Abstract
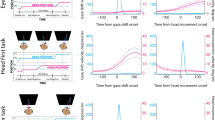
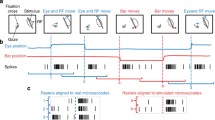
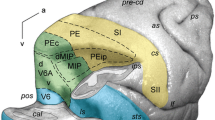
The ventral premotor cortex (PMv) of the macaque monkey contains neurons that respond both to visual and to tactile stimuli. For almost all of these “bimodal” cells, the visual receptive field is anchored to the tactile receptive field on the head or the arms, and remains stationary when the eyes fixate different locations. This study compared the responses of bimodal PMv neurons to a visual stimulus when the monkey was required to fixate a spot of light and when no fixation was required. Even when the monkey was not fixating and the eyes were moving, the visual receptive fields remained in the same location, near the associated tactile receptive field. For many of the neurons, the response to the visual stimulus was significantly larger when the monkey was not performing the fixation task. In control tests, the presence or absence of the fixation spot itself had little or no effect on the response to the visual stimulus. These results show that even when the monkey’s eye position is continuously changing, the neurons in PMv have visual receptive fields that are stable and fixed to the relevant body part. The reduction in response during fixation may reflect a shift of attention from the visual stimulus to the demands of the fixation task.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 April 1997 / Accepted: 16 July 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graziano, M., Gross, C. Visual responses with and without fixation: neurons in premotor cortex encode spatial locations independently of eye position. Exp Brain Res 118, 373–380 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050291
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050291