Abstract
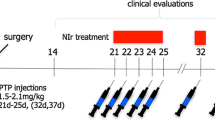
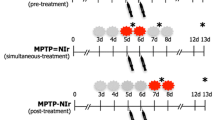
Intracranial application of red to infrared light, known also as photobiomodulation (PBM), has been shown to improve locomotor activity and to neuroprotect midbrain dopaminergic cells in rodent and monkey models of Parkinson’s disease. In this study, we explored whether PBM has any influence on the number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+cells and the expression of GDNF (glial-derived neurotrophic factor) in the striatum. Striatal sections of MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine)-treated mice and monkeys and 6-hydroxydopamine (6OHDA)-lesioned rats that had PBM optical fibres implanted intracranially (or not) were processed for immunohistochemistry (all species) or western blot analysis (monkeys). In our MPTP monkey model, which showed a clear loss in striatal dopaminergic terminations, PBM generated a striking increase in striatal TH+ cell number, 60% higher compared to MPTP monkeys not treated with PBM and 80% higher than controls. This increase was not evident in our MPTP mouse and 6OHDA rat models, both of which showed minimal loss in striatal terminations. In monkeys, the increase in striatal TH+ cell number in MPTP-PBM cases was accompanied by similar increases in GDNF expression, as determined from western blots, from MPTP and control cases. In summary, these results offer insights into the mechanisms by which PBM generates its beneficial effects, potentially with the use of trophic factors, such as GDNF.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker K-F, Schott C, Hipp S et al (2007) Quantitative protein analysis from formalin-fixed tissues: implications for translational clinical research and nanoscale molecular diagnosis. J Pathol 211:370–378. doi:10.1002/path.2107
Betarbet R, Turner R, Chockkan V et al (1997) Dopaminergic neurons intrinsic to the primate striatum. J Neurosci 17:6761–6768
Blandini F, Nappi G, Tassorelli C, Martignoni E (2000) Functional changes of the basal ganglia circuitry in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 62:63–88
Cossette M, Lecomte F, Parent A (2005) Morphology and distribution of dopaminergic neurons intrinsic to the human striatum. J Chem Neuroanat 29:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2004.08.007
d’Anglemont de Tassigny X, Pascual A, López-Barneo J (2015) GDNF-based therapies, GDNF-producing interneurons, and trophic support of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway. Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Front Neuroanat 9:10. doi:10.3389/fnana.2015.00010
Darlot F, Moro C, El Massri N et al (2016) Near-infrared light is neuroprotective in a monkey model of Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 79:59–75. doi:10.1002/ana.24542
Darmopil S, Muñetón-Gómez VC, de Ceballos ML et al (2008) Tyrosine hydroxylase cells appearing in the mouse striatum after dopamine denervation are likely to be projection neurones regulated by L-DOPA. Eur J Neurosci 27:580–592. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06040.x
Depboylu C (2014) Non-serine-phosphorylated tyrosine hydroxylase expressing neurons are present in mouse striatum, accumbens and cortex that increase in number following dopaminergic denervation. J Chem Neuroanat 56:35–44. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2014.02.001
Du X, Iacovitti L (1997) Multiple signaling pathways direct the initiation of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in cultured brain neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 50:1–8
Du X, Stull ND, Iacovitti L (1995) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor works coordinately with partner molecules to initiate tyrosine hydroxylase expression in striatal neurons. Brain Res 680:229–233
Dubach M, Schmidt R, Kunkel D et al (1987) Primate neostriatal neurons containing tyrosine hydroxylase: Immunohistochemical evidence. Neurosci Lett 75:205–210. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(87)90298-9
El Massri N, Johnstone DM, Peoples CL et al (2016a) The effect of different doses of near infrared light on dopaminergic cell survival and gliosis in MPTP-treated mice. Int J Neurosci 126:76–87. doi:10.3109/00207454.2014.994063
El Massri N, Moro C, Torres N et al (2016b) Near-infrared light treatment reduces astrogliosis in MPTP-treated monkeys. Exp Brain Res 1–8. doi:10.1007/s00221-016-4720-7
Gash DM, Zhang Z, Ai Y et al (2005) Trophic factor distribution predicts functional recovery in parkinsonian monkeys. Ann Neurol 58:224–233. doi:10.1002/ana.20549
Hamblin MR (2016) Shining light on the head: Photobiomodulation for brain disorders. BBA Clin 6:113–124. doi:10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.09.002
Heise CE, Mitrofanis J (2005) Reduction in parvalbumin expression in the zona incerta after 6OHDA lesion in rats. J Neurocytol 34:421–434. doi:10.1007/s11068-006-8728-y
Huot P, Lévesque M, Parent A (2007) The fate of striatal dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s chorea. Brain 130:222–232. doi:10.1093/brain/awl332
Huot P, Lévesque M, Morissette M et al (2008) L-Dopa treatment abolishes the numerical increase in striatal dopaminergic neurons in parkinsonian monkeys. J Chem Neuroanat 35:77–84. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2007.06.004
Johnstone DM, El Massri N, Moro C et al (2014) Indirect application of near infrared light induces neuroprotection in a mouse model of parkinsonism—an abscopal neuroprotective effect. Neuroscience 274:93–101. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.023
Johnstone DM, Moro C, Stone J et al (2016) Turning on lights to stop neurodegeneration: the potential of near infrared light therapy in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci 9:500. doi:10.3389/fnins.2015.00500
Jollivet C, Montero-Menei CN, Venier-Julienne M-C et al (2004) Striatal tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive neurons are induced by L-dihydroxyphenylalanine and nerve growth factor treatment in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Neurosci Lett 362:79–82. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.02.068
Liang HL, Whelan HT, Eells JT, Wong-Riley MTT (2008) Near-infrared light via light-emitting diode treatment is therapeutic against rotenone- and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion-induced neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 153:963–974. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.042
Mazloom M, Smith Y (2006) Synaptic microcircuitry of tyrosine hydroxylase-containing neurons and terminals in the striatum of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated monkeys. J Comp Neurol 495:453–469. doi:10.1002/cne.20894
Meng C, He Z, Xing D (2013) Low-level laser therapy rescues dendrite atrophy via upregulating BDNF expression: implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. J Neurosci 33:13505–13517. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0918-13.2013
Meredith GE, Farrell T, Kellaghan P et al (1999) Immunocytochemical characterization of catecholaminergic neurons in the rat striatum following dopamine-depleting lesions. Eur J Neurosci 11:3585–3596. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00774
Moro C, Torres N, El Massri N et al (2013) Photobiomodulation preserves behaviour and midbrain dopaminergic cells from MPTP toxicity: evidence from two mouse strains. BMC Neurosci 14:40. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-14-40
Moro C, El Massri N, Torres N et al (2014) Photobiomodulation inside the brain: a novel method of applying near-infrared light intracranially and its impact on dopaminergic cell survival in MPTP-treated mice. J Neurosurg 120:670–683. doi:10.3171/2013.9.JNS13423
Moro C, El Massri N, Darlot F, et al (2016) Effects of a higher dose of near-infrared light on clinical signs and neuroprotection in a monkey model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1648 Part A 19–26. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2016.07.005
Orme RP, Bhangal MS, Fricker RA (2013) Calcitriol imparts neuroprotection in vitro to midbrain dopaminergic neurons by upregulating GDNF expression. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062040
Oueslati A, Lovisa B, Perrin J et al (2015) Photobiomodulation suppresses alpha-synuclein-induced toxicity in an AAV-based rat genetic model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 10:e0140880. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0140880
Palfi S, Leventhal L, Chu Y et al (2002) Lentivirally delivered glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increases the number of striatal dopaminergic neurons in primate models of nigrostriatal degeneration. J Neurosci 22:4942–4954
Parent A, Hazrati L-N (1995) Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Brain Res Rev 20:91–127. doi:10.1016/0165-0173(94)00007-C
Paxinos G, Franklin K (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic press, California, USA
Paxinos G, Watson CR (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 5th edn. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, Boston
Paxinos G, Huang X, Toga A (1998) The Rhesus monkey brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, USA
Peoples C, Spana S, Ashkan K et al (2012) Photobiomodulation enhances nigral dopaminergic cell survival in a chronic MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:469–476. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.01.005
Porritt MJ, Batchelor PE, Hughes AJ et al (2000) New dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease striatum. The Lancet 356:44–45. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02437-5
Powner MB, Salt TE, Hogg C, Jeffery G (2016) Improving mitochondrial function protects bumblebees from neonicotinoid pesticides. PLOS One 11:e0166531. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0166531
Purushothuman S, Nandasena C, Johnstone DM et al (2013) The impact of near-infrared light on dopaminergic cell survival in a transgenic mouse model of parkinsonism. Brain Res 1535:61–70. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2013.08.047
Reinhart F, Massri NE, Darlot F et al (2014) 810 nm near-infrared light offers neuroprotection and improves locomotor activity in MPTP-treated mice. Neurosci Res. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2014.11.005
Reinhart F, El Massri N, Darlot F et al (2015) Evidence for improved behaviour and neuroprotection after intracranial application of near infrared light in a hemi-parkinsonian rat model. J Neurosurg 27:1–13
Reinhart F, El Massri N, Johnstone DM et al (2016) Near-infrared light (670 nm) reduces MPTP-induced parkinsonism within a broad therapeutic time window. Exp Brain Res. doi:10.1007/s00221-016-4578-8
Sandhu JK, Gardaneh M, Iwasiow R et al (2009) Astrocyte-secreted GDNF and glutathione antioxidant system protect neurons against 6OHDA cytotoxicity. Neurobiol Dis 33:405–414. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.11.016
Sebastián WS, Guillén J, Manrique M et al (2007) Modification of the number and phenotype of striatal dopaminergic cells by carotid body graft. Brain 130:1306–1316. doi:10.1093/brain/awm061
Shaw VE, Spana S, Ashkan K et al (2010) Neuroprotection of midbrain dopaminergic cells in MPTP-treated mice after near-infrared light treatment. J Comp Neurol 518:25–40. doi:10.1002/cne.22207
Shaw VE, Peoples C, Spana S et al (2012) Patterns of cell activity in the subthalamic region associated with the neuroprotective action of near-infrared light treatment in MPTP-Treated mice. Parkinsons Dis 296875. doi:10.1155/2012/296875
Sun M, Kong L, Wang X et al (2005) Comparison of the capability of GDNF, BDNF, or both, to protect nigrostriatal neurons in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1052:119–129. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.05.072
Tandé D, Höglinger G, Debeir T et al (2006) New striatal dopamine neurons in MPTP-treated macaques result from a phenotypic shift and not neurogenesis. Brain 129:1194–1200. doi:10.1093/brain/awl041
Tashiro Y, Sugimoto T, Hattori T et al (1989) Tyrosine hydroxylase-like immunoreactive neurons in the striatum of the rat. Neurosci Lett 97:6–10. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(89)90130-4
Trimmer PA, Schwartz KM, Borland MK et al (2009) Reduced axonal transport in Parkinson’s disease cybrid neurites is restored by light therapy. Mol Neurodegener 4:26. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-4-26
Ünal B, Shah F, Kothari J, Tepper JM (2013) Anatomical and electrophysiological changes in striatal TH interneurons after loss of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway. Brain Struct Funct 220:331–349. doi:10.1007/s00429-013-0658-8
Vos M, Lovisa B, Geens A et al (2013) Near-Infrared 808 nm light boosts complex IV-dependent respiration and rescues a Parkinson-related pink1 model. PLoS One 8:e78562. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078562
Weihe E, Depboylu C, Schuẗz B et al (2006) Three types of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive CNS neurons distinguished by dopa decarboxylase and VMAT2 co-expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:659–678. doi:10.1007/s10571-006-9053-9
Whelan HT, DeSmet KD, Buchmann EV et al (2008) Harnessing the cell’s own ability to repair and prevent neurodegenerative disease. SPIE Newsroom 24:1–3
Xenias HS, Ibáñez-Sandoval O, Koós T, Tepper JM (2015) Are striatal tyrosine hydroxylase interneurons dopaminergic? J Neurosci 35:6584–6599. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0195-15.2015
Xuan W, Vatansever F, Huang L et al (2013) Transcranial low-level laser therapy improves neurological performance in traumatic brain injury in mice: effect of treatment repetition regimen. PLoS One 8:e53454. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053454
Ying R, Liang HL, Whelan HT et al (2008) Pretreatment with near-infrared light via light-emitting diode provides added benefit against rotenone- and MPP+-induced neurotoxicity. Brain Res 1243:167–173. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.09.057
Acknowledgements
We are forever grateful to Michael J Fox Foundation, Credit Agricole Sud Rhones Alpes, Fondation Philanthropique Edmond J Safra, France Parkinson and the French National Research Agency (ANR Carnot Institute), Tenix corp and Salteri family and our industry partners for funding this work. We thank Sharon Spana, Diane Agay, Fannie Darlot, Guillaume Barboux, Clément Perrin, Cyril Zenga and Mylène D’Orchymont for excellent technical assistance and, in particular, many thanks to Donna Lai, Sheng Hua and James Kang for much help with the western blots. All authors contributed to the experiments and analysis of the results and NEM and JM to the writing of the manuscript. There are no conflicts of interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Massri, N., Lemgruber, A.P., Rowe, I.J. et al. Photobiomodulation-induced changes in a monkey model of Parkinson’s disease: changes in tyrosine hydroxylase cells and GDNF expression in the striatum. Exp Brain Res 235, 1861–1874 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-4937-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-4937-0