Abstract
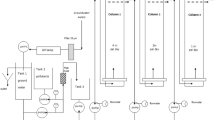
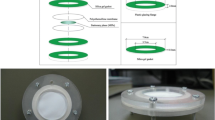
For more than 15 years, integrative passive sampling has been successfully used for monitoring contaminants in water, but no passive sampling device exists for strongly polar organic compounds, such as glyphosate. We thus propose a polar organic chemical integrative sampler (POCIS)-like tool dedicated to glyphosate and its main degradation product aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), and describe the laboratory calibration of such a tool for calculating the sampling rates of glyphosate and AMPA. This passive sampler consists of a POCIS with molecularly imprinted polymer as a receiving phase and a polyethersulfone diffusion membrane. The calibration experiment for the POCIS was conducted for 35 days in a continuous water-flow-through exposure system. The calibration results show that the sampling rates are 111 and 122 mL day-1 for glyphosate and AMPA respectively, highlighting the potential interest in and the applicability of this method for environmental monitoring. The influence of membrane porosity on the glyphosate sampling rate was also tested.

ᅟ



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan IJ, Vrana B, Greenwood R, Mills GA, Roig B, Gonzalez C. A "toolbox" for biological and chemical monitoring requirements for the European Union's Water Framework Directive. Talanta. 2006. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.043.
Vrana B, Allan I, Greenwood R, Mills G, Dominiak E, Svensson K, et al. Passive sampling techniques for monitoring pollutants in water. Trends Anal Chem. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2005.06.006.
Stuer-Lauridsen F. Review of passive accumulation devices for monitoring organic micropollutants in the aquatic environment. Environ Pollut. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.12.004.
Kot-Wasik A, Zabiegata B, Urbanowicz M, Dominiak E, Wasik A, Namiesnik J. Advances in passive sampling in environmental studies. Anal Chim Acta. 2007. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2007.09.013.
Söderström H, Lindberg RH, Fick J. Strategies for monitoring the emerging polar organic contaminants in water with emphasis on integrative passive sampling. J Chromatogr A. 2009. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.08.030.
European Commission. Guidance document no. 19. Guidance on surface water chemical monitoring under the Water Framework Directive. Technical report - 2009 - 025. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities; 2009.
Borggaard OK, Gimsing AL. Fate of glyphosate in soil and the possibility of leaching to ground and surface waters: a review. Pest Manag Sci. 2008. doi:10.1002/ps.1512.
Vereecken H. Mobility and leaching of glyphosate: a review. Pest Manag Sci. 2005. doi:10.1002/ps.1122.
Byer JD, Struger J, Klawunn P, Todd A, Sverko E. Low cost monitoring of glyphosate in surface waters using the ELISA method: an evaluation. Environ Sci Technol. 2008. doi:10.1021/es8005207.
Alvarez DA. Development of an integrative sampling device for hydrophilic organic contaminants in aquatic environments. PhD thesis, University of Missouri-Columbia: 1999.
Mazzella N, Dubernet JF, Delmas F. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium regimes in the operation of polar organic chemical integrative samplers. Application to the passive sampling of the polar herbicides in aquatic environments. J Chromatogr A. 2007. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.03.087.
Berho C, Togola A, Coureau C, Ghestem JP, Amalric L. Applicability of polar organic compound integrative samplers for monitoring pesticides in groundwater. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2013;20:5220–8. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1508-1.
MacLeod S, McClure E, Wong C. Laboratory calibration and field deployment of the polar organic chemical integrative sampler for pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater and surface water. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2007. doi:10.1897/07-238.1.
Alvarez DA, Petty JD, Huckins JN, Jones-Lepp TL, Getting DT, Goddard JP, et al. Development of a passive, in situ, integrative sampler for hydrophilic organic contaminants in aquatic environments. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2004. doi:10.1897/03-603.
Li H, Helm PA, Paterson G, Metcalfe CD. The effects of dissolved organic matter and pH on sampling rates for polar organic chemical integrative samplers (POCIS). Chemosphere. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.071.
Fauvelle V, Mazzella N, Delmas F, Madarassou K, Eon M, Budzinski H. Use of mixed-mode ion exchange sorbent for the passive sampling of organic acids by polar organic chemical integrative sampler (POCIS). Environ Sci Technol. 2012. doi:10.1021/es3035279.
Fauvelle V, Mazzella N, Belles A, Moreira A, Allan IJ, Budzinski H. Optimization of the polar organic chemical integrative sampler for the sampling of acidic and polar herbicides. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-7757-0.
Sánchez-Bayo F, Hyne RV, Desseille KL. An amperometric method for the detection of amitrole, glyphosate and its aminomethyl-phosphonic acid metabolite in environmental waters using passive samplers. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;675:125–31. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2010.07.013.
Fauvelle V, Nhu-Trang TT, Feret T, Madarassou K, Randon J, Mazzella N. Evaluation of TiO2 as a binding phase for the passive sampling of glyphosate and AMPA in an aquatic environment. Anal Chem. 2015. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00194.
Puzio K, Claude B, Amalric L, Berho C, Grellet E, Bayoudh S, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymer dedicated to the extraction of glyphosate in natural waters. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1361:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.07.043.
Ibrahim I, Togola A, Gonzalez C. Polar organic chemical integrative sampler (POCIS) uptake rates for 17 polar pesticides and degradation products: laboratory calibration. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2013. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1284-3.
Huckins JN, Booij K, Petty JD. Monitors of organic chemicals in the environment. Semipermeable membrane devices. New York: Springer; 2006.
Belles A, Pardon P, Budzinski H. Development of an adapted version of polar organic chemical integrative samplers (POCIS-nylon). Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406:1099–110. doi:10.1007/s00216-013-7286-2.
Kaserzon SL, Hawker DW, Kennedy K, Bartkow M, Carter S, Booij K, et al. Characterisation and comparison of the uptake of ionisable and polar pesticides, pharmaceuticals and personal care products by POCIS and Chemcatchers. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2014. doi:10.1039/c4em00392f.
Soulier C. Présence et devenir des alkylphénols, de leurs dérivés et des composés pharmaceutiques dans les effluents. Intérêt des échantillonneurs passifs. Thesis, University od Bordeaux 1. http://ori-oai.u-bordeaux1.fr/pdf/2012/SOULIER_CORALIE_2012.pdf.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the French National Research Agency (ANR) for its financial support of the ECOTECH 2011 ORIGAMI project ANR-11-ECOT-0003. H.M. Kluijver edited the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 180 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berho, C., Claude, B., Coisy, E. et al. Laboratory calibration of a POCIS-like sampler based on molecularly imprinted polymers for glyphosate and AMPA sampling in water. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 2029–2035 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-0150-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-0150-4