Abstract
Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry (MS) was used in an imaging mode to interrogate the lipid profiles of thin tissue sections of 11 sample pairs of human papillary renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and adjacent normal tissue and nine sample pairs of clear cell RCC and adjacent normal tissue. DESI-MS images showing the spatial distributions of particular glycerophospholipids (GPs) and free fatty acids in the negative ion mode were compared to serial tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Increased absolute intensities as well as changes in relative abundance were seen for particular compounds in the tumor regions of the samples. Multivariate statistical analysis using orthogonal projection to latent structures treated partial least square discriminate analysis (PLS-DA) was used for visualization and classification of the tissue pairs using the full mass spectra as predictors. PLS-DA successfully distinguished tumor from normal tissue for both papillary and clear cell RCC with misclassification rates obtained from the validation set of 14.3% and 7.8%, respectively. It was also used to distinguish papillary and clear cell RCC from each other and from the combined normal tissues with a reasonable misclassification rate of 23%, as determined from the validation set. Overall DESI-MS imaging combined with multivariate statistical analysis shows promise as a molecular pathology technique for diagnosing cancerous and normal tissue on the basis of GP profiles.

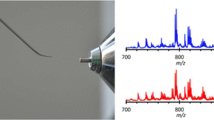
Molecular disease diagnostics by DESI without sample preparation. a Good information is obtained by mapping the distribution of individual compounds in the tissue (e.g., PI(18:0/20:4). b Even better discrimination between tumor and healthy tissue is achieved using PLS-DA to consider all the data after having established through a training set of samples the features that correlate with disease as recognized by standard H&E stain pathological examination





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athar M (2002) Oxidative stress and experimental carcinogenesis. Indian J Exp Biol 40(6):656–667
Sakai K, Okuyama H, Yura J, Takeyama H, Shinagawa N, Tsuruga N, Kato K, Miura K, Kawase K, Tsujimura T, Naruse T, Koike A (1992) Composition and turnover of phospholipids and neutral lipids in human breast-cancer and reference tissues. Carcinogenesis 13(4):579–584
Shimma S, Sugiura Y, Hayasaka T, Hoshikawa Y, Noda T, Setou M (2007) MALDI-based imaging mass spectrometry revealed abnormal distribution of phospholipids in colon cancer liver metastasis. J Chromatogr B: AnalTechnol Biomed Life Sci 855(1):98–103
Aboagye EO, Bhujwalla ZM (1999) Malignant transformation alters membrane choline phospholipid metabolism of human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 59(1):80–84
Glunde K, Jie C, Bhujwalla ZM (2004) Molecular causes of the aberrant choline phospholipid metabolism in breast cancer. Cancer Res 64(12):4270–4276
Alonso T, Morgan RO, Marvizon JC, Zarbl H, Santos E (1988) Malignant transformation by ras and other oncogenes produces common alterations in inositol phospholipid signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85(12):4271–4275
Alonso T, Santos E (1990) Increased intracellular glycerophosphoinositol is a biochemical marker for transformation by membrane-associated and cytoplasmic oncogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 171(1):14–19
Valitutti S, Cucchi P, Colletta G, Di Filippo C, Corda D (1991) Transformation by the k-ras oncogene correlates with increases in phospholipase a2 activity, glycerophosphoinositol production and phosphoinositide synthesis in thyroid cells. Cell Signal 3(4):321–332
Yamaji-Hasegawa A, Tsujimoto M (2006) Asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in biomembranes. Biol Pharm Bull 29(8):1547–1553
Utsugi T, Schroit AJ, Connor J, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ (1991) Elevated expression of phosphatidylserine in the outer-membrane leaflet of human tumor-cells and recognition by activated human blood monocytes. Cancer Res 51(11):3062–3066
Zwaal RFA, Comfurius P, Bevers EM (2005) Surface exposure of phosphatidylserine in pathological cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 62(9):971–988
Chaurio RA, Janko C, Munoz LE, Frey B, Herrmann M, Gaipl US (2009) Phospholipids: key players in apoptosis and immune regulation. Molecules 14(12):4892–4914
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K, Arihiro K (2006) Tumor-driven evolution of immunosuppressive networks during malignant progression. Cancer Res 66(11):5527–5536
Sandra F, Esposti MD, Ndebele K, Gona P, Knight D, Rosenquist M, Khosravi-Far R (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand alters mitochondrial membrane lipids. Cancer Res 65(18):8286–8297
Mollinedo F, Gajate C, Martin-Santamaria S, Gago F (2004) Et-18-och3 (edelfosine): a selective antitumour lipid targeting apoptosis through intracellular activation of fas/cd95 death receptor. Curr Med Chem 11(24):3163–3184
Wiseman JM, Ifa DR, Song Q, Cooks RG (2006) Tissue imaging at atmospheric pressure using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry. Angew Chem Int Ed 45(43):7188–7192
Chaurand P, Cornett DS, Caprioli RM (2006) Molecular imaging of thin mammalian tissue sections by mass spectrometry. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17(4):431–436
Cornett DS, Reyzer ML, Chaurand P, Caprioli RM (2007) MALDI imaging mass spectrometry: molecular snapshots of biochemical systems. Nat Meth 4(10):828–833
Xu BJ, Gonzalez AL, Kikuchi T, Yanagisawa K, Massion PP, Wu H, Mason SE, Olson SJ, Shyr Y, Carbone DP, Caprioli RM (2008) MALDI-MS derived prognostic protein markers for resected non-small cell lung cancer. Proteomics Clin Appl 2(10–11):1508–1517
Doroshenko VM, Laiko VV, Taranenko NI, Berkout VD, Lee HS (2002) Recent developments in atmospheric pressure MALDI mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom 221(1):39–58
Fletcher JS, Lockyer NP, Vaidyanathan S, Vickerman JC (2007) TOF-SIMS 3D biomolecular imaging of Xenopus laevis oocytes using buckminsterfullerene (c-60) primary ions. Anal Chem 79(6):2199–2206
Winograd N (2003) Prospects for imaging TOF-SIMS: from fundamentals to biotechnology. Appl Surf Sci 203:13–19
Nemes P, Barton AA, Vertes A (2009) Three-dimensional imaging of metabolites in tissues under ambient conditions by laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81(16):6668–6675
Nemes P, Barton AA, Li Y, Vertes A (2008) Ambient molecular imaging and depth profiling of live tissue by infrared laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 80(12):4575–4582
Nemes P, Vertes A (2007) Laser ablation electrospray ionization for atmospheric pressure, in vivo, and imaging mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 79(21):8098–8106
Kertesz V, Ford MJ, Van Berkel GJ (2005) Automation of a surface sampling probe/electrospray mass spectrometry system. Anal Chem 77(22):7183–7189
Shelley JT, Ray SJ, Hieftje GM (2008) Laser ablation coupled to a flowing atmospheric pressure afterglow for ambient mass spectral imaging. Anal Chem 80(21):8308–8313
Schafer KC, Denes J, Albrecht K, Szaniszlo T, Balog J, Skoumal R, Katona M, Toth M, Balogh L, Takats Z (2009) In vivo, in situ tissue analysis using rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(44):8240–8242
Takats Z, Wiseman JM, Gologan B, Cooks RG (2004) Mass spectrometry sampling under ambient conditions with desorption electrospray ionization. Science 306(5695):471–473
Dill AL, Ifa DR, Manicke NE, Zheng OY, Cooks RG (2009) Mass spectrometric imaging of lipids using desorption electrospray ionization. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 877(26):2883–2889
Kertesz V, Van Berkel GJ (2008) Improved imaging resolution in desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22(17):2639–2644
Wiseman JM, Puolitaival SM, Takats Z, Cooks RG, Caprioli R (2005) Mass spectrometric profiling of intact biological tissue by using desorption electrospray ionization. Angew Chem Int Ed 44(43):7094–7097
Dill AL, Ifa DR, Manicke NE, Costa AB, Ramos-Vara JA, Knapp DW, Cooks RG (2009) Lipid profiles of canine invasive transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder and adjacent normal tissue by desorption electrospray ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81(21):8758–8764
Eberlin LS, Dill AL, Costa AB, Ifa DR, Cheng L, Masterson T, Koch M, Ratliff TL, Cooks RG (2010) Cholesterol sulfate imaging in human prostate cancer tissue by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 82(9):3430–3434
Eberlin LS, Dill AL, Golby AJ, Ligon KL, Wiseman JM, Cooks RG, Agar NYR (2010) Discrimination of human astrocytoma subtypes by lipid analysis using desorption electrospray ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(34):5953–5956
Cheng LA, Williamson SR, Zhang SB, MacLennan GT, Montironi R, Lopez-Beltran A (2010) Understanding the molecular genetics of renal cell neoplasia: implications for diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 10(6):843–864
Manicke NE, Kistler T, Ifa DR, Cooks RG, Ouyang Z (2009) High-throughput quantitative analysis by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 20(2):321–325
Eberlin LS, Ifa DR, Wu C, Cooks RG (2010) Three-dimensional visualization of mouse brain by lipid analysis using ambient ionization mass spectrometry. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(5):873–876.
Ifa DR, Wiseman JM, Song QY, Cooks RG (2007) Development of capabilities for imaging mass spectrometry under ambient conditions with desorption electrospray ionization (DESI). Int J Mass Spectrom 259:8–15
Trygg J, Wold S (2002) Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J Chemom 16(3):119–128.
Team RDC (2009) R: a language and environment for statistical computing (trans: Book citations: Books without editor: E. Wingender GRiE, VCH, Weinheim, 1993, p. 215. Books with editor: T. D. In: Atwood JL, Davies JED, MacNicol DD, Vögtle F, Suslick KS (eds) Tullius in Comprehensive supramolecular chemistry, vol. 5, Pergamon, Oxford, 1996, pp 317–343.). Vienna, Austria
Wehrens RM, Mevik BH (2007) PLS: partial least squares regression (PLSR) and principal component regression (PCR) R package versiion 21-0 http://meviknet/work/software/plshtml
De Meyer T, Sinnaeve D, Van Gasse B, Tsiporkova E, Rietzschel ER, De Buyzere ML, Gillebert TC, Bekaert S, Martins JC, Van Criekinge W (2008) NMR-based characterization of metabolic alterations in hypertension using an adaptive, intelligent binning algorithm. Anal Chem 80(10):3783–3790
Pulfer M, Murphy RC (2003) Electrospray mass spectrometry of phospholipids. Mass Spectrom Rev 22(5):332–364
Manicke NE, Wiseman JM, Ifa DR, Cooks RG (2008) Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) of phospholipids and sphingolipids: ionization, adduct formation, and fragmentation. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19(4):531–543
Hsu FF, Turk J (2000) Characterization of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate, and phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry: a mechanistic study. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 11(11):986–999
Hsu FF, Turk J (2008) Structural characterization of unsaturated glycerophospholipids by multiple-stage linear ion-trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19(11):1681–1691
Hsu FF, Turk J (2005) Studies on phosphatidylserine by tandem quadrupole and multiple stage quadrupole ion-trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization: structural characterization and the fragmentation processes. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 16(9):1510–1522
Murphy RC (1993) Mass spectrometry of lipids. Plenum, New York
Nefliu M, Smith JN, Venter A, Cooks RG (2008) Internal energy distributions in desorption electrospray ionization (DESI). J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19(3):420–427
Clarke R, Ressom HW, Wang AT, Xuan JH, Liu MC, Gehan EA, Wang Y (2008) The properties of high-dimensional data spaces: implications for exploring gene and protein expression data. Nat Rev Cancer 8(1):37–49
Lechevallier E (2007) Core biopsy of solid renal masses under ct guidance. Eur Urol Suppl 6(8):540–543
Acknowledgments
We thank the Purdue University Center for Cancer Research and its director, Timothy Ratliff, for assistance in obtaining the human kidney cancer samples. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (Grant 1 R21 EB00 9459-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 869 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dill, A.L., Eberlin, L.S., Zheng, C. et al. Multivariate statistical differentiation of renal cell carcinomas based on lipidomic analysis by ambient ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 398, 2969–2978 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4259-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4259-6