Abstract
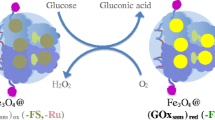
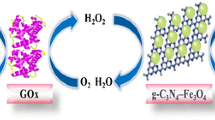
Immobilization of bioactive molecules on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles is of great interest, because the magnetic properties of these bioconjugates promise to greatly improve the delivery and recovery of biomolecules in biomedical applications. Here we present the preparation and functionalization of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles 20 nm in diameter and the successful covalent conjugation of the enzyme glucose oxidase to the amino-modified nanoparticle surface. Functionalization of the magnetic nanoparticle surface with amino groups greatly increased the amount and activity of the immobilized enzyme compared with immobilization procedures involving physical adsorption. The enzymatic activity of the glucose oxidase-coated magnetic nanoparticles was investigated by monitoring oxygen consumption during the enzymatic oxidation of glucose using a ruthenium phenanthroline fluorescent complex for oxygen sensing. The glucose oxidase-coated magnetite nanoparticles could function as nanometric glucose sensors in glucose solutions of concentrations up to 20 mmol L−1. Immobilization of glucose oxidase on the nanoparticles also increased the stability of the enzyme. When stored at 4°C the nanoparticle suspensions maintained their bioactivity for up to 3 months.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R167–R181
Tartaj P, Morales MP, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, Gonzalez-Carreno T, Serra CJ (2003) The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R182–R197
3. Gu H, Ho P-L, Tsang KWT, Yu C-W, Xu B (2003) Using biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles to capture gram-negative bacteria at an ultra-low concentration. Chem Commun 1966–1967
Bucak S, Jones DA, Laibinis PE, Hatton A (2003) Protein separations using colloidal magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol Prog 19:477–484
Liao M-H, Chen D-H (2002) Preparation and characterization of a novel magnetic nano-adsorbent. J Mater Chem 12:3654–3659
Tong XD, Xue B, Sun Y (2001) A novel magnetic affinity support for protein adsorption and purification. Biotechnol Prog 17:134–139
Mine Y (1997) Separation of Salmonella enteritidis from experimentally contaminated liquid eggs using a hen IgY immobilized immunomagnetic separation system. J Agric Food Chem 45:3723–3727
Ugelstad J, Prestvik WS, Stenstad P, Kilaas L, Kvalheim G (1998) Selective cell separation with monosized magnetizable polymer beads. In: Nowak H (ed) Magnetism in medicine. Wiley-VCH, Berlin, pp 471–488
Sonti SV, Bose A (1995) Cell separation using protein A-coated magnetic nanoclusters. J Coll Interface Sci 170:575–585
Hancock JP, Kemshead JT (1993) A rapid and highly selective approach to cell separations using an immunomagnetic colloid. J Immunol Methods 164:51–60
Dyal A, Loos K, Noto M, Chang SW, Spagnoli C, Shafi KVPM, Ulman A, Cowman M, Gross RA (2003) Activity of candida rugosa lipase immobilized on γ-Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125:1684–1685
Huang S-H, Liao M-H, Chen D-H (2003) Direct binding and characterization of Lipase onto magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol Prog 19:1095–1100
Chen D-H, Liao M-H (2002) Preparation and characterization of YADH-bound magnetic nanoparticles. J Mol Catal B Enzyme 16:283–291
Wang SQ, Yoshimoto M, Fukunaga K, Nakao K (2003) Optimal covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase-containing liposomes for highly stable biocatalyst in bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 83:444–453
Yang XH, Hua L, Gong HQ, Tan SN (2003) Covalent immobilization of an enzyme (glucose oxidase) onto a carbon sol-gel silicate composite surface as a biosensing platform. Anal Chim Acta 478:67–75
16. Ying L, Kang ET, Neoh KG (2002) Covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase on microporous membranes prepared from poly(vinylidene fluoride) with grafted poly(acrylic acid) side chains. J Membr Sci 208:361–374
Shimomura M, Kojima N, Oshima K, Yamauchi T, Miyauchi S (2001) Covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase on film prepared by electrochemical copolymerization of thiophene-3-acetic acid and 3-methylthiophene for glucose sensing. Polym J 33:629–631
Bautista FM, Campelo JM, Garcia A, Jurado A, Luna D, Marinas JM, Romero AA (2001) Properties of a glucose oxidase covalently immobilized on amorphous AlPO4 support. J Mol Catal B-Enzyme 11:567–577
Ramanathan K, Pandey SS, Kumar R, Gulati A, Surya A, Murthy N, Malhotra BD (2000) Covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase to Poly(O-Amino benzoic acid) for application to glucose biosensor. J Appl Polym Sci 78:662–667
Zhang Y-Q, Zhu J, Gu R-A (1999) Improved biosensor for glucose based on glucose oxidase-immobilized silk fibroin membrane. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 75:215–233
Li ZF, Kang ET, Neoh KG, Tan KL (1998) Covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase on the surface of polyaniline films graft copolymerized with acrylic acid. Biomaterials 19:45–53
Kojima K, Yamauchi T, Shimomura M, Miyauchi S (1998) Covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase on poly[1-(2-carboxyethyl)pyrrole] film for glucose sensing. Polymer 39:2079–2082
Suye S, Kumon Y, Ishigaki A (1998) Immobilization of glucose oxidase on poly-(l-lysine)-modified polycarbonate membrane. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 27:245–248
Shimomura M, Kikuchi H, Yamauchi T (1996) Covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase on magnetic nanoparticles via graft polymerization of acrylic acid. J M S Pure Appl Chem A33:1687–1697
Fang M, Grant PS, McShane MJ, Sukhorukov GB, Golub VO, Lvov YM (2002) Magnetic bio/nanoreactor with multilayer shells of glucose oxidase and inorganic nanoparticles. Langmuir 18:6338–6344
Xu H, Aylott JW, Kopelman R (2002) Fluorescent nano-PEBBLE sensors designed for intracellular glucose imaging. Analyst 127:1471–1477
Wang F-H, Yoshitake T, Kim DK, Muhammed M, Bjelke O, Kehr J (2003) Determination of conjugation efficiency of antibodies and proteins to the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J Nanoparticle Res 5:137–146
Tedesco AC, Oliveira DM, Lacava ZGM, Azevedo RB, Lima ECD, Gansau C, Buske N, Morais PC (2003) Determination of binding constant Kb of biocompatible, ferrite-based magnetic fluids to serum albumin. J Appl Phys 93:6704–6706
Nishimura K, Hasegawa M, Ogura Y, Nishi T, Kataoka K, Handa H (2002) 4°C preparation of ferrite nanoparticles having protein molecules immobilized in their surfaces. J Appl Phys 91:8555–8556
Liao M-H, Chen D-H (2002) Characteristics of magnetic nanoparticles-bound YADH in water/AOT/isooctane microemulsions. J Mol Catal B Enzyme 18:81–87
Hyeon T, Lee SS, Park J, Chung Y, Na HB (2001) Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse maghemite nanocrystallites without a size-selection process. J Am Chem Soc 123:12798–12801
Sun S, Zeng H (2002) Size-controlled synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124:8204–8205
Caruntu D, Remond Y, Chou NH, Jun M-J, Caruntu G, He J, Goloverda G, O‘Connor C, Kolesnichenko V (2002) Reactivity of 3d transition metal cations in diethylene glycol solutions. Synthesis of transition metal ferrites with the structure of discrete nanoparticles complexed with long-chain carboxylate anions. Inorg Chem 41:6137–6146
Tada M, Hatanaka S, Sanbonsugi H, Matsushita N, Abe M (2003) Method for synthesizing ferrite nanoparticles 30 nm in diameter on neutral pH condition for biomedical applications. J Appl Phys 93:7566–7568
Ji J, Rosenzweig N, Jones I, Rosensweig Z (2001) Molecular oxygen-sensitive fluorescent lipobeads for intracellular oxygen measurements in murine macrophages. Anal Chem 73:3521–3527
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Brian Cushing and Professor Weilie Zhou for their assistance in the X-ray diffraction and TEM measurements. This work was supported by DARPA Grant no. MDA -972-03-C-0100 and by NSF Grant no. CHE-0314027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi, L.M., Quach, A.D. & Rosenzweig, Z. Glucose oxidase–magnetite nanoparticle bioconjugate for glucose sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 380, 606–613 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2770-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2770-3