Abstract
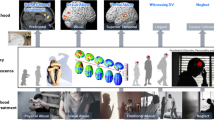
Recently, there has been a surge of interest in the possibility that microbial communities inhabiting the human gut could affect cognitive development and increase risk for mental illness via the “microbiome-gut-brain axis.” Infancy likely represents a critical period for the establishment of these relationships, as it is the most dynamic stage of postnatal brain development and a key period in the maturation of the microbiome. Indeed, recent reports indicate that characteristics of the infant gut microbiome are associated with both temperament and cognitive performance. The neural circuits underlying these relationships have not yet been delineated. To address this gap, resting-state fMRI scans were acquired from 39 1-year-old human infants who had provided fecal samples for identification and relative quantification of bacterial taxa. Measures of alpha diversity were generated and tested for associations with measures of functional connectivity. Primary analyses focused on the amygdala as manipulation of the gut microbiota in animal models alters the structure and neurochemistry of this brain region. Secondary analyses explored functional connectivity of nine canonical resting-state functional networks. Alpha diversity was significantly associated with functional connectivity between the amygdala and thalamus and between the anterior cingulate cortex and anterior insula. These regions play an important role in processing/responding to threat. Alpha diversity was also associated with functional connectivity between the supplementary motor area (SMA, representing the sensorimotor network) and the inferior parietal lobule (IPL). Importantly, SMA-IPL connectivity also related to cognitive outcomes at 2 years of age, suggesting a potential pathway linking gut microbiome diversity and cognitive outcomes during infancy. These results provide exciting new insights into the gut-brain axis during early human development and should stimulate further studies into whether microbiome-associated changes in brain circuitry influence later risk for psychopathology.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs R (2010) What does the amygdala contribute to social cognition? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1191:42–61
Alcauter S, Lin W, Smith JK, Goldman BD, Reznick JS, Gilmore JH, Gao W (2014a) Frequency of spontaneous BOLD signal shifts during infancy and correlates with cognitive performance. Dev Cogn Neurosci 12C:40–50
Alcauter S, Lin W, Smith JK, Short SJ, Goldman BD, Reznick JS, Gilmore JH, Gao W (2014b) Development of thalamocortical connectivity during infancy and its cognitive correlations. J Neurosci 34:9067–9075
Amaral DG (2003) The amygdala, social behavior, and danger detection. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1000:337–347
Baas D, Aleman A, Kahn RS (2004) Lateralization of amygdala activation: a systematic review of functional neuroimaging studies. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 45:96–103
Backhed F et al (2015) Dynamics and stabilization of the human gut microbiome during the first year of life. Cell Host Microbe 17:852
Banks SJ, Eddy KT, Angstadt M, Nathan PJ, Phan KL (2007) Amygdala-frontal connectivity during emotion regulation. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 2:303–312
Bercik P, Denou E, Collins J, Jackson W, Lu J, Jury J, Deng Y, Blennerhassett P, Macri J, McCoy KD, Verdu EF, Collins SM (2011) The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 141:599–609 609 e591–593, 609.e3
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34:537–541
Canteras NS, Resstel LB, Bertoglio LJ, Carobrez Ade P, Guimaraes FS (2010) Neuroanatomy of anxiety. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 2:77–96
Carabotti M, Scirocco A, Maselli MA, Severi C (2015) The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann Gastroenterol 28:203–209
Carlson AL, Xia K, Azcarate-Peril MA, Goldman BD, Ahn M, Styner MA, Thompson AL, Geng X, Gilmore JH, Knickmeyer RC (2018) Infant gut microbiome associated with cognitive development. Biol Psychiatry 83:148–159
Catani M, ffytche DH (2005) The rises and falls of disconnection syndromes. Brain 128:2224–2239
Christian LM, Galley JD, Hade EM, Schoppe-Sullivan S, Kamp Dush C, Bailey MT (2015) Gut microbiome composition is associated with temperament during early childhood. Brain Behav Immun 45:118–127
Clarke G, Grenham S, Scully P, Fitzgerald P, Moloney RD, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2013) The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol Psychiatry 18:666–673
Degnan KA, Fox NA (2007) Behavioral inhibition and anxiety disorders: multiple levels of a resilience process. Dev Psychopathol 19:729–746
Desbonnet L, Garrett L, Clarke G, Kiely B, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2010) Effects of the probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis in the maternal separation model of depression. Neuroscience 170:1179–1188
Diaz Heijtz R, Wang S, Anuar F, Qian Y, Bjorkholm B, Samuelsson A, Hibberd ML, Forssberg H, Pettersson S (2011) Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:3047–3052
Duval ER, Javanbakht A, Liberzon I (2015) Neural circuits in anxiety and stress disorders: a focused review. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:115–126
Eklund A, Nichols TE, Knutsson H (2016) Cluster failure: why fMRI inferences for spatial extent have inflated false-positive rates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:7900–7905
Fransson P, Aden U, Blennow M, Lagercrantz H (2011) The functional architecture of the infant brain as revealed by resting-state fMRI. Cereb Cortex 21:145–154
Gao W, Lin W, Grewen K, Gilmore JH (2016) Functional connectivity of the infant human brain: plastic and modifiable. Neuroscientist
Gao W, Alcauter S, Smith J, Gilmore J, Lin W (2014b) Development of human brain cortical network architecture during infancy. Brain Struct Funct. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0710-3
Gao W, Zhu H, Giovanello KS, Smith JK, Shen D, Gilmore JH, Lin W (2009) Evidence on the emergence of the brain’s default network from 2-week-old to 2-year-old healthy pediatric subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:6790–6795
Gao W, Alcauter S, Elton A, Hernandez-Castillo CR, Smith JK, Ramirez J, Lin W (2014a) Functional network development during the first year: relative sequence and socioeconomic correlations. Cereb Cortex
Gao W, Grewen K, Knickmeyer RC, Qiu A, Salzwedel A, Lin W, Gilmore JH (2018) A review on neuroimaging studies of genetic and environmental influences on early brain development. NeuroImage
Gartstein MA, Bridgett DJ, Rothbart MK, Robertson C, Iddins E, Ramsay K, Schlect S (2010) A latent growth examination of fear development in infancy: contributions of maternal depression and the risk for toddler anxiety. Dev Psychol 46:651–668
Gilmore JH, Knickmeyer RC, Gao W (2018) Imaging structural and functional brain development in early childhood. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:123–137
Gilmore JH, Schmitt JE, Knickmeyer RC, Smith JK, Lin W, Styner M, Gerig G, Neale MC (2010) Genetic and environmental contributions to neonatal brain structure: a twin study. Hum Brain Mapp 31:1174–1182
Gilmore JH, Lin W, Prastawa MW, Looney CB, Vetsa YS, Knickmeyer RC, Evans DD, Smith JK, Hamer RM, Lieberman JA, Gerig G (2007) Regional gray matter growth, sexual dimorphism, and cerebral asymmetry in the neonatal brain. J Neurosci 27:1255–1260
Grewen K, Salzwedel AP, Gao W (2015) Functional connectivity disruption in neonates with prenatal marijuana exposure. Front Hum Neurosci 9:601
Hirshfeld-Becker DR, Micco J, Henin A, Bloomfield A, Biederman J, Rosenbaum J (2008) Behavioral inhibition. Depress Anxiet 25:357–367
Hoban AE, Stilling RM, Ryan FJ, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Claesson MJ, Clarke G, Cryan JF (2016) Regulation of prefrontal cortex myelination by the microbiota. Transl Psychiatry 6:e774
Jessen S, Grossmann T (2016) The developmental emergence of unconscious fear processing from eyes during infancy. J Exp Child Psychol 142:334–343
Jones E (2000) The thalamus. Cambridge University, Cambridge
Kalisch R, Gerlicher AM (2014) Making a mountain out of a molehill: on the role of the rostral dorsal anterior cingulate and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex in conscious threat appraisal, catastrophizing, and worrying. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 42:1–8
Klumpp H, Angstadt M, Phan KL (2012) Insula reactivity and connectivity to anterior cingulate cortex when processing threat in generalized social anxiety disorder. Biol Psychol 89:273–276
Knickmeyer RC, Xia K, Lu Z, Ahn M, Jha SC, Zou F, Zhu H, Styner M, Gilmore JH (2017) Impact of demographic and obstetric factors on infant brain volumes: a population neuroscience study. Cereb Cortex 27:5616–5625
Knickmeyer RC, Gouttard S, Kang C, Evans D, Wilber K, Smith JK, Hamer RM, Lin W, Gerig G, Gilmore JH (2008) A structural MRI study of human brain development from birth to 2 years. J Neurosci 28:12176–12182
Koenig JE, Spor A, Scalfone N, Fricker AD, Stombaugh J, Knight R, Angenent LT, Ley RE (2011) Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(Suppl 1):4578–4585
Li Y, Li S, Wei C, Wang H, Sui N, Kirouac GJ (2010) Changes in emotional behavior produced by orexin microinjections in the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 95:121–128
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228–8235
Lozupone C, Hamady M, Knight R (2006) UniFrac--an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinform 7:371
Luczynski P, Whelan SO, O’Sullivan C, Clarke G, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2016) Adult microbiota-deficient mice have distinct dendritic morphological changes: differential effects in the amygdala and hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 44:2654–2666
Masten AS, Cicchetti D (2010) Developmental cascades. Dev Psychopathol 22:491–495
Mullen EM (1995) Mullen scales of early learning. American Guidance Service, Inc, Circle Pines, MN
Neufeld KA, Kang N, Bienenstock J, Foster JA (2011a) Effects of intestinal microbiota on anxiety-like behavior. Commun Integr Biol 4:492–494
Neufeld KM, Kang N, Bienenstock J, Foster JA (2011b) Reduced anxiety-like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ-free mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil 23:255–264 e119
Papez JW (1995) A proposed mechanism of emotion. 1937. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 7:103–112
Penzo MA, Robert V, Tucciarone J, De Bundel D, Wang M, Van Aelst L, Darvas M, Parada LF, Palmiter RD, He M, Huang ZJ, Li B (2015) The paraventricular thalamus controls a central amygdala fear circuit. Nature 519:455–459
Ressler KJ (2010) Amygdala activity, fear, and anxiety: modulation by stress. Biol Psychiatry 67:1117–1119
Rogers GB, Keating DJ, Young RL, Wong ML, Licinio J, Wesselingh S (2016) From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: mechanisms and pathways. Mol Psychiatry 21:738–748
Salzwedel AP, Grewen KM, Vachet C, Gerig G, Lin W, Gao W (2015) Prenatal drug exposure affects neonatal brain functional connectivity. J Neurosci 35:5860–5869
Salzwedel AP, Stephens RL, Goldman BD, Lin W, Gilmore JH, Gao W (2018) Development of amygdala functional connectivity during infancy and its relationship with 4-year behavioral outcomes. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging
Shi F, Yap PT, Wu G, Jia H, Gilmore JH, Lin W, Shen D (2011) Infant brain atlases from neonates to 1- and 2-year-olds. PLoS One 6:e18746
Shin LM, Liberzon I (2010) The neurocircuitry of fear, stress, and anxiety disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:169–191
Singh-Curry V, Husain M (2009) The functional role of the inferior parietal lobe in the dorsal and ventral stream dichotomy. Neuropsychologia 47:1434–1448
Smith SM, Fox PT, Miller KL, Glahn DC, Fox PM, Mackay CE, Filippini N, Watkins KE, Toro R, Laird AR, Beckmann CF (2009) Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13040–13045
Smyser CD, Inder TE, Shimony JS, Hill JE, Degnan AJ, Snyder AZ, Neil JJ (2010) Longitudinal analysis of neural network development in preterm infants. Cereb Cortex 20:2852–2862
Stilling RM, Ryan FJ, Hoban AE, Shanahan F, Clarke G, Claesson MJ, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2015) Microbes & neurodevelopment--absence of microbiota during early life increases activity-related transcriptional pathways in the amygdala. Brain Behav Immun 50:209–220
Wagner G, Koch K, Reichenbach JR, Sauer H, Schlosser RG (2006) The special involvement of the rostrolateral prefrontal cortex in planning abilities: an event-related fMRI study with the Tower of London paradigm. Neuropsychologia 44:2337–2347
Acknowledgements
Jennifer Prater was the lead study coordinator with assistance from Dianne Evans and Wendy Neuheimer. We are grateful to the research assistants collecting 2-year cognitive data: Margaret Hamilton Fox, Mallory Turner, Margo Williams, Haley Parrish Black, and Emma Brink. Joe Blocher and Rachel Steiner at the Neuro Image Research and Analysis Laboratories provided image processing support.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (R01DA042988, R01DA043678, R21NS088975, R21DA043171, R03DA036645 to WG; R01MH070890 and R01HD053000 to JHG; R01 MH092335 and R33MH104330 to RKS; T32 NS007432 to ALC) and Cedars-Sinai Precision Medicine Initiative Award and institutional support to WG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
RCK is a co-investigator and WG is a consultant on a grant sponsored by Nestle/Wyeth (RDNN201704/4520562240); RCK has also received travel support to present at the 7th Annual Wyeth Nutrition Science Center Global Summit. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to a Special Issue on Microbiome in Psychiatry & Psychopharmacology
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, W., Salzwedel, A.P., Carlson, A.L. et al. Gut microbiome and brain functional connectivity in infants-a preliminary study focusing on the amygdala. Psychopharmacology 236, 1641–1651 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5161-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5161-8