Abstract
Background and rationale
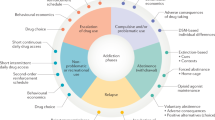
An enormous amount of resources has been devoted to the development of pharmacotherapies for drug addiction, with relatively little or no long-term success reported. The current review argues that a successful drug addiction treatment program will likely be one that focuses on both the neural mechanisms and the environmental contingencies that mediate drug use. Further, because the neural mechanisms and environmental factors that support abstinence in humans are similar in laboratory animals, several animal models of abstinence and relapse have been developed. Thus, this review also compares the similarities in the mechanisms that lead to abstinence between animals and humans.
Objective
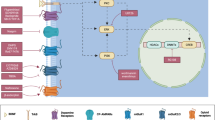
We evaluate the construct and face validities of the behavioral strategies that help support human drug abstinence. Further, we crucially evaluate animal models by assessing their validity and utility in addressing human behavior that leads to long-term abstinence.
Conclusions
We found that the behavioral strategies with the greatest likelihood of supporting long-term abstinence are those that are carried out in drug addicts’ natural setting(s) and while drug is readily available. Further, the behavioral strategies that may be most successful in supporting abstinence in humans are those that employ both positive consequences for abstinent related behavior and negative consequences for continued drug seeking or taking. Moreover, the animal models of abstinence and relapse that more closely represent the factors that support long-term abstinence in humans are those that limit their use of extinction or forced abstinence and present negative consequences for drug seeking and taking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SH (2005) Imbalance between drug and non-drug reward availability: a major risk factor for addiction. Eur J Pharmacol 526:9–20
American Psychiatric Association (eds) (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5® Am Psychiatric Pub
Bachteler D, Economidou D, Danysz W, Ciccocioppo R, Spanagel R (2005) The effects of acamprosate and neramexane on cue-induced reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior in rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1104–1110
Barnea-Ygael N, Yadid G, Yaka R, Ben-Shahar O, Zangen A (2012) Cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in the rat “conflict”: effect of prolonged home-cage confinement. Psychopharmacology 219:875–883
Belin D, Balado E, Piazza PV, Deroche-Gamonet V (2009) Pattern of intake and drug craving predict the development of cocaine addiction-like behavior in rats. Biol Psychiatry 65:863–868
Bevins RA, Besheer J (2005) Novelty reward as a measure of anhedonia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:707–714
Bordnick PS, Elkins RL, Orr TE, Walters P, Thyer BA (2004) Evaluating the relative effectiveness of three aversion therapies designed to reduce craving among cocaine abusers. Behav Interv 19:1–24
Bossert JM, Liu SY, Lu L, Shaham Y (2004) A role of ventral tegmental area glutamate in contextual cue-induced relapse to heroin seeking. J Neurosci 24:10726–10730
Bouton ME (2002) Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: sources of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biol Psychiatry 52:976–986
Bouton ME (2004) Context and behavioral processes in extinction. Learn Mem 11:485–494
Bouton ME, Bolles RC (1979) Contextual control of the extinction of conditioned fear. Learn Motiv 10:445–466
Bouton ME, Ricker ST (1994) Renewal of extinguished responding in a second context. Anim Learn Behav 22:317–324
Bouton ME, Swartzentruber D (1991) Sources of relapse after extinction in Pavlovian and instrumental learning. Clin Psychol Rev 11:123–140
Bouton ME, Todd TP, Vurbic D, Winterbauer NE (2011) Renewal after the extinction of free operant behavior. Learn Behav 39:57–67
Carroll ME (1993) The economic context of drug and non-drug reinforcers affects acquisition and maintenance of drug-reinforced behavior and withdrawal effects. Drug Alcohol Depend 33:201–210
Carroll ME, Boe IN (1982) Increased intravenous drug self-administration during deprivation of other reinforcers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:563–567
Carroll ME, Comer SD (1996) Animal models of relapse. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 4:11–18
Carroll KM, Onken LS (2005) Behavioral therapies for drug abuse. Am J Psychiatry 162:1452–1460
Carroll ME, Lac ST, Nygaard SL (1989) A concurrently available nondrug reinforcer prevents the acquisition or decreases the maintenance of cocaine reinforced behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 97:23–29
Chaudhri N, Sahuque LL, Janak PH (2008) Context-induced relapse of conditioned behavioral responding to ethanol cues in rats. Biol Psychiatry 64:203–210
Chauvet C, Lardeux V, Goldberg SR, Jaber M, Solinas M (2009) Environmental enrichment reduces cocaine seeking and reinstatement induced by cues and stress but not by cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2767–2778
Childress AR, McLellan AT, Ehrman R, O’Brien CP (1988) Classically conditioned responses in opioid and cocaine dependence: a role in relapse? NIDA Res Monogr 84:25–43
Childress AR, Hole AV, Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, McLellan AT, O’Brien CP (1993) Cue reactivity and cue reactivity interventions in drug dependence. NIDA Res Monogr 137(73):95
Ciccocioppo R, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2002) Effect of selective blockade of μ1 or δ opioid receptors on reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:391–399
Collins BN, Brandon TH (2002) Effects of extinction context and retrieval cues on alcohol cue reactivity among nonalcoholic drinkers. J Consult Clin Psychol 70:390–397
Conklin CA, Tiffany ST (2002) Applying extinction research and theory to cue-exposure addiction treatments. Addiction 97:155–167
Cooper A, Barnea-Ygael N, Levy D, Shaham Y, Zangen A (2007) A conflict rat model of cue-induced relapse to cocaine seeking. Psychopharmacology 194:117–125
Copemann CD, Shaw PL (1976) A behaviorally-oriented treatment program for drug addiction: a preliminary report. Am J Public Health 66:286–287
Cosgrove KP, Hunter RG, Carroll ME (2002) Wheel-running attentates intravenous cocaine self-administration in rats: sex differences. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:663–671
Crombag HS, Shaham Y (2002) Renewal of drug seeking by contextual cues after prolonged extinction in rats. Behav Neurosci 116:169–173
Crombag H, Bossert JM, Koya E, Shaham Y (2008) Context-induced relapse to drug seeking: a review. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:3233–3243
De Wit H, Stewart J (1983) Drug reinstatement of heroin-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 79:29–31
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004) Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305:1014–1017
Diergaarde L, De Vries W, Raasø H, Schoffelmeer AM, De Vries TJ (2008) Contextual renewal of nicotine seeking in rats and its suppression by the cannabinoid-1 receptor antagonist Rimonabant (SR141716A). Neuropharmacology 55:712–716
Economidou D, Pelloux Y, Robbins TW, Dalley JW, Everitt BJ (2009) High impulsivity predicts relapse to cocaine-seeking after punishment-induced abstinence. Biol Psychiatry 65:851–856
Epstein DH, Preston KL (2003) The reinstatement model and relapse prevention: a clinical perspective. Psychopharmacology 168:31–41
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006) Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacology 189:1–16
Falba T, Teng H, Sindelar JL, Gallo WT (2005) The effect of involuntary job loss on smoking intensity and relapse. Addiction 100:1330–1339
Feltenstein MW, See RE (2008) The neurocircuitry of addiction: an overview. Br J Pharmacol 154:261–274
Frawley PJ, Smith JW (1990) Chemical aversion therapy in the treatment of cocaine dependence as part of a multimodal treatment program: treatment outcome. J Subst Abuse Treat 7:21–29
Fuchs RA, Ramirez DR, Bell GH (2008) Nucleus accumbens shell and core involvement in drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 200:545–556
Grimm JW (2002) Effect of cocaine and sucrose withdrawal period on extinction behavior, cue-induced reinstatement, and protein levels of the dopamine transporter and tyrosine hydroxylase in limbic and cortical areas in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:379–388
Grimm JW, Hope BT, Wise RA, Shaham Y (2001) Incubation of cocaine craving after withdrawal. Nature 412:141–142
Grimm JW, Osincup D, Wells B, Manaois M, Fyall A (2008) Environmental enrichment attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of sucrose seeking in rats. Behav Pharmacol 19:777–785
Grimm JW, Weber R, Barnes J, Koerber J, Dorsey K, Glueck E (2013) Brief exposure to novel or enriched environments reduces sucrose cue-reactivity and consumption in rats after 1 or 30 days of forced abstinence from self-administration. PLoS ONE 8(e54164):1–9
Hall SM, Havassy BE, Wassermann DA (1990) Commitment to abstinence and acute stress in relapse to alcohol, opiates and nicotine. J Consult Clin Psychol 58:175–181
Haug NA, Svikis DS, DiClemente C (2004) Motivational enhancement therapy for nicotine dependence in methadone-maintained pregnant women. Psychol Addict Behav 18:289–292
Higgins ST, Budney AJ, Bickel WK, Foerg FE, Donham R (1994) Incentives improve outcome in outpatient behavioral treatment of cocaine dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:568–576
Higgins ST, Heil SH, Lussier JP (2004) Clinical implications of reinforcement as a determinant of substance use disorders. Annu Rev Psychol 55:431–461
Higgins ST, Budney AJ, Bickel WK, Hughes JR, Foerg F, Badger G (2005) Achieving cocaine abstinence with a behavioral approach. Am J Psychiatry 150:763–769
Jenkins TN, Warner LH, Warden CJ (1926) Standard apparatus for the study of animal motivation. J Comp Psychol 6:361–382
Kalant H (1977) Comparative aspects of tolerance to, and dependence on, alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates. In: Gross MM (ed) Alcohol intoxication and withdrawal. Plenum Press, New York, pp 169–186
Katz EC, Chutuape MA, Jones H, Jasinski DR, Fingerhood M, Stitzer M (2004) Abstinence incentive effects in a short-term outpatient detoxification program. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 12:262–268
Kearns DN, Weiss SJ (2007) Contextual renewal of cocaine seeking in rats and its attenuation by the conditioned effects of an alternative reinforcer. Drug Alcohol Depend 90:193–202
Kerkhof I, Vansteenwegen D, Baeyens F, Hermans D (2011) Counterconditioning: An effective technique for changing conditioned preferences. Exp Psych 58:31–38
Koob GF (2000) Neurobiology of addiction: toward the development of new therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 909:170–185
Koob GF, Lloyd GK, Mason BJ (2009) Development of pharmacotherapies for drug addiction: a Rosetta Stone approach. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:500–515
Kreek MJ, LaForge KS, Butelman E (2002) Pharmacotherapy of addictions. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:710–726
Leitenberg H, Rawson RA, Bath K (1970) Reinforcement of competing behavior during extinction. Science 169:301–303
Leitenberg H, Rawson RA, Mulick JA (1975) Extinction and reinforcement of alternative behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol 88:640–647
Lenoir M, Ahmed SH (2007) Supply of a nondrug substitute reduces escalated heroin consumption. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2272–2282
Lett BT, Grant VL, Byrne MJ, Koh MT (2000) Pairings of a distinctive chamber with the after effect of wheel running produce conditioned place preference. Appetite 34:87–94
Long JA, Volpp KG (2008) Patient opinions regarding ‘pay for performance for patients’. J Gen Intern Med 23:1647–1652
Lovibond PF, Dickinson A (1982) Counterconditioning of appetitive and defensive CRs in rabbits. J Comp Physiol Psychol 34:115–126
Lu L, Grimm JW, Hope BT, Shaham Y (2004) Incubation of cocaine craving after withdrawal: a review of preclinical data. Neuropharmacology 47:214–226
Lynch WJ, Piehl KB, Acosta G, Peterson AB, Hemby SE (2010) Aerobic exercise attenuates reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior and associated neuroadaptations in the prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 68:774–777
Marchant NJ, Li X, Shaham Y (2013) Recent developments in animal models of drug relapse. Curr Opin Neurobiol 453–476
Mattson BJ, Williams S, Rosenblatt JS, Morrell JI (2001) Comparison of two positive reinforcing stimuli: pups and cocaine throughout the postpartum period. Behav Neurosci 115:683–694
McLellan AT, Childress AR, Ehrman R, O’Brien CP (1986) Extinguishing conditioned responses during opiate dependence treatment: turning extinguishing laboratory findings into clinical procedures. J Subst Abuse Treat 3:33–40
Meil WM, See RE (1996) Conditioned cued recovery of responding following prolonged withdrawal from self-administered cocaine in rats: an animal model of relapse. Behav Pharmacol 7:754–763
Neisewander JL, Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Tran-Nguyen LT, Palmer A, Marshall JF (2000) Fos protein expression and cocaine-seeking behavior in rats after exposure to a cocaine self-administration environment. J Neurosci 20:798–805
O’Brien CP (2005) Anticraving medications for relapse prevention: a possible new class of psychoactive medications. Am J Psychiatry 162:1423–1431
O’Brien CP, Childress AR, McLellan AT, Woody GE, Maany I (1988) Pharmacological and behavioral treatments of cocaine dependence: controlled studies. J Clin Psychiatry 49:17–22
Panksepp J, Nelson E, Bekkedal M (1997) Brain systems for the mediation of social separation-distress and social-reward. Evolutionary antecedents and neuropeptide intermediaries. Ann NY Acad Sci 807:78–100
Panlilio LV, Thorndike EB, Schindler CW (2003) Reinstatement of punishment-suppressed opioid self-administration in rats: an alternative model of relapse to drug abuse. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 168:229–235
Panlilio LV, Thorndike EB, Schindler CW (2005) Lorazepam reinstates punishment-suppressed remifentanil self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 179:374–382
Pavlov IP (1927) Conditioned reflexes. Oxford University Press, London
Peck CA, Bouton ME (1990) Context and performance in aversive-to-appetitive and appetitive-to-aversive transfer. Learn Motiv 21:1–31
Peck J, Wercberger R, Kariyeva E, Ranaldi R (2013) Cue-induced resumption of heroin and cocaine seeking in rats using a conflict model of abstinence and relapse. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 228(4):651–658
Pelloux Y, Everitt BJ, Dickinson A (2007) Compulsive drug seeking by rats under punishment: effects of drug taking history. Psychopharmacology 194:127–137
Piazza PV, Deroche-Gamonet V (2013) A multistep general theory of transition to addiction. Psychopharmacology 3:387–413
Pickens CL, Airavaara M, Theberge F, Fanous S, Hope BT, Shaham Y (2011) Neurobiology of incubation of drug craving. Trends Neurosci 34:411–420
Podlesnik CA, Jimenez-Gomez C, Shahan TA (2006) Resurgence of alcohol seeking produced by discontinuing non-drug reinforcement as an animal model of drug relapse. Behav Pharmacol 17:369–374
Quick SL, Pyszczynski AD, Colston KA, Shahan TA (2011) Loss of alternative non-drug reinforcement induces relapse of cocaine-seeking in rats: role of dopamine D1 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:1015–1020
Ranaldi R, Kest K, Zellner M, Hachimine-Semperbrom P (2011) Environmental enrichment, administered after establishment of cocaine self-administration, reduces lever pressing in extinction and during a cocaine context renewal test. Behav Pharmacol 22:347–353
Reynolds GS (1961) Contrast, generalization, and the process of discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav 4:289–294
Rodefer JS, Carroll ME (1996) Progressive ratio and behavioral economic evaluation of the reinforcing efficacy of orally delivered phencyclidine and ethanol in monkeys: effects of feeding conditions. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 128:265–273
Rose JE, Levin ED (1991) Inter-relationships between conditioned and primary reinforcement in the maintenance of cigarette smoking. Br J Addict 86:605–609
Saunders BT, Yager LM, Robinson TE (2013) Cue-evoked cocaine “craving”: role of dopamine in the accumbens core. J Neurosci 33:13989–14000
Schnabel J (2009) Neuroscience: rethinking rehab. Nature 458:25–27
Schottenfeld RS, Pantalon MV, Chawarski MC, Makes J (2000) Community reinforcement approach for combined opioid and cocaine dependence. Patterns of engagement in alternate activities. J Subst Abuse Treat 18:255–261
Schottenfeld RS, Chawarski MC, Pakes JR, Pantalon MV, Carroll KM, Kosten TR (2005) Methadone versus buprenorphine with contingency management or performance feedback for cocaine and opioid dependence. Am J Psychiatry 162:340–349
Setlow B (2008) Undoing cocaine’s consequences on behavior and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16829–16830
Shaham Y, Miczek KA (2003) Reinstatement-toward a model of relapse. Psychopharmacology 168:1–2
Shaham Y, Stewart J (1995) Stress reinstates heroin self-administration behavior in drug-free animals: an effect mimicking heroin, not withdrawal. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 119:334–341
Silverman K, Wong CJ, Higgins ST, Brooner RK, Montoya ID, Contoreggi C, Preston KL (1996) Increasing opiate abstinence through voucher-based reinforcement therapy. Drug Alcohol Depend 41:157–165
Sinha R, Shaham Y, Heilig M (2011) Translational and reverse translational research on the role of stress in drug craving and relapse. Psychopharmacology 218:69–82
Skinner BF (1938) The behavior of organisms: an experimental analysis. Appleton Century Crofts, New York
Smith SG, Davis WM (1974) Punishment of amphetamine and morphine self-administration behavior. Psychol Rec 24:477–480
Smith MA, Schmidt KT, Iordanou JC, Mustroph ML (2008) Aerobic exercise decreases the positive-reinforcing effects of cocaine. Drug Alcohol Depend 98:129–135
Solinas M, Thiriet N, Chauvet C, Jaber M (2010) Prevention and treatment of drug addiction by environmental enrichment. Prog Neurobiol 92:572–592
Stolerman I (1992) Drugs of abuse: behavioural principles, methods and terms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:170–176
Thewissen R, Snijders SJ, Havermans RC, van den Hout M, Jansen A (2006) Renewal of cue-elicited urge to smoke: implications for cue exposure treatment. Behav Res Ther 44:1441–1449
Thiel KJ, Sanabria F, Pentkowski NS, Neisewander JL (2009) Anti-craving effects of environmental enrichment. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:1151–1156
Todd TP, Winterbauer NE, Bouton ME (2012) Effects of the amount of acquisition and contextual generalization on the renewal of instrumental behavior after extinction. Learn Behav 40:145–157
Van Gucht D, Baeyens F, Vansteenwegen D, Hermans D, Beckers T (2010) Counterconditioning reduces cue-induced craving and actual cue-elicited consumption. Emotion 10:688–695
Vanderschuren LJ, Everitt BJ (2004) Drug seeking becomes compulsive after prolonged cocaine self-administration. Science 305:1017–1019
Weiss F, Maldonado-Vlaar CS, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Smit DL, Ben-Shahar O (2000) Control of cocaine-seeking behavior by drug associated stimuli in rats: effects on recovery of extinguished operant-responding and extracellular dopamine levels in amygdala and nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4321–4326
Wikler A (1973) Dynamics of drug dependence, implication of a conditioning theory for research and treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 28:611–616
Winterbauer NE, Bouton ME (2010) Mechanisms of resurgence of an extinguished instrumental behavior. J Exp Psychol 36:343–353
Wise RA (1988) The neurobiology of craving: implications for the understanding and treatment of addiction. J Abnorm Psychol 97:118–132
Zlebnik NE, Anker JJ, Gliddon LA, Carroll ME (2010) Reduction of extinction and reinstatement of cocaine seeking by wheel running in female rats. Psychopharmacology 209:113–125
Zlebnik NE, Anker JJ, Carroll ME (2012) Exercise to reduce the escalation of cocaine self-administration in adolescent and adult rats. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 224:387–400
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Bruce Brown and Dr. Bertram Ploog for critical comments on earlier versions of this paper.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peck, J.A., Ranaldi, R. Drug abstinence: exploring animal models and behavioral treatment strategies. Psychopharmacology 231, 2045–2058 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3517-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3517-2