Abstract
Rationale
Tiagabine is an anticonvulsant drug which may also have sleep-enhancing properties. It acts by inhibiting reuptake at the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporter (GAT-1).
Objectives
The aim of the study was to determine whether tiagabine acted as a discriminative stimulus and, if so, whether other GABAergic compounds would generalise to it.
Materials and methods
Rats were trained to discriminate tiagabine (30 mg/kg p.o.) from vehicle, and generalisation to drugs that modulate GABA was assessed.
Results
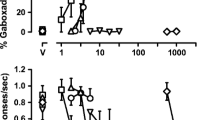
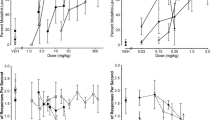
Gaboxadol (5–20 mg/kg p.o.), a selective extrasynaptic GABAA agonist, generalised to tiagabine, although the extent of the generalisation was inconclusive. Indiplon (1 mg/kg p.o.), a benzodiazepine-like hypnotic, also partially generalised to tiagabine, although zolpidem and S-zopiclone did not. Baclofen, a GABAB receptor agonist, and gabapentin, which increases synaptic GABA, did not generalise to tiagabine. (+)-Bicuculline (3 mg/kg i.p.), a GABAA receptor antagonist, blocked the tiagabine cue, but the less brain-penetrant salt form, bicuculline methochloride, had no effect.
Conclusions
These data suggest that tiagabine generates a discriminative stimulus in rats, and provides a central GABA-mediated cue, but is distinct from the other GABAergic compounds tested.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkins CE, Pillai GV, Kerby J, Bonnert TP, Haldon C, McKernan RM, Gonzalez JE, Oades K, Whiting PJ, Simpson PB (2001) a4b3d GABAA receptors characterized by fluorescence resonance energy transfer-derived measurements of membrane potential. J Biol Chem 276:38934–38939
Andrews N, Loomis S, Blake R, Ferrigan L, Singh L, McKnight AT (2001) Effect of gabapentin-like compounds on development and maintenance of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Psychopharmacology 157:381–387
Armstrong RW, Steinbok P, Cochrane DD, Kube SD, Fife SE, Farrell K (1997) Intrathecally administered baclofen for treatment of spasticity of cerebral origin. J Neurosurg 87:409–414
Borden LA, Dhar TGM, Smith KE, Weinshank RL, Branchek TA, Gluchowski C (1994) Tiagabine, SK&F 89976-A, CI-966 and NNC-711 are selective for the cloned GABA transporter GAT-1. Eur J Pharmacol (Molecular Pharmacology Section) 269:219–244
Braestrup C, Nielsen EB, Sonnewald U, Knutsen LJ, Andersen KE, Jansen JA, Frederiksen K, Andersen PH, Mortensen A, Suzdak P (1990) (R)-N-[4,4-bis(3-methyl-2-thienyl)but-3-en-1-yl]nipecotic acid binds with high affinity to the brain gamma-aminobutyric acid uptake carrier. J Neurochem 54:639–647
Bristow LJ, Cook GP, Patel S, Curtis N, Mawer I, Kulagowski JJ (1998) Discriminative stimulus properties of the putative dopamine D3 receptor agonist, (+)-PD 128907: role of presynaptic dopamine D2 autoreceptors. Neuropharmacology 37:793–802
Brodie MJ (1995) Tiagabine pharmacology in profile. Epilepsia 36(suppl 6):S7–S9
Brown N, Kerby J, Bonnert TP, Whiting PJ, Wafford KA (2002) Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell lines expressing human a4b3d GABAA receptors. Br J Pharmacol 136:965–974
Carter LP, Unzeitig AW, Wu H, Chen W, Coop A, Koek W, France CP (2004) The discriminative stimulus effects of g-hydroxybutyrate and related compounds in rats discriminating baclofen or diazepam: the role of GABAA and GABAB receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:540–547
Crestani F, Martin JR, Mohler H, Rudolph U (2000) Mechanism of action of the hypnotic zolpidem in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 131:1251–1254
Czapinski P, Blaszczyk B, Czuczwar SJ (2005) Mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 5:3–14
Dalby NO, Nielsen EB (1997) Comparison of the preclinical anticonvulsant profiles of tiagabine, lamotrigine, gabapentin and vigabatrin. Epilepsy Res 28:63–72
Davies M, Newell JG, Derry JMC, Martin IL, Dunn SMJ (2000) Characterization of the interaction of zopiclone with γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Mol Pharmacol 58:756–762
Field MJ, Oles RJ, Lewis AS, McCleary S, Hughes J, Singh L (1997) Gabapentin (neurontin) and S-(+)-3-isobutylgaba represent a novel class of selective antihyperalgesic agents. Br J Pharmacol 121:1513–1522
Foster AC, Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Lewis D, Joppa M, Chen TK, Bozigian HP, Gross RS, Gogas KR (2004) In vivo characterization of indiplon, a novel pyrazolopyrimidine sedative-hypnotic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311:547–559
Gee NS, Brown JP, Dissanayake VUK, Offord J, Thrulow R, Woodruff GN (1996) The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (neurontin), binds to the a2d subunit of a calcium channel. J Biol Chem 271:5768–5776
Grech DM, Balster RL (1994) Discriminative stimulus effects of presynaptic GABA agonists in pentobarbital-trained rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 47:5–11
Grech DM, Balster RL (1997) The discriminative stimulus effects of muscimol in rats. Psychopharmacology 129:339–347
Jones HE, Balster RL (1998) Muscimol-like discriminative stimulus effects of GABA agonists in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:319–326
Jursky F, Tamura S, Tamura A, Mandiyan S, Nelson H, Nelson NM (1994) Structure, function and brain localisation of neurotransmitter transporters. J Exp Biol 196:283–295
Lancel M, Faulhaber J, Deisz RA (1998) Effect of the GABA uptake inhibitor tiagabine on sleep and EEG power spectra in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 123:1471–1477
Leach JP, Brodie MJ (1998) Tigabine. Lancet 351:203–207
Lelas S, Spealman RD, Rowlett JK (2000) Using behavior to elucidate receptor mechanisms: a review of the discriminative stimulus effects of benzodiazepines. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 8:294–311
Liang JL, Chen F, Krstew E, Cowen MS, Carroll FY, Crawford D, Beart PM, Lawrence AJ (2006) The GABA(B) receptor allosteric modulator CGP7930, like baclofen, reduces operant self-administration of ethanol in alcohol-preferring rats. Neuropharmacology 50:632–639
Löscher W, Hönack D, Taylor CP (1991) Gabapentin increases aminooxyacetic acid-induced GABA accumulation in several regions of rat brain. Neurosci Lett 128:150–154
Luszczki J, Swiader M, Czuczwar M, Kis J, Czuczwar SJ (2003) Interactions of tiagabine with some antiepileptics in the maximal electroshock in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:319–327
Malitschek B, Ruegg D, Heid J, Kaupmann K, Bittiger H, Frostl W, Bettler B, Kuhn R (1998) Developmental changes of agonist affinity at GABABR1 receptor variants in rat brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 12:56–64
Mathias S, Wetter TC, Steiger A, Lancel M (2001) The GABA uptake inhibitor tiagabine promotes slow wave sleep in normal elderly subjects. Neurobiol Aging 22:247–253
Maurer R (1979) The GABA agonist THIP, a muscimol analogue, does not interfere with the benzodiazepine binding site on rats’ cortical membranes. Neurosci Lett 12:65–68
McDonald LM, Sheppard WF, Staveley SM, Sohal B, Tattersall FD, Hutson PH (2007) Gaboxadol, a selective extrasynaptic GABA A agonist, does not generalise to other sleep-enhancing drugs: a rat drug discrimination study. Neuropharmacology 52:844–853
McNamara RK, Skelton RW (1996) Baclofen, a selective GABAB receptor agonist, dose-dependently impairs spatial learning in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:303–308
Nielsen EB, Valentine JD, Holohean AM, Appel JB (1983) Benzodiazepine receptor mediated discriminative cues: effects of GABA-ergic drugs and inverse agonists. Life Sci 33:2213–2220
Nielsen EB, Suzdak PD, Andersen KE, Knutsen LJS, Sonnewald U, Braestrup C (1991) Characterisation of tiagabine (NO-328), a new, potent and selective GABA uptake inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 196:257–266
Overton DA (1991) Historical context of state dependent learning and discriminative drug effects. Behav Pharmacol 2:253–264
Rauch RJ, Stolerman IP (1987) Midazolam cue in rats: effects of drugs acting on GABA and 5-hydroxytryptamine systems, anticonvulsants and sedatives. J Psychopharmacol 2:71–80
Schachter SC (1999) A review of the antiepileptic drug tiagabine. Clin Neuropharmacol 22:312–317
Sills GJ (2006) The mechanisms of action of gabapentin and pregabalin. Current Opinion Pharmacology 6:108–113
Smith SE, Parvez NS, Chapman AG, Meldrum BS (1995) The g-aminobutyric acid uptake inhibitor, tiagabine, is anticonvulsant in two animal models of reflex epilepsy. Eur J Pharmacol 273:259–265
Storustovu S, Ebert B (2006) Pharmacological characterisation of agonists at d-containing GABAA receptors: functional selectivity for extrasynaptic receptors is dependent on absence of g2. J Pharmacol Exp Therapeut 316:1351–1359
Tariq M, Arshaduddin M, Biary N, Al Moutaery K, Al Deeb S (2001) Baclofen attenuates harmaline-induced tremors in rats. Neurosci Lett 312:79–82
Wafford KA, Thompson SA, Thomas D, Sikela J, Wilcox AS, Whiting PJ (1996) Functional characterisation of human g-aminobutyric acidA receptors containing the a4 subunit. J Pharmacol Exp Therapeut 50:670–678
Winter JC (1981) The stimulus properties of gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Psychopharmacology 73:372–375
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to Professor Ian Stolerman for his excellent advice on designing these studies and to Dr. Keith Wafford for his invaluable help in discussing the data. Also, special thanks to Andrew Jack for excellent statistical advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDonald, L.M., Sheppard, W.F., Staveley, S.M. et al. Discriminative stimulus effects of tiagabine and related GABAergic drugs in rats. Psychopharmacology 197, 591–600 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1077-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1077-z