Abstract
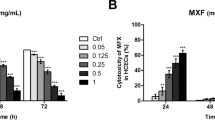
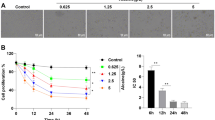
Norfloxacin, a frequently used ocular antibiotic, might have cytotoxic effect on human corneal endothelial cells (HCECs), subsequently damage the cornea and finally impair human vision. However, the possible mechanisms of cytotoxicity of norfloxacin to HCEC line are unclear. Herein, we investigated the cytotoxicity of norfloxacin and its underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms using in vitro cultured non-transfected HCECs and verified the cytotoxicity with cat corneal endothelium in vivo. In the present study, the cytotoxicity of norfloxacin in the in vitro cultured HCECs was recognized by causing abnormal morphology such as cell shrinkage and detachment from plate bottom, and decline of viability of in vitro cultured HCECs. Then, its cytotoxicity was verified by inducing reduction of cell density and morphological abnormality of in vivo cat corneal endothelial cells. Furthermore, the cytotoxicity of norfloxacin in HCECs was corroborated as apoptosis by elevation of plasma membrane permeability, S phase arrest, phosphatidylserine externalization, DNA fragmentation, and apoptotic body formation in in vitro cultured HCECs and apoptosis-like swollen cells in the in vivo model. Moreover, norfloxacin induced extrinsic death receptor-mediated apoptosis pathway by activating caspase-2/-8/-3 and intrinsic mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis pathway by downregulating anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and upregulating of pro-apoptotic Bad, which disrupted mitochondrial transmembrane potential, subsequently upregulated cytoplasmic cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor and finally activated caspase-9/-3. Generally, norfloxacin induces HCE cell apoptosis via a death receptor-mediated and mitochondrion-dependent signaling pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCE:
-
Human corneal endothelium
- HCEC:
-
Human corneal endothelial cell
- CCEC:
-
Cat corneal endothelial cell
- DMEM/F12:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium/Ham’s nutrient mixture F-12 (1:1) medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- MTT:
-
Methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium
- FCM:
-
Flow cytometry
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- ECD:
-
Corneal endothelial cell density
- CCT:
-
Central corneal thickness
- PM:
-
Plasma membrane
- PS:
-
Phosphatidylserine
- AO/EB:
-
Acridine orange/ethidium bromide
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
- ΔΨm:
-
Mitochondrial transmembrane potential
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- PBST:
-
PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- RIPA:
-
Radio immunoprecipitation assay
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- Cyt. c:
-
Cytochrome c
- AIF:
-
Apoptosis-inducing factor
- JC-1:
-
5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolocarbocyanine iodide
References
Ayaki M, Yaguchi S, Iwasawa A, Koide R (2008) Cytotoxicity of ophthalmic solutions with and without preservatives to human corneal endothelial cells, epithelial cells and conjunctival epithelial cells. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 36(6):553–559
Ayaki M, Taguchi Y, Soda M, Yaguchi S, Iwasawa A, Koide R (2010) Cytotoxicity of antibiotic medications used for infection and inflammation control after cataract surgery in cultured corneal endothelial cells. Biocontrol Sci 15(3):97–102
Ayaki M, Iwasawa A, Niwano Y (2012) In vitro assessment of the cytotoxicity of six antibiotic antibiotics to four cultured ocular surface cell lines. Biocontrol Sci 17(2):93–99
Beck R, van Keyserlingk J, Fischer U, Guthoff R, Drewelow B (1999) Penetration of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin into the aqueous humor using different topical application modes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 237(2):89–92
Bezwada P, Clark LA, Schneider S (2008) Intrinsic cytotoxic effects of fluoroquinolones on human corneal keratocytes and endothelial cells. Curr Med Res Opin 24(2):419–424
Cai J, Yang J, Jones DP (1998) Mitochondrial control of apoptosis: the role of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta 1366(1–2):139–149
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, Adams JM (2014) Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:49–63
Dallaporta B, Marchetti P, de Pablo MA, Maisse C, Duc HT, Me’tivier D, Zamzami N, Geuskens M, Kroemer G (1999) Plasma membrane potential in thymocyte apoptosis. J Immunol 162:6534–6542
Fadok VA, de Cathelineau A, Daleke DL, Henson PM, Bratton DL (2001) Loss of phospholipid asymmetry and surface exposure of phosphatidylserine is required for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages and fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 276:1071–1077
Fan D, Fan TJ (2017) Clonidine induces apoptosis of human corneal epithelial cells through death receptors-mediated, mitochondria-dependent signaling pathway. Toxicol Sci 156(1):252–260
Fan T, Han L, Cong R, Liang J (2005) Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai 37:719–727
Fan T, Zhao J, Ma X, Xu X, Zhao W, Xu B (2011) Establishment of a continuous untransfected human corneal endothelial cell line and its biocompatibility to denuded amniotic membrane. Mol Vis 17:469–480
Fan T, Ma X, Zhao J, Wen Q, Hu X, Yu H, Shi W (2013) Transplantation of tissue-engineered human corneal endothelium in cat models. Mol Vis 19:400–407
Fan WY, Wang DP, Wen Q, Fan TJ (2017) The cytotoxic effect of oxybuprocaine on human corneal epithelial cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Hum Exp Toxicol 36(8):765–775
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE, Didelot C, Kroemer G (2006) Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 13:1423–1433
Gogolin S, Ehemann V, Becker G, Brueckner LM, Dreidax D, Bannert S, Nolte I, Savelyeva L, Bell E, Westermann F (2013) CDK4 inhibition restores G(1)-S arrest in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells in the context of doxorubicin-induced DNA damage. Cell Cycle 12:1091–1104
Hassell JR, Birk DE (2010) The molecular basis of corneal transparency. Exp Eye Res 91(3):326–335
Jin Z, El-Deiry WS (2005) Overview of cell death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 4:139–163
Joyce NC (2003) Proliferative capacity of the corneal endothelium. Prog Retin Eye Res 22:359–389
Karmakar I, Haldar S, Chakraborty M, Chaudhury K, Dewanjee S, Haldar PK (2016) Regulation of apoptosis through bcl-2/bax proteins expression and DNA damage by Zanthoxylum alatum. Pharm Biol 54(3):503–508
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD (1997) The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science 275:1132–1136
Knight T, Luedtke D, Edwards H, Taub JW, Ge Y (2019) A delicate balance—the BCL-2 family and its role in apoptosis, oncogenesis, and cancer therapeutics. Biochem Pharmacol 162:250–261
Lee SA, Kim YJ, Lee CS (2013) Brefeldin A induces apoptosis by activating the mitochondrial and death receptor pathways and inhibits focal adhesion kinase-mediated cell invasion. Basic Clin Pharmacol 113:329–338
Li Y, Wen Q, Fan T, Ge Y, Yu M, Sun L, Zhao Y (2015) Dose dependent cytotoxicity of pranoprofen in cultured human corneal endothelial cells by inducing apoptosis. Drug Chem Toxicol 38:16–21
Lobner D (2000) Comparison of the LDH and MTT assays for quantifying cell death: validity for neuronal apoptosis? J Neurosci Methods 96:147–152
Matthews GM, Newbold A, Johnstone RW (2012) Intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathway signaling as determinants of histone deacetylase inhibitor antitumor activity. Adv Cancer Res 116:165–197
McArthur K, Kile BT (2018) Apoptotic caspases: multiple or mistaken identities? Trends Cell Biol 28(6):475–493
Miao Y, Sun Q, Wen Q, Qiu Y, Ge Y, Yu MM, Fan TJ (2014) Cytotoxic effects of betaxolol on healthy corneal endothelial cells both in vitro and in vivo. Int J Ophthalmol 7:14–21
Napoletano F, Baron O, Vandenabeele P, Mollereau B, Fanto M (2019) Intersections between regulated cell death and autophagy. Trends Cell Biol 29(4):323–338
Narita M, Shimizu S, Ito T, Chittenden T, Lutz RJ, Matsuda H, Tsujimoto Y (1998) Bax interacts with the permeability transition pore to induce permeability transition and cytochrome c release in isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:14681–14686
Natarajan SK, Becker DF (2012) Role of apoptosis-inducing factor, proline dehydrogenase, and NADPH oxidase in apoptosis and oxidative stress. Cell Health Cytoskelet 2012:11–27
Rodriguez-Enriquez S, He L, Lemasters JJ (2004) Role of mitochondrial permeability transition pores in mitochondrial autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(12):2463–2472
Santucci R, Sinibaldi F, Cozza P, Polticelli F, Fiorucci L (2019) Cytochrome c: an extreme multifunctional protein with a key role in cell fate. Int J Biol Macromol 136:1237–1246
Sedlackova L, Korolchuk VI (2019) Mitochondrial quality control as a key determinant of cell survival. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res 1866(4):575–587
Shan M, Fan TJ (2016) Cytotoxicity of carteolol to human corneal epithelial cells by inducing apoptosis via triggering the Bcl-2 family protein-mediated mitochondrial pro-apoptotic pathway. Toxicol in Vitro 35:36–42
Tian CL, Wen Q, Fan TJ (2015) Cytotoxicity of atropine to human corneal epithelial cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis. Exp Toxicol Pathol 67(10):517–524
Van Opdenbosch N, Lamkanfi M (2019) Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and disease. Immunity 50(6):1352–1364
von Keyserlingk J, Beck R, Fischer U, Hehl E, Guthoff R (1997) Penetration of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin into the aqueous humour of patients by different antibiotic application modes. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 3-4:251–255
Wen Q, Fan TJ, Bai SR, Sui YL (2015) Cytotoxicity of proparacaine to human corneal endothelial cells in vitro. J Toxicol Sci 40:427–436
Wen Q, Fan TJ, Tian CL (2016) Cytotoxicity of atropine to human corneal endothelial cells by inducing mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 241:1457–1465
White MK, Cinti CA (2004) Morphologic approach to detect apoptosis based on electron microscopy. Methods Mol Biol 285:105–111
Yu HZ, Li YH, Wang RX, Zhou X, Yu MM, Ge Y, Zhao J, Fan TJ (2014) Cytotoxicity of lidocaine to human corneal endothelial cells in vitro. Basic Clin Pharmacol 114:352–359
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1106000/2018YFC1106001) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TF planned the experiment, provided financial support, and performed data analysis. SW executed the experiment and performed data analysis. GJ planned the experiment, performed data analysis, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, TJ., Wu, SX. & Jiang, GJ. Apoptotic effects of norfloxacin on corneal endothelial cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 77–88 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01711-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01711-5