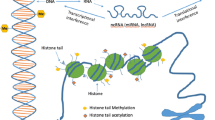
Abstract
The increasing incidence of pulmonary inflammation and lung cancer, as well as exacerbation of pre-existing chronic lung diseases by exposure to airborne pollutants, e.g., particulate matter and cigarette smoke, is becoming a major public health concern in the world. However, the exact mechanisms of pulmonary injury from exposure to these airborne insults have not been fully elucidated. Nevertheless, accumulating evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) may play a unique role in the regulation of airborne agent-induced lung inflammation and carcinogenesis. Since epigenetic modifications are heritable and reversible, this may provide a new insight into the relationship of miRNAs and environmental pollution-related lung disorders. The aim of this review was to update our existing knowledge regarding the mechanisms by which airborne pollutants altering miRNA profiles in the lung, specifically for cigarette smoke and airborne particulate matter, and the potential biological roles of miRNAs in the initiation of pulmonary inflammation and lung cancer, as well as the regulation of underlying genetic susceptibility to these environmental stressors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baccarelli AA, Zheng Y, Zhang X et al (2014) Air pollution exposure and lung function in highly exposed subjects in Beijing, China: a repeated-measure study. Part Fibre Toxicol 11(1):51. doi:10.1186/s12989-014-0051-7
Balansky R, Ganchev G, Iltcheva M, Steele VE, D’Agostini F, De Flora S (2007) Potent carcinogenicity of cigarette smoke in mice exposed early in life. Carcinogenesis 28(10):2236–2243. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm122
Balansky R, Izzotti A, D’Agostini F et al (2014) Assay of lapatinib in murine models of cigarette smoke carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 35(10):2300–2307. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgu154
Bleck B, Grunig G, Chiu A et al (2013) MicroRNA-375 regulation of thymic stromal lymphopoietin by diesel exhaust particles and ambient particulate matter in human bronchial epithelial cells. J Immunol 190(7):3757–3763. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1201165
Bollati V, Marinelli B, Apostoli P et al (2010) Exposure to metal-rich particulate matter modifies the expression of candidate microRNAs in peripheral blood leukocytes. Environ Health Perspect 118(6):763–768. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901300
Bollati V, Angelici L, Rizzo G et al (2014) Microvesicle-associated microRNA expression is altered upon particulate matter exposure in healthy workers and in A549 cells. J Appl Toxicol JAT. doi:10.1002/jat.2987
Bourdon JA, Saber AT, Halappanavar S et al (2012) Carbon black nanoparticle intratracheal installation results in large and sustained changes in the expression of miR-135b in mouse lung. Environ Mol Mutagen 53(6):462–468. doi:10.1002/em.21706
Cao J, Li W, Tan J et al (2009) Association of ambient air pollution with hospital outpatient and emergency room visits in Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 407(21):5531–5536. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.07.021
Cho WC (2007) OncomiRs: the discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer 6:60
Cho WC, Kwan CK, Yau S, So PP, Poon PC, Au JS (2011) The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 15(9):1127–1137
Cui FM, Li JX, Chen Q et al (2013) Radon-induced alterations in micro-RNA expression profiles in transformed BEAS2B cells. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 76(2):107–119. doi:10.1080/15287394.2013.738176
Cui P, Huang Y, Han J, Song F, Chen K (2014) Ambient particulate matter and lung cancer incidence and mortality: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Pub Health. doi:10.1093/eurpub/cku145
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer. Ann Rev Pathol 9:287–314. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104715
Faxuan W, Qin Z, Dinglun Z et al (2012) Altered microRNAs expression profiling in experimental silicosis rats. J Toxicol Sci 37(6):1207–1215
Feil R, Fraga MF (2011) Epigenetics and the environment: emerging patterns and implications. Nat Rev Genet 13(2):97–109. doi:10.1038/nrg3142
Fry RC, Rager JE, Bauer R et al (2014) Air toxics and epigenetic effects: ozone altered microRNAs in the sputum of human subjects. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 306(12):L1129–L1137. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00348.2013
Gross TJ, Powers LS, Boudreau RL et al (2014) A microRNA processing defect in smokers’ macrophages is linked to SUMOylation of the endonuclease DICER. J Biol Chem 289(18):12823–12834. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.565473
Guo LJ, Zhao A, Chen RJ, Kan HD, Kuang XY (2014) Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Outpatient Visits for Acute Bronchitis in a Chinese City. Biomed Environ Sci BES 27(11):833–840. doi:10.3967/bes2014.121
Halappanavar S, Jackson P, Williams A et al (2011) Pulmonary response to surface-coated nanotitanium dioxide particles includes induction of acute phase response genes, inflammatory cascades, and changes in microRNAs: a toxicogenomic study. Environ Mol Mutagen 52(6):425–439. doi:10.1002/em.20639
Hamra GB, Guha N, Cohen A et al (2014) Outdoor particulate matter exposure and lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Health Perspect 122(9):906–911. doi:10.1289/ehp.1408092
Hesterberg TW, Long CM, Bunn WB, Sax SN, Lapin CA, Valberg PA (2009) Non-cancer health effects of diesel exhaust: a critical assessment of recent human and animal toxicological literature. Crit Rev Toxicol 39(3):195–227. doi:10.1080/10408440802220603
IARC (2013) Outdoor air pollution a leading environmental cause of cancer deaths. The International Agency for Research on Cancer. http://www.iarc.fr/en/mediacentre/pr/2013/pdfs/pr221_E.pdf
Izzotti A, Pulliero A (2014) The effects of environmental chemical carcinogens on the microRNA machinery. Int J Hyg Environ Health 217(6):601–627. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2014.01.001
Izzotti A, Bagnasco M, Cartiglia C et al (2005) Chemoprevention of genome, transcriptome, and proteome alterations induced by cigarette smoke in rat lung. Eur J Cancer 41(13):1864–1874. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2005.04.011
Izzotti A, Calin GA, Arrigo P, Steele VE, Croce CM, De Flora S (2009a) Downregulation of microRNA expression in the lungs of rats exposed to cigarette smoke. FASEB J official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 23(3):806–812. doi:10.1096/fj.08-121384
Izzotti A, Calin GA, Steele VE, Croce CM, De Flora S (2009b) Relationships of microRNA expression in mouse lung with age and exposure to cigarette smoke and light. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 23(9):3243–3250. doi:10.1096/fj.09-135251
Izzotti A, Calin GA, Steele VE et al (2010a) Chemoprevention of cigarette smoke-induced alterations of microRNA expression in rat lungs. Cancer Prev Res 3(1):62–72. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0202
Izzotti A, Larghero P, Cartiglia C et al (2010b) Modulation of microRNA expression by budesonide, phenethyl isothiocyanate and cigarette smoke in mouse liver and lung. Carcinogenesis 31(5):894–901. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq037
Izzotti A, Larghero P, Longobardi M et al (2011) Dose-responsiveness and persistence of microRNA expression alterations induced by cigarette smoke in mouse lung. Mutat Res 717(1–2):9–16. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.12.008
Izzotti A, Balansky R, D’Agostini F et al (2013) Relationships between pulmonary micro-RNA and proteome profiles, systemic cytogenetic damage and lung tumors in cigarette smoke-exposed mice treated with chemopreventive agents. Carcinogenesis 34(10):2322–2329. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt178
Jardim MJ (2011) MicroRNAs: implications for air pollution research. Mutat Res 717(1–2):38–45. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.03.014
Jardim MJ, Fry RC, Jaspers I, Dailey L, Diaz-Sanchez D (2009) Disruption of microRNA expression in human airway cells by diesel exhaust particles is linked to tumorigenesis-associated pathways. Environ Health Perspect 117(11):1745–1751. doi:10.1289/ehp.0900756
Jie Y, Houjin H, Xun M, Kebin L, Xuesong Y, Jie X (2014) Relationship between pulmonary function and indoor air pollution from coal combustion among adult residents in an inner-city area of southwest China. Braz J Med Biol Res 47(11):982–989
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G et al (2007) The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res 67(16):7713–7722. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1083
Kalscheuer S, Zhang X, Zeng Y, Upadhyaya P (2008) Differential expression of microRNAs in early-stage neoplastic transformation in the lungs of F344 rats chronically treated with the tobacco carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone. Carcinogenesis 29(12):2394–2399. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn209
Kishore A, Borucka J, Petrkova J, Petrek M (2014) Novel insights into miRNA in lung and heart inflammatory diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2014:259131. doi:10.1155/2014/259131
Kleeberger SR (2003) Genetic aspects of susceptibility to air pollution. Eur Respir J Suppl 40:52s–56s
Liu L, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Greenlee AR, Han Z (2010) Overexpressed miR-494 down-regulates PTEN gene expression in cells transformed by anti-benzo (a) pyrene-trans-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide. Life Sci 86(5–6):192–198. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2009.12.002
Lobanenkov V, Loukinov D, Pugacheva E (2011) Environmental epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Keystone symposia on molecular and cellular biology. The Grove Park Hotel & Spa, Ashville, NC, USA, 27 March-1 April 2011. Epigenomics 3(3):261–266. doi:10.2217/epi.11.25
Moller P, Folkmann JK, Forchhammer L et al (2008) Air pollution, oxidative damage to DNA, and carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 266(1):84–97. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.030
Motta V, Angelici L, Nordio F et al (2013) Integrative analysis of miRNA and inflammatory gene expression after acute particulate matter exposure. Toxicol Sci 132(2):307–316. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kft013
Nymark P, Guled M, Borze I et al (2011) Integrative analysis of microRNA, mRNA and aCGH data reveals asbestos- and histology-related changes in lung cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer 50(8):585–597. doi:10.1002/gcc.20880
Peng J, Xu X, Mace BE et al (2013) Estrogen metabolism within the lung and its modulation by tobacco smoke. Carcinogenesis 34(4):909–915. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs402
Rager JE, Smeester L, Jaspers I, Sexton KG, Fry RC (2011) Epigenetic changes induced by air toxics: formaldehyde exposure alters miRNA expression profiles in human lung cells. Environ Health Perspect 119(4):494–500. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002614
Rager JE, Moeller BC, Doyle-Eisele M, Kracko D, Swenberg JA, Fry RC (2013) Formaldehyde and epigenetic alterations: microRNA changes in the nasal epithelium of nonhuman primates. Environ Health Perspect 121(3):339–344. doi:10.1289/ehp.1205582
Ristovski ZD, Miljevic B, Surawski NC et al (2012) Respiratory health effects of diesel particulate matter. Respirology 17(2):201–212. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02109.x
Saunders MA, Liang H, Li WH (2007) Human polymorphism at microRNAs and microRNA target sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(9):3300–3305. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611347104
Schembri F, Sridhar S, Perdomo C et al (2009) MicroRNAs as modulators of smoking-induced gene expression changes in human airway epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(7):2319–2324. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806383106
See SW, Wang YH, Balasubramanian R (2007) Contrasting reactive oxygen species and transition metal concentrations in combustion aerosols. Environ Res 103(3):317–324. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2006.08.012
Shusterman D (2007) Trigeminally-mediated health effects of air pollutants: sources of inter-individual variability. Hum Exp Toxicol 26(3):149–157. doi:10.1177/0960327107070550
Song Q, Christiani DC, Wang Xiaorong, Ren J (2014) The global contribution of outdoor air pollution to the incidence, prevalence, mortality and hospital admission for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Pub Health 11(11):11822–11832. doi:10.3390/ijerph111111822
Van Pottelberge GR, Mestdagh P, Bracke KR et al (2011) MicroRNA expression in induced sputum of smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183(7):898–906. doi:10.1164/rccm.201002-0304OC
Wang M, Ye Y, Qian H et al (2010) Common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs are associated with risk of coal workers’ pneumoconiosis. J Hum Genet 55(1):13–17. doi:10.1038/jhg.2009.112
Wang F, Li C, Liu W, Jin Y (2014) Modulation of microRNA expression by volatile organic compounds in mouse lung. Environ Toxicol 29(6):679–689. doi:10.1002/tox.21795
Wilker EH, Baccarelli A, Suh H, Vokonas P, Wright RO, Schwartz J (2010) Black carbon exposures, blood pressure, and interactions with single nucleotide polymorphisms in microRNA processing genes. Environ Health Perspect 118(7):943–948. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901440
Wilker EH, Alexeeff SE, Suh H, Vokonas PS, Baccarelli A, Schwartz J (2011) Ambient pollutants, polymorphisms associated with microRNA processing and adhesion molecules: the Normative Aging Study. Environ Health 10:45. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-10-45
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S (2009) Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol 11(3):228–234. doi:10.1038/ncb0309-228
Wong CM, Vichit-Vadakan N, Vajanapoom N et al (2010) Part 5. Public health and air pollution in Asia (PAPA): a combined analysis of four studies of air pollution and mortality. Res Rep 154:377–418
Wong IC, Ng YK, Lui VW (2014) Cancers of the lung, head and neck on the rise: perspectives on the genotoxicity of air pollution. Chin J Cancer 33(10):476–480. doi:10.5732/cjc.014.10093
Wu J, Yang T, Li X et al (2013) Alteration of serum miR-206 and miR-133b is associated with lung carcinogenesis induced by 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 267(3):238–246. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.01.002
Xi S, Yang M, Tao Y et al (2010) Cigarette smoke induces C/EBP-beta-mediated activation of miR-31 in normal human respiratory epithelia and lung cancer cells. PLoS One 5(10):e13764. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013764
Xi S, Xu H, Shan J et al (2013) Cigarette smoke mediates epigenetic repression of miR-487b during pulmonary carcinogenesis. J Clin Investig 123(3):1241–1261. doi:10.1172/JCI61271
Zago M, Rico de Souza A, Hecht E et al (2014) The NF-kappaB family member RelB regulates microRNA miR-146a to suppress cigarette smoke-induced COX-2 protein expression in lung fibroblasts. Toxicol Lett 226(2):107–116. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.01.020
Zhang B, Pan X (2009) RDX induces aberrant expression of microRNAs in mouse brain and liver. Environ Health Perspect 117(2):231–240. doi:10.1289/ehp.11841
Zhao Y, Xu Y, Li Y et al (2013) NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation leading to EMT via miR-200c is involved in cell transformation induced by cigarette smoke extract. Toxicological sciences: an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 135(2):265–276. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kft150
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31172278 and 31472191 to XL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jun Wei and Feng Li have contributed equally in this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Li, F., Yang, J. et al. MicroRNAs as regulators of airborne pollution-induced lung inflammation and carcinogenesis. Arch Toxicol 89, 677–685 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1462-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1462-4