Abstract
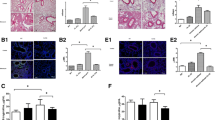
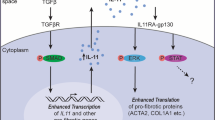
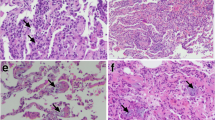
Klotho is a recently discovered antiaging protein. Although many researchers are investigating the roles of Klotho in chronic kidney diseases and cancer, however, there are no studies on the roles of Klotho in chronic pulmonary diseases. The purpose of this study was to define the role of Klotho in pulmonary fibrosis using a murine model of ovalbumin (OVA)-induced chronic asthma and in BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells. In an in vivo experiment, mice were sensitized by intraperitoneal injection of OVA (20 μg/mouse), followed 1 week later by an airway challenge with 1 % OVA solution delivered three times a week for 4 weeks. In an in vitro experiment, we investigated the effects of stimulated with interleukin (IL)-4 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α on Klotho protein and VEGF and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1/Smad3 signaling in BEAS-2B cells. Klotho decreased and VEGF and TGF-β1 levels increased with increasing duration of OVA challenge. Similar findings were found for the expression of these proteins in lung tissue. The collagen content in lung tissue increased with repeated OVA challenge. In the in vitro experiment, Klotho expression decreased and VEGF and TGF-β1/Smad3 expression increased after IL-4 (50 ng/mL) and TNF-α (50 ng/mL) stimulation. Pretreatment with 25, 50, and 100 ng/mL of Klotho protein significantly attenuated the increases in VEGF and TGF-β1/Smad3 expression levels after IL-4 and TNF-α treatment, and reduced α-smooth muscle actin expression in concentration-dependent manner. Klotho protein inhibited the fibrotic response by suppressing VEGF and TGF-β1/Smad3 expression. These results suggest that Klotho protein may be crucial to inhibiting fibrosis associated with chronic airway diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camilli TC, Xu M, O’Connell MP, Chien B, Frank BP, Subaran S, Indig FE, Morin PJ, Hewitt SM, Weeraratna AT (2011) Loss of Klotho during melanoma progression leads to increased filamin cleavage, increased Wnt5A expression, and enhanced melanoma cell motility. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 24:175–186
Chen B, Wang X, Zhao W, Wu J (2010) Klotho inhibits growth and promotes apoptosis in human lung cancer cell line A549. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:99
Chetta A, Zanini A, Foresi A, D’lppolito R, Tipa A, Castagnaro A, Baraldo S, Neri M, Saetta M, Olivieri D (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation and bronchial wall remodeling in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 35:1437–1442
Doi S, Zou Y, Togao O, Pastor JV, John GB, Wang L, Shiizaki K, Gotschall R, Schiavi S, Yorioka N, Takahashi M, Boothman DA, Kuro-o M (2011) Klotho inhibits transforming growth factor-beta1(TGF-beta1) signaling and suppresses renal fibrosis and cancer metastasis in mice. J Biol Chem 286:8655–8665
Foley SC, Mogas AK, Olivenstein R, Fiset PO, Chakir J, Bourbeau J, Emst P, Lemere C, Martin JG, Hamid Q (2007) Increased expression of ADAM33 and ADAM8 with disease progression in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 199:863–871
Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, Matsumoto K, Maruoka S, Horie T (2001) Transforming growth factor-β1 induces phenotypic modulation of human lung fibroblasts to myofibroblast through a c-jun-NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:356–363
Hsieh CC, Kuro-o M, Rosenblatt KP, Brobey R, Papaconstantinou J (2010) The ASK1-signalosome regulates p38 MAPK activity in response to levels of endogenous oxidative stress in the Klotho mouse models of aging. Aging 2:597–611
Kazi A, Lotfi SS, Goncharova EA, Tliba O, Amrani Y, Krymskaya VP, Lazaar AL (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor-induced secretion of fibronectin is ERK dependent. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:539–545
Kohan M, Muro AF, Bader R, Berkman N (2011) The extra domain A of fibronection is essential for allergen-induced airway fibrosis and hyperresponsiveness in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127:439–446
Kuro-o M (2006) Klotho as a regulator of fibroblast growth factor signaling and phosphate/calcium metabolism. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15:437–441
Kuro-o M (2009) Klotho and aging. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:1049–1058
Kuro-o M (2010) Klotho. Pflugers Arch 459:333–343
Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Kawaguchi H, Suga T, Utsugi T, Ohyama Y, Kurabayashi M, Kaname T, Kume E, Iwasaki H, Iida A, Shiraki-Iida T, Nishikawa S, Nabeshima YI (1997) Mutation of the mouse Klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 390:45–51
Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Clark JD, Pastor JV, Nandi A, Gurnani P, McGuinness OP, Chikuda H, Yamaguchi M, Kawaguchi H, Shimomura I, Takayama Y, Herz J, Kahn CR, Rosenblatt KP, Kuro-o M (2005) Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 309:1829–1833
Lee CG, Link H, Baluk P, Homer RJ, Chapoval S, Bhandari V, Kang MJ, Cohn L, Kim YK, McDonald DM, Elias JA (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces remodeling and enhances Th2-mediated sensitization and inflammation in the lung. Nat Med 10:1095–1103
Lee KS, Park SJ, Kim SR, Min KH, Lee KY, Choe YH, Hong SH, Lee YR, Kim JS, Hong SJ, Lee YC (2008) Inhibition of VEGF blocks TGF-β1 production through a PI3 K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur Respir J 31:523–531
Lee CG, Ma B, Takyar S, Ahangari F, Delacruz C, He CH, Elias JA (2011a) Studies of vascular endothelial growth factor in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 8:512–515
Lee MY, Lee JA, Seo CS, Ha H, Lee NH, Shin HK (2011b) Protective effects of Mentha haplocalyx ethanol extract (MH) in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Phytother Res 25:863–869
Li ZD, Bork JP, Krueger B, Patsenker E, Schulze-Krebs A, Hahn EG, Schuppan D (2005) VEGF induces proliferation, migration, and TGF-beta1 expression in mouse glomerular endothelial cells via mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:1049–1060
Lin HY, Moustakas A (1994) TGF-beta receptors: structure and function. Cell Mol Biol 40:337–349
Moerno JA, Izquierdo MC, Sanchez-Nino MD, Suarez-Alvarez B, Lopez-Larrea C, Jakubowski A, Blanco J, Ramirez R, Selgas R, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A, Sanz AB (2011) The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal Klotho expression through NFκB. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1315–1325
Moustakas A, Heldin CH (2009) The regulation of TGF-beta signal transduction. Development 136:3699–3714
Phan SH (2002) The myofibroblast in pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 122:286–289
Qin W, Chung AC, Huang XR, Meng XM, Hui DS, Yu CM, Sung JJ, Lan HY (2011) TGF-β/Smad3 signaling promotes renal fibrosis by inhibiting miR-29. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1462–1474
Scotton CJ, Chambers RC (2007) Molecular targets in pulmonary fibrosis: the myofibroblast in focus. Chest 132:1311–1321
Sheppard D (2006) Transforming growth factor beta: a central modulator of pulmonary and airway inflammation and fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:413–417
Sugiura H, Yoshida T, Shiohira S, Kohei J, Mitobe M, Kurosu H, Kuro-o M, Nitta K, Tsuchiya K (2012) Reduced Klotho expression level in kidney aggravates renal interstitial fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 302:1252–1264
Thurston RD, Larmonier CB, Majewski PM, Ramalingam R, Midura-Kiela M, Laubitz D, Vandewalle A, Besselsen DG, Muhlbauer M, Jobin C, Kiela PR, Ghishan FK (2010) Tumor necrosis factor and inferferon-gamma down-regulate Klotho in mice with colitis. Gastroenterology 138:1384–1394
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Iijima K, Hasegawa H, Okawa K, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2006) Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 444:770–774
Usuki J, Matsuda K, Azuma A, Kudoh S, Gemma A (2012) Sequential analysis of myofibroblast differentiation and transforming growth factor-β1/Smad pathway activation in murine pulmonary fibrosis. J Nippon Med Sch 79:46–59
Vasquez-Pinto LM, Nantel F, Sirois P, Jancar S (2010) Bradykinin B(1) receptor antagonist R954 inhibits eosinophil activation/proliferation/migration and increases TGF-beta and VEGF in a murine model of asthma. Neuropeptides 44:107–113
Wang Y, Sun Z (2009) Current understanding of klotho. Ageing Res Rev 8:43–51
Xiong YY, Wu FH, Wang JS, Li J, Kong LY (2012) Attenuation of airway hyperreactivity and T helper cell type 2 responses by coumarins from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. J Ethonopharmacol 141:314–321
Yamamoto M, Clark JD, Pastor JV, Gurnani P, Nandi A, Kurosu H, Miyoshi M, Ogawa Y, Castrillon DH, Rosenblatt KP, Kuro-o M (2005) Regulation of oxidative stress by the anti-aging hormone Klotho. J Biol Chem 280:38029–38034
Zhang K, Rekhter MD, Gordon D, Phan SH (1994) Myofibroblasts and their role in lung collagen gene expression during pulmonary fibrosis. A combined immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study. Am J Pathol 145:114–125
Zhao Y, Banerjee S, Dey N, Lejeune WS, Sarkar PS, Brobey R, Rosenblatt KP, Tilton RG, Choudhary S (2011) Klotho depletion contributes to increased inflammation in kidney of the db/db mouse model of diabetes via RelA (serine)536 phosphorylation. Diabetes 60:1907–1916
Acknowledgments
This research was part of a project (Evidence Based Medicine for Herbal Formula) funded by the Basic Herbal Medicine Research Group at the Korean Institute of Oriental Medicine.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, IS., Shin, HK., Kim, JC. et al. Role of Klotho, an antiaging protein, in pulmonary fibrosis. Arch Toxicol 89, 785–795 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1282-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1282-y