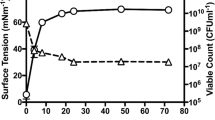
Abstract
The rich diversity of marine macroalgae and their associated bacterial flora represent a potential reservoir of bioactive compounds with valuable biotechnological and pharmaceutical use. Heterotrophic bacteria associated with the intertidal macroalgae were isolated and evaluated for their pharmacological properties using various in vitro models. Among 148 cultivable isolates, more than 50% were dominated by γ-Proteobacteria and Firmicutes, wherein 53 of them showed consistent antibacterial activity against a broad spectrum of clinically significant pathogens. The bacteria were characterized by extensive microbiological, molecular and chemical identification tools. The heterotrophs Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MTCC 12716 and Shewanella algae MTCC 12715 isolated from a red marine macroalga Hypnea valentiae exhibited potential anti-infective properties against multidrug-resistant pathogens, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (minimum inhibitory concentration of 6.25–12.5 µg/mL). The organic extract of B. amyloliquefaciens displayed significantly greater antioxidative properties (IC90 < 1 mg/mL) and the activities showed considerable positive correlation (r2 > 0.8, P < 0.05) with the inhibitory activities against angiotensin converting enzyme-I, pro-inflammatory cyclooxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, which were associated with hypertension, inflammation, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia, respectively. The applications of nuclear magnetic resonance-based fingerprinting to analyze the characteristic signals in the solvent extracts and to correlate them with the pharmaceutical properties were underlined. The heterotrophic bacterium B. amyloliquefaciens MTCC 12716 might, therefore, serve as a potential therapeutic candidate to develop products with wide pharmaceutical applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ademiluyi AO, Oboh G (2013) Soybean phenolic-rich extracts inhibit key-enzymes linked to type-2 diabetes (α-amylase and α-glucosidase) and hypertension (angiotensin-I converting enzyme) in-vitro. Exp Toxicol Pathol 65:305–309
Ali AIB, Bour ME, Ktari L, Bolhuis H, Ahmed M, Boudabbous A, Stal LJ (2012) Jania rubens-associated bacteria: molecular identification and antimicrobial activity. J Appl Phycol 24:525–534
Al-Zereini WA (2014) Bioactive crude extracts from four bacterial isolates of marine sediments from Red Sea, Gulf of Aqaba, Jordan. Jordan J Biol Sci 7:133–137
Amalaradjou MAR, Venkitanarayanan K (2014) Antibiofilm effect of octenidine hydrochloride on Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and VRSA. Pathogens 3:404–416
Archer NK, Mazaitis MJ, Costerton JW (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: properties, regulation, and roles in human disease. Virulence 2:445–459
Armstrong E, Yan L, Boyd KG, Wright CP, Burgess JG (2001) The symbiotic role of marine microbes on living surfaces. Hydrobiol 461:37–40
Atkinson AB, Robertson JI (1979) Captopril in the treatment of clinical hypertension and cardiac failure. Lancet 2:836–839
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79
Baylac S, Racine P (2003) Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by essential oils and other natural fragrant extracts. Int J Aromather 13:138–142
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier M, Berset C (1995) Use of free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT - Food Sci Technol 28:25–30
Chakraborty K, Thilakan B, Raola VK (2014) Polyketide family of novel antibacterial 7-O-methyl-5′-hydroxy-3′-heptenoate macrolactin from seaweed-associated Bacillus subtilis MTCC 10403. J Agric Food Chem 62:12194–12208
Chakraborty K, Thilakan B, Raola VK (2017a) Antimicrobial polyketide furanoterpenoids from seaweed-associated heterotrophic bacterium Bacillus subtilis MTCC 10403. Phytochemistry 142:112–125
Chakraborty K, Thilakan B, Chakraborty RD, Raola VK, Joy M (2017b) O-heterocyclic derivatives with antibacterial properties from marine bacterium Bacillus subtilis associated with seaweed, Sargassum myriocystum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:569–583
Charlier C, Michaux C (2003) Dual inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) as a new strategy to provide safer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Med Chem 38:645–659
Davidson BS (1995) New dimensions in natural products research: cultured marine microorganisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol 6:284–291
Debbab A, Aly AH, Lin WH, Proksch P (2010) Bioactive compounds from marine bacteria and fungi. Microb Biotechnol 5:544–563
Dostal DE, Baker KM (1999) The cardiac renin-angiotensin system: conceptual, or a regulator of cardiac function? Circ Res 85:643–650
Elahi MM, Matata BM (2006) Free radicals in blood: evolving concepts in the mechanism of ischemic heart disease. Arch Biochem Biophys 450:78–88
Gao DQ, Huang XQ, Lu CP, Wu SY (2000) Characteristic of the hemolysin of Edwardsiella tarda. Chin J Zoon 16:53–55
Gram L, Melchiorsen J, Bruhn JB (2010) Antibacterial activity of marine culturable bacteria collected from a global sampling of ocean surface waters and surface swabs of marine organisms. Mar Biotechnol 12:439–451
Hollants J, Leliaert F, Clerck OD, Willems A (2012) What we can learn from sushi: a review on seaweed-bacterial associations. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 83:1–16
Holmquist B, Bunning P, Riordan JF (1979) A continuous spectrophotometric assay for angiotensin converting enzyme. Anal Biochem 95:540–548
Isnansetyo A, Horikawa M, Kamei Y (2001) In vitro anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity of 2,4- diacetylphloroglucinol produced by Pseudomonas sp. AMSN isolated from a marine alga. J Antimicrob Chemother 47:724–725
Jamal MT, Morris PC, Hansen R, Jamieson DJ, Burgess GJ, Austinm B (2006) Recovery and characterization of a 30.7-kDa protein from Bacillus licheniformis associated with inhibitory activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococci, and Listeria monocytogenes. Mar Biotechnol 8:587–592
Kennedy J, Baker P, Piper C, Cotter PD, Walsh M, Mooij MJ, Bourke MB, Rea MC, O'Connor PM, Ross RP, Hill C, O'Gara F, Marchesi JR, Dobson AD (2009) Isolation and analysis of bacteria with antimicrobial activities from the marine sponge Haliclona simulans collected from Irish waters. Mar Biotechnol 11:384–396
Krieg NR, Holt JG (1984) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore
Lachnit T, Meske D, Wahl M, Harder T, Schmitz R (2011) Epibacterial community patterns on marine macroalgae are host-specific but temporally variable. Environ Microbiol 13:655–665
Larsen LN, Dahl E, Bremer J (1996) Peroxidative oxidation of leuco-dichlorofluorescein by prostaglandin H synthase in prostaglandin biosynthesis from polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1299:47–53
Li JW, Vederas JC (2009) Drug discovery and natural products: end of an era or an endless frontier? Science 325:161–165
Li G-Y, Li B-G, Yang T, Yin J-H, Qi H-Y, Liu G-Y, Zhang G-L (2005) Sesterterpenoids, terretonins A-D, and an alkaloid, asterrelenin, from Aspergillus terreus. J Nat Prod 68:1243–1246
Maciejak A, Leszczynska A, Warchol I, Gora M, Kaminska J, Plochocka D, Kapcinska MW, Tulacz D, Siedlecka J, Swiezewska E, Sojka M, Danikiewicz W, Odolczyk N, Szkopinska A, Sygitowicz G, Burzynska B (2013) The effects of statins on the mevalonic acid pathway in recombinant yeast strains expressing human HMG-CoA reductase. BMC Biotechnol 13:68
Maisuthisakul P, Pasuk S, Ritthiruangdej P (2008) Relationship between antioxidant properties and chemical composition of some Thai plants. J Food Compost Anal 21:229–240
Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Larijani B, Abdollahi M (2015) Targeting metabolic disorders by natural products. J Diabetes Metab Disord 14:57
Manthey A, Reuter G (1989) Microbial synthesis of metabolites with anti-hypertensive activity: aspects of fermentation derived inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE. J Basic Microbiol 29:623–639
Molinski TF, Dalisay DS, Lievens SL, Saludes JP (2009) Drug development from marine natural products. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:69–85
National Research Council (1999) From monsoons to microbes: understanding the ocean’s role in human health. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.17226/6368
Kurian NK, Nair HP, Bhat HG (2015) Evaluation of anti-inflammatory property of melanin from marine Bacillus spp. BTCZ31. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 8:251–255
Okamura M, Shimazaki K, Nakata T, Chida N, Miyatake T, Maemoku H, Tsutsumi H, Nakamura T, Yamaguchi C, Ogawa M (1992) Submarine active faults in the northwestern part of Beppu Bay, Japan-On a new technique for submarine active fault survey. Mem Geol Soc Jpn 40:65–74
Pandey S, Sree A, Dash SS, Sethi DP, Chowdhury L (2013) Diversity of marine bacteria producing beta-glucosidase inhibitors. Microb Cell Fact 12:35
Paul VJ, Ritson-Williams R, Sharp K (2011) Marine chemical ecology in benthic environments. Nat Prod Rep 28:345–388
Penesyan A, Marshall-Jones Z, Holmstrom C, Kjelleberg S, Egan S (2009) Antimicrobial activity. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:113–124
Penesyan A, Kjelleberg S, Egan S (2010) Development of novel drugs from marine surface associated microorganisms. Mar Drugs 8:438–459
Quevrain E, Roue M, Bourguet-Kondracki IM (2014) Assessing the potential bacterial origin of the chemical diversity in calcareous sponges. J Mar Sci Tech 22:36–49
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26:1231–1237
Rehm BHA (2010) Bacterial polymers: biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:578–592
Scott J (2004) Pathophysiology and biochemistry of cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14:271–279
Susilowati R, Sabdono A, Widowati I (2015) Isolation and characterization of bacteria associated with brown algae Sargassum spp. from Panjang Island and their antibacterial activities. Procedia Environ Sci 23:240–246
Tabbene O, Gharbi D, Slimene IB, Elkahoui S, Alfeddy MN, Cosette P, Mangoni ML, Jouenne T, Limam F (2012) Antioxidative and DNA protective effects of bacillomycin D-like lipopeptides produced by b-38 strain. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168:2245–2256
Tang JS, Zhao F, Gao H, Dai Y, Yao ZH, Hong K, Li J, Ye WC, Yao XS (2010) Characterization and online detection of surfactin isomers based on HPLC-MS(n) analyses and their inhibitory effects on the overproduction of nitric oxide and the release of TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS induced macrophages. Mar Drugs 8:2605–2618
Thilakan B, Chakraboty K, Chakraborty RD (2016) Antimicrobial properties of cultivable bacteria associated with seaweeds in Gulf of Mannar of South East Coast of India. Can J Microbiol 62:668–681
Turick CE, Caccavo F Jr, Tisa LS (2008) Pyomelanin is produced by Shewanella algae BrY and affected by exogenous iron. Can J Microbiol 54:334–339
Webster NS, Taylor MW (2012) Marine sponges and their microbial symbionts: love and other relationships. Environ Microbiol 14:335–346
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Wiese J, Thiel V, Nagel K, Staufenberger T, Imhoff JF (2009) Diversity of antibiotic-active bacteria associated with the brown alga Laminaria saccharina from the Baltic Sea. Mar Biotechnol 11:287–300
Wright E Jr, Scism-Bacon JL, Glass LC (2006) Oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: the role of fasting and postprandial glycemia. Int J Clin Pract 60:308–314
Zeng L, Han X, Chen HM, Lin W, Yan XJ (2005) Marine bacteria associated with marine macro organisms: the potential antimicrobial resources. Ann Microbiol 55:119–124
Zhu K, Ding X, Julotok M, Wilkinson BJ (2005) Exogenous isoleucine and fatty acid shortening ensure the high content of anteiso-C15:0 fatty acid required for low-temperature growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8002–8007
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funding under Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment (Grant No. 040/FSHP-LSS/2014/KSCSTE). The authors are thankful to Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi for providing facilities to carry out the work. The authors gratefully thank the Director, National Centre for Aquatic Animal Health of Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin to provide us with the pathogenic organisms. The authors thank the Director, Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute and Dean, Faculty of Marine Sciences, Lakeside Campus, Cochin University of Science and Technology for support. Thanks are due to the Head, Marine Biotechnology Division, Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute for facilitating the research activity.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research involving human or animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kizhakkekalam, V.K., Chakraborty, K. Pharmacological properties of marine macroalgae-associated heterotrophic bacteria. Arch Microbiol 201, 505–518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1592-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1592-1