Abstract
Summary
The association of trabecular bone score (TBS) with fracture risk and its added predictive value to FRAX® for clinical use have never been independently evaluated in a Chinese population. TBS may improve the predictive power of FRAX® for clinical use in older Chinese men.
Introduction
Trabecular bone score (TBS) of lumbar spine on Dual X-ray densitometry provides information on bone architecture. We therefore examined the additive value of TBS to FRAX® in predicting major osteoporotic fractures (MOFs) in older Chinese people.
Methods
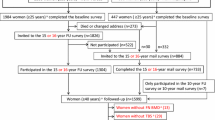
Four thousand community-dwelling Chinese men and women aged ≥65 years were followed up for fracture incidence for an average period of 9.94 and 8.82 years, respectively. At baseline, areal BMD of hip and lumbar spine were measured by DXA, TBS was estimated for the lumbar spine, and FRAX® for 10-year risk of MOFs (hip, clinical spine, shoulder, and wrist) was estimated. Cox regression model was used to evaluate the associations between TBS and FRAX® with the MOFs risk. The area under receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC), integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), and category-based net reclassification improvement (NRI) were applied to evaluate the improved prediction ability.
Results
During the follow-up, 126 men and 215 women had at least one incident MOF. Each SD decrease in TBS was significantly associated with incident MOFs, with HR (95%CI) of 1.53 (1.30–1.80) and 1.40 (1.22–1.61) in men and women, respectively. TBS-adjusted FRAX® predicts better than FRAX® with a significantly increased AUC and IDI in men. Using specific intervention thresholds, TBS-adjusted FRAX® brings about 5 % overall correct reclassification for MOFs prediction than FRAX® in men. The increased correct MOFs risk classifications were not significant in older women.
Conclusions
TBS-adjusted FRAX® may improve the predictive power of FRAX® on MOFs for clinical use in older Chinese men.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papaioannou A, Morin S, Cheung AM, Atkinson S, Brown JP, Feldman S, Hanley DA, Hodsman A, Jamal SA, Kaiser SM, Kvern B, Siminoski K, Leslie WD (2010) 2010 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada: summary. CMAJ 182:1864–1873
Kanis JA, Hans D, Cooper C, Baim S, Bilezikian JP, et al. (2011) Interpretation and use of FRAX in clinical practice. Osteoporos Int 22:2395–2411
DB H, JA K, Baim S, JP B, Binkley N, JA C, JE C, Cooper C, Dawson-Hughes B, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, WD L, EM L, MM L, EV MC, SE P, Poiana C, Rizzoli R (2011) Joint official positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and International Osteoporosis Foundation on FRAX®. Executive summary of the 2010 position development conference on interpretation and use of FRAX® in clinical practice. J Clin Densitom 14:171–180
Johnell O, Kanis JA, Oden A, Johansson H, De Laet C, Delmas P, Eisman JA, Fujiwara S, Kroger H, Mellstrom D, Meunier PJ, Melton LJ 3rd, O'Neill T, Pols H, Reeve J, Silman A, Tenenhouse A (2005) Predictive value of BMD for hip and other fractures. J Bone Miner Res 20:1185–1194
Schousboe JT, Shepherd JA, Bilezikian JP, Baim S (2013) Executive summary of the 2013 International Society for Clinical Densitometry Position Development Conference on bone densitometry. J Clin Densitom 16:455–466
Wang M, Bolland M (2015) Grey a. Management recommendations for osteoporosis in clinical guidelines, Clin Endocrinol (Oxf)
Siris ES, Chen YT, Abbott TA, Barrett-Connor E, Miller PD, Wehren LE, Berger ML (2004) Bone mineral density thresholds for pharmacological intervention to prevent fractures. Arch Intern Med 164:1108–1112
National Osteoporosis Foundation (2014) Clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. National Osteoporosis Foundation, Washington, DC
Marques A, Ferreira RJ, Santos E, Loza E, Carmona L, da Silva JA (2015) The accuracy of osteoporotic fracture risk prediction tools: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1958–1967
Tremollieres FA, Pouilles JM, Drewniak N, Laparra J, Ribot CA, Dargent-Molina P (2010) Fracture risk prediction using BMD and clinical risk factors in early postmenopausal women: sensitivity of the WHO FRAX tool. J Bone Miner Res 25:1002–1009
Ensrud KE, Lui LY, Taylor BC, Schousboe JT, Donaldson MG, Fink HA, Cauley JA, Hillier TA, Browner WS, Cummings SR (2009) A comparison of prediction models for fractures in older women: is more better? Arch Intern Med 169:2087–2094
Hans D, Barthe N, Boutroy S, Pothuaud L, Winzenrieth R, Krieg MA (2011) Correlations between trabecular bone score, measured using anteroposterior dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry acquisition, and 3-dimensional parameters of bone microarchitecture: an experimental study on human cadaver vertebrae. J Clin Densitom 14:302–312
Roux JP, Wegrzyn J, Boutroy S, Bouxsein ML, Hans D, Chapurlat R (2013) The predictive value of trabecular bone score (TBS) on whole lumbar vertebrae mechanics: an ex vivo study. Osteoporos Int 24:2455–2460
Muschitz C, Kocijan R, Haschka J, Pahr D, Kaider A, Pietschmann P, Hans D, Muschitz GK, Fahrleitner-Pammer A, Resch H (2015) TBS reflects trabecular microarchitecture in premenopausal women and men with idiopathic osteoporosis and low-traumatic fractures. Bone 79:259–266
Silva BC, Leslie WD, Resch H, Lamy O, Lesnyak O, Binkley N, McCloskey EV, Kanis JA, Bilezikian JP (2014) Trabecular bone score: a noninvasive analytical method based upon the DXA image. J Bone Miner Res 29:518–530
Hans D, Goertzen AL, Krieg MA, Leslie WD (2011) Bone microarchitecture assessed by TBS predicts osteoporotic fractures independent of bone density: the Manitoba study. J Bone Miner Res 26:2762–2769
Iki M, Tamaki J, Kadowaki E, Sato Y, Dongmei N, Winzenrieth R, Kagamimori S, Kagawa Y, Yoneshima H (2014) Trabecular bone score (TBS) predicts vertebral fractures in Japanese women over 10 years independently of bone density and prevalent vertebral deformity: the Japanese population-based osteoporosis (JPOS) cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 29:399–407
Briot K, Paternotte S, Kolta S, Eastell R, Reid DM, Felsenberg D, Gluer CC, Roux C (2013) Added value of trabecular bone score to bone mineral density for prediction of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women: the OPUS study. Bone 57:232–236
Boutroy S, Hans D, Sornay-Rendu E, Vilayphiou N, Winzenrieth R, Chapurlat R (2013) Trabecular bone score improves fracture risk prediction in non-osteoporotic women: the OFELY study. Osteoporos Int 24:77–85
Lamy O, Metzger M, Krieg MA, Aubry-Rozier B, Stoll D, Hans D (2011) OsteoLaus: prediction of osteoporotic fractures by clinical risk factors and DXA, IVA and TBS. Rev Med Suisse 7:2130–2136
Leslie WD, Aubry-Rozier B, Lix LM, Morin SN, Majumdar SR, Hans D (2014) Spine bone texture assessed by trabecular bone score (TBS) predicts osteoporotic fractures in men: the Manitoba Bone Density Program. Bone 67:10–14
Del Rio LM, Winzenrieth R, Cormier C, Di Gregorio S (2013) Is bone microarchitecture status of the lumbar spine assessed by TBS related to femoral neck fracture? A Spanish case-control study. Osteoporos Int 24:991–998
McCloskey EV, Oden A, Harvey NC, Leslie WD, Hans D, et al. (2015) A meta-analysis of trabecular bone score in fracture risk prediction and its relationship to FRAX. J Bone Miner Res 31(5):940–948
Harvey NC, Gluer CC, Binkley N, McCloskey EV, Brandi ML, Cooper C, Kendler D, Lamy O, Laslop A, Camargos BM, Reginster JY, Rizzoli R, Kanis JA (2015) Trabecular bone score (TBS) as a new complementary approach for osteoporosis evaluation in clinical practice. Bone 78:216–224
Silva BC, Broy SB, Boutroy S, Schousboe JT, Shepherd JA, Leslie WD (2015) Fracture risk prediction by non-BMD DXA measures: the 2015 ISCD official positions part 2: trabecular bone score. J Clin Densitom 18:309–330
Chan DC, McCloskey EV, Chang CB, Lin KP, Lim LC, Tsai KS, Yang RS (2016) Establishing and evaluating FRAX probability thresholds in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. doi:10.1016/j.jfma.2016.03.006
Kwok AW, Gong JS, Wang YX, Leung JC, Kwok T, Griffith JF, Leung PC (2013) Prevalence and risk factors of radiographic vertebral fractures in elderly Chinese men and women: results of Mr. OS (Hong Kong) and Ms. OS (Hong Kong) studies. Osteoporos Int 24:877–885
Bonnick S, Faulkner K, Miller P, McClung M International society for clinical densitometry. M. R. ISCD certification course: clinical track. Version 5. 2000.
World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases at the University of Sheffield, UK FRAX calculation tool (Hong Kong). Available at: http://www.shef.ac.uk/FRAX/tool.aspx?country¼20. Accessed July 10, 2014.
McCloskey EV, Oden A, Harvey NC, Leslie WD, Hans D, Johansson H, Kanis JA (2015) Adjusting fracture probability by trabecular bone score. Calcif Tissue Int 96:500–509
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44:837–845
Leening MJ, Vedder MM, Witteman JC, Pencina MJ, Steyerberg EW (2014) Net reclassification improvement: computation, interpretation, and controversies: a literature review and clinician's guide. Ann Intern Med 160:122–131
Wolbers M, Koller MT, Witteman JC, Steyerberg EW (2009) Prognostic models with competing risks: methods and application to coronary risk prediction. Epidemiology 20:555–561
Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB Sr, D’Agostino RB Jr, Vasan RS (2008) Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Stat Med 27:157–172 discussion 207-112
Kennedy K, Pencina M A SAS® macro to compute added predictive ability of new markers predicting a dichotomous outcome. In: SouthEeast SAS Users Group Annual Meeting roceedings 2010; http://analytics.ncsu.edu/sesug/2010/SDA07.Kennedy.pdf.
Kwok T, Su Y, Khoo CC, Leung J, Kwok A, Orwoll E, Woo J, Leung PC (2016) Predictors of non-vertebral fracture in older Chinese men and women: Mr. OS and Ms. OS (Hong Kong). J Bone Miner Metab. doi:10.1007/s00774-016-0761-z
Leslie WD, Johansson H, Kanis JA, Lamy O, Oden A, McCloskey EV, Hans D (2014) Lumbar spine texture enhances 10-year fracture probability assessment. Osteoporos Int 25:2271–2277
Schousboe JT, Vo T, Taylor BC, Cawthon PM, Schwartz AV, Bauer DC, Orwoll ES, Lane NE, Barrett-Connor E, Ensrud KE (2015) Prediction of incident major osteoporotic and hip fractures by trabecular bone score (TBS) and prevalent radiographic vertebral fracture in older men. J Bone Miner Res 31(3):690–697
Iki M, Fujita Y, Tamaki J, Kouda K, Yura A, Sato Y, Moon JS, Winzenrieth R, Okamoto N, Kurumatani N (2015) Trabecular bone score may improve FRAX® prediction accuracy for major osteoporotic fractures in elderly Japanese men: the Fujiwara-kyo osteoporosis risk in men (FORMEN) cohort study. Osteoporos Int 26:1841–1848
Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, Lewiecki EM, Tanner B, Randall S, Lindsay R (2014) Clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 25:2359–2381
Cheung E, Cheung CL, Kung AW, Tan KC (2014) Possible FRAX-based intervention thresholds for a cohort of Chinese postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 25:1017–1023
Kanis JA, McCloskey EV, Johansson H, Strom O, Borgstrom F, Oden A (2008) Case finding for the management of osteoporosis with FRAX—assessment and intervention thresholds for the UK. Osteoporos Int 19:1395–1408
Kanis JA, Johansson H, Oden A, McCloskey EV (2012) The distribution of FRAX®-based probabilities in women from Japan. J Bone Miner Metab 30:700–705
Nguyen TV, Center JR, Sambrook PN, Eisman JA (2001) Risk factors for proximal humerus, forearm, and wrist fractures in elderly men and women: the Dubbo osteoporosis epidemiology study. Am J Epidemiol 153:587–595
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all the participants dedicated in contributing to the study and The Chinese University of Hong Kong Jockey Club Centre for Osteoporosis Care and Control for supporting the study. The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health R01 grant AR049439–01A1 and the Research Grants Council Earmarked Grant CUHK4101/02M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
ᅟ
None.
ᅟ
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 140 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Leung, J., Hans, D. et al. The added value of trabecular bone score to FRAX® to predict major osteoporotic fractures for clinical use in Chinese older people: the Mr. OS and Ms. OS cohort study in Hong Kong. Osteoporos Int 28, 111–117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3741-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3741-1