Abstract
Summary
Treatment with molecular hydrogen alleviates microgravity-induced bone loss through abating oxidative stress, restoring osteoblastic differentiation, and suppressing osteoclast differentiation and osteoclastogenesis.
Introduction
Recently, it has been suggested that hydrogen gas exerts a therapeutic antioxidant activity by selectively reducing cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS). The aim of the present study was to elucidate whether treatment with molecular hydrogen alleviated bone loss induced by modeled microgravity in rats.
Methods
Hindlimb suspension (HLS) and rotary wall vessel bioreactor were used to model microgravity in vivo and in vitro, respectively. Sprague–Dawley rats were exposed to HLS for 6 weeks to induced bone loss and simultaneously administrated with hydrogen water (HW). Then, we investigated the effects of incubation with hydrogen-rich medium (HRM) on MC3T3-E1 and RAW264.7 cells exposed to modeled microgravity.
Results
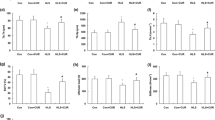
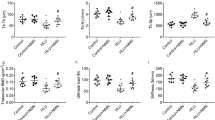
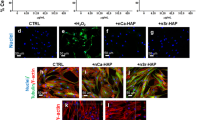
Treatment with HW alleviated HLS-induced reduction of bone mineral density, ultimate load, stiffness, and energy in femur and lumbar vertebra. Treatment with HW alleviated HLS-induced augmentation of malondialdehyde content and peroxynitrite content and reduction of total sulfhydryl content in femur and lumbar vertebra. In cultured MC3T3-E1 cells, incubation with HRM inhibited modeled microgravity-induced ROS formation, reduction of osteoblastic differentiation, increase of ratio of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand to osteoprotegerin, inducible nitric oxide synthetase upregulation, and Erk1/2 phosphorylation. In cultured RAW264.7, incubation with HRM aggravated modeled microgravity-induced ROS formation, osteoclastic differentiation, and osteoclastogenesis.
Conclusion
Treatment with molecular hydrogen alleviates microgravity-induced bone loss in rats. Molecular hydrogen could thus be envisaged as a nutritional countermeasure for spaceflight but remains to be tested in humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanc S, Normand S, Ritz P, Pachiaudi C, Vico L, Gharib C, Gauquelin-Koch G (1998) Energy and water metabolism, body composition, and hormonal changes induced by 42 days of enforced inactivity and simulated weightlessness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:4289–4297
Fowler JF Jr (1991) Physiological changes during spaceflight. Cutis 48:291–295
Vernikos J (1996) Human physiology in space. BioEssays 18:1029–1037
Riggs BL, Khosla S, Melton LJ 3rd (1998) A unitary model for involutional osteoporosis: estrogen deficiency causes both type I and type II osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and contributes to bone loss in aging men. J Bone Miner Res 13:763–773
Vico L, Lafage-Proust MH, Alexandre C (1998) Effects of gravitational changes on the bone system in vitro and in vivo. Bone 22:95S–100S
Kim H, Iwasaki K, Miyake T, Shiozawa T, Nozaki S, Yajima K (2003) Changes in bone turnover markers during 14-day 6 degrees head-down bed rest. J Bone Miner Metab 21:311–315
Rai B, Kaur J, Catalina M, Anand SC, Jacobs R, Teughels W (2011) Effect of simulated microgravity on salivary and serum oxidants, antioxidants, and periodontal status. J Periodontol 82:1478–1482
Chen HL, Qu LN, Li QD, Bi L, Huang ZM, Li YH (2009) Simulated microgravity-induced oxidative stress in different areas of rat brain. Sheng Li Xue Bao 61:108–114
Momken I, Stevens L, Bergouignan A, Desplanches D, Rudwill F, Chery I, Zahariev A, Zahn S, Stein TP, Sebedio JL, Pujos-Guillot E, Falempin M, Simon C, Coxam V, Andrianjafiniony T, Gauquelin-Koch G, Picquet F, Blanc S (2011) Resveratrol prevents the wasting disorders of mechanical unloading by acting as a physical exercise mimetic in the rat. FASEB J 25:3646–3660
Shagimardanova EI, Gusev OA, Sychev VN, Levinskikh MA, Sharipova MR, Il'inskaia ON, Bingham G, Sugimoto M (2010) Stress response genes expression analysis of barley Hordeum vulgare under space flight environment. Mol Biol (Mosk) 44:831–838
Bradamante S, Villa A, Versari S, Barenghi L, Orlandi I, Vai M (2010) Oxidative stress and alterations in actin cytoskeleton trigger glutathione efflux in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:1376–1385
Wang J, Zhang J, Bai S, Wang G, Mu L, Sun B, Wang D, Kong Q, Liu Y, Yao X, Xu Y, Li H (2009) Simulated microgravity promotes cellular senescence via oxidant stress in rat PC12 cells. Neurochem Int 55:710–716
Linnane AW, Eastwood H (2006) Cellular redox regulation and prooxidant signaling systems, a new perspective on the free radical theory of aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1067:47
Sendur OF, Turan Y, Tastaban E, Serter M (2009) Antioxidant status in patients with osteoporosis, a controlled study. Joint Bone Spine 76:514
Kondo H, Yumoto K, Alwood JS, Mojarrab R, Wang A, Almeida EA, Searby ND, Limoli CL, Globus RK (2010) Oxidative stress and gamma radiation-induced cancellous bone loss with musculoskeletal disuse. J Appl Physiol 108:152–161
Wolf RL, Cauley JA, Pettinger M, Jackson R, Lacroix A, Leboff MS, Lewis CE, Nevitt MC, Simon JA, Stone KL, Wactawski-Wende J (2005) Lack of a relation between vitamin and mineral antioxidants and bone mineral density: results from the Women’s Health Initiative. Am J Clin Nutr 82:581–588
Talaulikar VS, Chambers T, Manyonda I (2012) Exploiting the antioxidant potential of a common vitamin: could vitamin C prevent postmenopausal osteoporosis? J Obstet Gynaecol Res 38:253–257
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S, Ohta S (2007) Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med 13:688–694
Zayzafoon M, Gathings WE, McDonald JM (2004) Modeled microgravity inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and increases adipogenesis. Endocrinol 145:2421–2432
Mosekilde L, Danielsen CC, Knudsen UB (1993) The effects of aging and ovariectomy on the vertebral bone mass and biomechanical properties of mature rats. Bone 14:1–6
Katsumata T, Nakamura T, Ohnishi H, Sakurawa T (1995) Intermittent cyclical etidronate treatment maintains the mass, structure and the mechanical property of bone in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res 10:921–931
Elks CM, Mariappan N, Haque M, Guggilam A, Majid DS, Francis J (2009) Chronic NF-kB blockade reduces cytosolic and mitochondrial oxidative stress and attenuates renal injury and hypertension in SHR. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296:F298–305
Saxena R, Pan G, Dohm ED, McDonald JM (2011) Modeled microgravity and hindlimb unloading sensitize osteoclast precursors to RANKL mediated osteoclastogenesis. J Bone Miner Metab 29:111–122
Hollander J, Gore M, Fiebig R, Mazzeo R, Ohishi S, Ohno H, Ji LL (1998) Spaceflight downregulates antioxidant defense systems in rat liver. Free Radic Biol Med 24:385–390
Reich KA, Chen YW, Thompson PD, Hoffman EP, Clarkson PM (2012) Forty-eight hours of unloading and 24 h of reloading lead to changes in global gene expression patterns related to ubiquitination and oxidative stress in humans. J Appl Physiol 109:1404–1415
Al-Ajmi N, Braidman IP, Moore D (1996) Effect of clinostat rotation on differentiation of embryonic bone in vitro. Adv Space Res 17:189–192
Nakamura H, Kumei Y, Morita S, Shimokawa H, Ohya K, Shinomiya K (2003) Suppression of osteoblastic phenotypes and modulation of pro- and anti-apoptotic features in normal human osteoblastic cells under a vector-averaged gravity condition. J Med Dent Sci 50:167–176
Sarkar D, Nagaya T, Koga K, Nomura Y, Gruener R, Seo H (2000) Culture in vector-averaged gravity under clinostat rotation results in apoptosis of osteoblastic ROS 17/2.8 cells. J Bone Miner Res 15:489–498
Qian A, Di S, Gao X, Zhang W, Tian Z, Li J, Hu L, Yang P, Yin D, Shang P (2009) cDNA microarray reveals the alterations of cytoskeleton-related genes in osteoblast under high magneto-gravitational environment. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 41:561–577
Rucci N, Rufo A, Alamanou M, Teti A (2007) Modeled microgravity stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by increasing osteoblast RANKL/OPG ratio. J Cell Biochem 100:464–473
Boehrs J, Zaharias RS, Laffoon J, Ko YJ, Schneider GB (2008) Three-dimensional culture environments enhance osteoblast differentiation. J Prosthodont 17:517–521
Makihira S, Kawahara Y, Yuge L, Mine Y, Nikawa H (2008) Impact of the microgravity environment in a 3-dimensional clinostat on osteoblast- and osteoclast-like cells. Cell Biol Int 32:1176–1181
Ontiveros C, McCabe LR (2003) Simulated microgravity suppresses osteoblast phenotype, Runx2 levels and AP-1 transactivation. J Cell Biochem 88:427–437
Pardo SJ, Patel MJ, Sykes MC, Platt MO, Boyd NL, Sorescu GP, Xu M, van Loon JJ, Wang MD, Jo H (2005) Simulated microgravity using the Random Positioning Machine inhibits differentiation and alters gene expression profiles of 2T3 preosteoblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C1211–1121
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, Tan HL, Timms E, Capparelli C, Morony S, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Van G, Itie A, Khoo W, Wakeham A, Dunstan CR, Lacey DL, Mak TW, Boyle WJ, Penninger JM (1999) OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature 397:315–323
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G, Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D, Pattison W, Campbell P, Sander S, Van G, Tarpley J, Derby P, Lee R, Boyle WJ (1997) Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 89:309–319
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ (1999) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev 20:345–357
Zhang R, Ran HH, Ma J, Bai YG, Lin LJ (2012) NAD(P)H oxidase inhibiting with apocynin improved vascular reactivity in tail-suspended hindlimb unweighting rat. J Physiol Biochem 68:99–105
Wang MT, Huang Z, Yang R, Su J, Mai YX, Zhou HC, Deng WM (2010) Disruption of the microfilament cytoskeleton induced by simulated microgravity affects NO/NOS system of osteoblasts. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 30:1658–1662
Yan L, Yinghui T, Bo Y, Gang Z, Xian X, Lu Z (2011) Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide on nitric oxide production in osteoblasts: an experimental study. Cell Biol Int 35:757–765
Chen RM, Chen TL, Chiu WT, Chang CC (2005) Molecular mechanism of nitric oxide-induced osteoblast apoptosis. J Orthop Res 23:462–468
Park BG, Yoo CI, Kim HT, Kwon CH, Kim YK (2005) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in osteoblastic cells. Toxicol 215:115–125
Lee NK, Choi YG, Baik JY, Han SY, Jeong DW, Bae YS, Kim N, Lee SY (2005) A crucial role for reactive oxygen species in RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Blood 106:852–859
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 56 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Shuang, F., Chen, D.M. et al. Treatment of hydrogen molecule abates oxidative stress and alleviates bone loss induced by modeled microgravity in rats. Osteoporos Int 24, 969–978 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-012-2028-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-012-2028-4