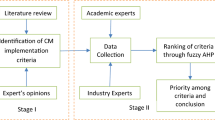
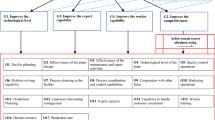
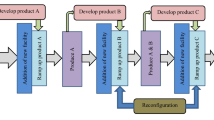
Abstract
“Productivity is never an accident, it is always the result of a commitment to excellence, intelligent planning, and focused approach,” the phrase by Paul J. Meyer, an American businessman, has everything explained within it. Various quality improvement tools and techniques along with their integration have been attempted in the past for enhancing productivity levels in large-scale organizations across the globe. Similarly, new unification of these techniques can bring positive results even in a small- and medium-sized enterprise (SME). Authors, in this case study, use the synergy of two approaches, namely, “Shainin system” and “fuzzy analytical hierarchy process (AHP)” to enhance the productivity of a system. Shainin system stands close to a set of instruments that are clear to understand and easy to be applied, whereas AHP technique has a proven potential in decision-making and evaluation. Results, after successful implementation, indicate a monetary saving of $100,000, which is substantial for a SME. Emphasis is put on a coherent step-wise implementation of both the strategies and linking them together to inculcate the best potential outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao Y (1997) QFD: past, present, and future. In: International Symposium on Quality Function Deployment. p 19
Aksu B, Baynal K (2010) Shainin and Taguchi methods and their comparison on an application. In: International Symposium on Computing in Science & Engineering. pp 801–809
Antony J (1999) Spotting the key variables using Shainin’s variables search design. Logist Inf Manag 12:325–331. doi:10.1108/09576059910284140
Arshinder, Kanda A, Deshmukh SG (2007) Coordination in supply chains: an evaluation using fuzzy logic. Prod Plan Control 18:420–435. doi:10.1080/09537280701430994
Balan S (2015) Multi-response optimisation using Grey relational analysis and Shainin design of experiments Srinivasan Balan. Int J Qual Eng Technol 5:57–78
Beg J, Shunmugam MS (2003) Application of fuzzy logic in the selection of part orientation and probe orientation sequencing for prismatic parts. Int J Prod Res 41:2799–2815. doi:10.1080/0020754031000095130
Bhote K (1999) World class quality: using design of experiments to make it happen, 2nd edn. AMACOM Div American Mgmt Assn
Bilgen B, Şen M (2012) Project selection through fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and a case study on six sigma implementation in an automotive industry. Prod Plan Control 23:2–25. doi:10.1080/09537287.2010.537286
Boaden R (1997) What is total quality management… and does it matter. Total Qual Manag 8:25
Chang C, Wu C, Chen H (2008) Using expert technology to select unstable slicing machine to control wafer slicing quality via fuzzy AHP. Expert Syst Appl 34:2210–2220. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2007.02.042
Chen C (2000) Extensions of the TOPSIS for group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst 114:1–9
Chen C, Klein C (1997) An efficient approach to solving fuzzy MADM problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 88:51–67
Chen JK (2007) Utility priority number evaluation for FMEA. J Fail Anal Prev 7:321–328. doi:10.1007/s11668-007-9060-2
Chen LH, Kao C, Kuo S et al (1996) Productivity diagnosis via fuzzy clustering and classification: an application to machinery industry. Omega 24:309–319. doi:10.1016/0305-0483(96)00002-3
Cigolini R, Rossi T (2008) Evaluating supply chain integration: a case study using fuzzy logic. Prod Plan Control 19:242–255. doi:10.1080/09537280801916249
Cox S, Garside J, Kotsialos A (2012) Concise process improvement—a process variation diagnosis tool. In: International MATADOR Conference. pp 1–5
Cox S, Garside J, Kotsialos A, Vitanov V (2013) Concise process improvement definition with case studies. Int J Qual Reliab Manag 30:970–990. doi:10.1108/IJQRM-03-2012-0029
Danijela T, Alev Taskin G, Slavko A et al (2013) An evaluation of quality goals by using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methodology. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 25(3):547–556
De Mast J, Schippers W, Does RJMM, Van den Heuvel E (2000) Steps and strategies in process improvement. Qual Reliab Eng Int 16:301–311
Fazil BM, Kesavan R (2014) Vendor selection in supply chain management using ISM and ANP. IOSR J Mech Civ Eng 81–89
Goodman J, Wyld DC (2001) The hunt for the red X: a case study in the use of Shainin design of experiment (DOE) in an industrial honing operation. Manag Res News 24:1–17. doi:10.1108/01409170110782919
Gupta H, Garg D, Gupta R (2011) Applicability of just in time in technical institution: a survey. J Eng Technol 1:31–36. doi:10.4103/0976-8580.74564
Gupta R, Verma PL, Manoria A, Bajpai L (2016) Simplifying six sigma methodology using Shainin DOE. Int J Adv Eng Res Dev 3:363–368
Hwang C-L, Lai Y-J, Liu T-Y (1993) A new approach for multiple objective decision making. Comput Oper Res 20:889–899. doi:10.1016/0305-0548(93)90109-V
Inman RR, Blumenfeld DE, Huang N, Li J (2003) Designing production systems for quality: research opportunities from an automotive industry perspective. Int J Prod Res 41:1953–1971. doi:10.1080/0020754031000077293
Jegadheeson AJ, Karunamoorthy L, Arun Kumar N et al (2012) Evolutionary approach in process improvement—a case study in auto electrical alternator manufacturing. J Adv Manuf Syst 11:27–50. doi:10.1142/S0219686712500035
Kaushik P, Khanduja D, Mittal K, Jaglan P (2012) A case study: application of six sigma methodology in a small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprise. TQM J 24:4–16. doi:10.1108/17542731211191186
Kaushik P, Mittal K (2015) A general model for problem solving in manufacturing or service organizations. J Eng Technol. doi:10.4103/0976-8580.158566
Kuhlang P, Edtmayr T, Sihn W (2011) Methodical approach to increase productivity and reduce lead time in assembly and production-logistic processes. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 4:24–32. doi:10.1016/j.cirpj.2011.02.001
Lee A, Chen W-C, Chang C-J (2008) A fuzzy AHP and BSC approach for evaluating performance of IT department in the manufacturing industry in Taiwan. Expert Syst Appl 34:96–107
Liu H, Liu L, Liu N, Mao L (2012) Risk evaluation in failure mode and effects analysis with extended VIKOR method under fuzzy environment. Expert Syst Appl 39:12926–12934
Logothetis N (1990) A perspective on Shainin’s approach to experimental design for quality improvement. Qual Reliab Eng Int 6:195–202
Lu LYY, Wu CH, Kuo T (2007) Environmental principles applicable to green supplier evaluation by using multi-objective decision analysis. Int J Prod Res 45:4317–4331. doi:10.1080/00207540701472694
Luthra S, Mangla SK, Xu L, Diabat A (2016) Using AHP to evaluate barriers in adopting sustainable consumption and production initiatives in a supply chain. Int J Prod Econ. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.04.001
Mangla SK, Kumar P, Barua MK (2015) Risk analysis in green supply chain using fuzzy AHP approach: a case study. Resour Conserv Recycl 104:375–390. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.01.001
Michalos G, Fysikopoulos A, Makris S et al (2015) Multi criteria assembly line design and configuration—an automotive case study. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 9:69–87. doi:10.1016/j.cirpj.2015.01.002
Mittal K, Khanduja D, Kaushik P (2011) Leveraging APQP methodology to drive improvement in SME: a case study. Int J Contemp Pract 1:38–51
Mittal K, Tewari PC, Khanduja D, Kaushik P (2016) Application of fuzzy TOPSIS MADM approach in ranking & underlining the problems of plywood industry in India. Cogent Eng 3:1–11
Mooren J, de Mast J, Does RJMM (2012) Quality quandaries*: the case of premature drill wear out. Qual Eng 24:354–359. doi:10.1080/08982112.2011.652584
Mourtzis D, Papakostas N, Makris S et al (2008) Supply chain modeling and control for producing highly customized products. CIRP Ann - Manuf Technol 57:451–454. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.106
Onut S, Kara SS, Mert S (2009) Selecting the suitable material handling equipment in the presence of vagueness. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44:818–828. doi:10.1007/s00170-008-1897-3
Opricovic S, Tzeng G-H (2004) Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Oper Res 156:445–455
Prashar A (2016) Using Shainin DOE for six sigma: an Indian case study. Prod Plan Control 27:83–101. doi:10.1080/09537287.2015.1078515
Prashar A (2015) Using Shainin DOE for six sigma: an Indian case study. Prod Plan Control 27:83–101. doi:10.1080/09537287.2015.1078515
Rathi R, Khanduja D, Sharma SK (2015) Six sigma project selection using fuzzy TOPSIS decision making approach. Manag Sci Lett 5:447–456. doi:10.5267/j.msl.2015.3.009
Rowlands H, Wang LIREN (2000) An approach of fuzzy logic evaluation and control in SPC. Qual Reliab Eng Int 16:91–98
Saaty T (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48:9–26
Saaty T (2008) Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Serv Sci 1:83–98
Shainin P, Shainin R (1997) Managing statistical engineering. In: 51st Annual Quality Congress Proceedings. pp 818–832
Shainin R (1993) Strategies for technical problem solving. Qual Eng 5:433–438
Shanmugam B, Kalaichelvan K (2014) Rejection reduction of vacuum pump type alternator assembly. IOSR J Mech Civ Eng 3:51–58
Singh RK, Khilwani N, Tiwari MK (2007) Justification for the selection of a reconfigurable manufacturing system: a fuzzy analytical hierarchy based approach. Int J Prod Res 45:3165–3190. doi:10.1080/00207540600844043
Steiner S, MacKay R (1997) Strategies for variation reduction. Qual Eng 10:125–136
Thomas A, Antony J (2004) Applying Shainin’s variables search methodology in aerospace applications. Assem Autom 24:184–191. doi:10.1108/01445150410529973
Verma AK, Srividya A, Mannikar AV et al (2004) Shainin method: edge over other DOE techniques. IEEE Int Eng Manag Conf 3:1110–1113. doi:10.1109/IEMC.2004.1408864
Yadollahi Farsi J, SiahkaliMoradi J, Jamali B (2012) Which product would be chosen? A fuzzy VIKOR method for evaluation and selection of products in terms of customers’ point of view; case study: Iranian cell phone market. Decis Sci Lett 1:23–32
Yin KH, Choo HL, Halim D, Rudd C (2013) Multi-response parameters optimisation for energy-efficient injection moulding process via dynamic Shainin DOE method. Key Eng Mater 554–557:1669–1682. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.554-557.1669
Zadeh L (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf Sci (Ny) 8:199–249
Zammori F, Gabbrielli R (2012) ANP/RPN: a multi criteria evaluation of the risk priority number. Qual Reliab Eng Int 28:85–104. doi:10.1002/qre.1217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, K., Tewari, P.C. & Khanduja, D. Productivity improvement under manufacturing environment using Shainin system and fuzzy analytical hierarchy process: a case study. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 407–421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0123-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0123-6