Abstract
Purpose
Concerns exist regarding prosthetic positioning and post-operative limb alignment in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA). In this study, we hypothesized deviations of the post-op anatomical femoro-tibial angle (aFTA) and the tibial component alignment to be factors influencing UKA survivorship. Moreover, by a comparison between all-poly and metal back UKAs, we hypothesized that prosthetic design plays a role in implant survivorship.
Methods
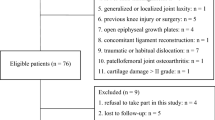
One hundred ninety-five medial UKAs were performed on 176 patients by two experienced surgeons and one low-UKA user. One hundred and forty-seven UKAs were included in the study: 72 all-poly and 75 metal back. Measurements were performed on radiographs: mechanical femoro-tibial angle, Cartier angle, aFTA and tibial posterior slope (PS) on pre-op radiographs; femoral and tibial component varus/valgus, aFTA and tibial component PS on post-op radiographs.
Results
At an average follow-up of 61 months (min. 30, max. 107), 147 UKAs were evaluated: The reported survivorship rate was 93.1 %. Eleven implants underwent revision: ten all-poly and one metal back. No differences were reported between the two groups in the radiographic measurements. Significant radiographic differences were reported between revised and not revised UKAs: Revised UKAs were associated with overcorrection of the pre-op Cartier angle and under correction of pre-op aFTA. Most of revised UKAs were performed by the low-volume UKA surgeon.
Conclusions
Surgeon’s experience is essential to achieve good results in UKA: Preserving the tibial epiphyseal axis and avoiding excessive or insufficient corrections of the pre-operative limb alignment are predictor of successful replacement, while prosthetic designs, models and fixation geometry do not affect UKA outcome.
Level of evidence
IV.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. https://aoanjrr.dmac.adelaide.edu.au/documents/10180/60142/Annual%20Report%202012?version=1.2&t=1355186837517
Bruni D, Akkawi I, Iacono F, Raspugli GF, Gagliardi M, Nitri M, Grassi A, Zaffagnini S, Bignozzi S, Marcacci M (2013) Minimum thickness of all-poly tibial component unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in patients younger than 60 years does not increase revision rate for aseptic loosening. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(11):2462–2467
Cheng T, Pan X, Liu T, Zhang X (2012) Tibial component designs in primary total knee arthroplasty: should we reconsider all-polyethylene component? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(8):1438–1449
Clarius M, Hauck C, Seeger JB, Pritsch M, Merle C, Aldinger PR (2010) Correlation of positioning and clinical results in Oxford UKA. Int Orthop 34(8):1145–1151
Collier MB, Eickmann TH, Sukezaki F, McAuley JP, Engh GA (2006) Patient, implant, and alignment factors associated with revision of medial compartment unicondylar arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 21(6 Suppl 2):108–115
Cossey AJ, Spriggins AJ (2005) The use of computer-assisted surgical navigation to prevent malalignment in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20(1):29–34
Furnes O, Espehaug B, Lie SA, Vollset SE, Engesaeter LB, Havelin LI (2007) Failure mechanisms after unicompartmental and tricompartmental primary knee replacement with cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(3):519–525
Gulati A, Chau R, Simpson DJ, Dodd CA, Gill HS, Murray DW (2009) Influence of component alignment on outcome for unicompartmental knee replacement. Knee 16(3):196–199
Harnett NI, Tregonning R, Rothwell A, Hobbs T (2010) The Oxford phase 3 unicompartimental knee arthroplasty—an audit of revisions. The New Zealand experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(SUPP I):224
Hernigou P, Deschamps G (2004) Alignment influences wear in the knee after medial unicompartmental arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 423:161–165
Heyse TJ, Khefacha A, Peersman G, Cartier P (2012) Survivorship of UKA in the middle-aged. Knee 19(5):585–591
Marmor L (1988) Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Ten- to 13-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:14–20
Newman J, Pydisetty RV, Ackroyd C (2009) Unicompartmental or total knee replacement: the 15-year results of a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91(1):52–57
Pandit H, Jenkins C, Gill HS, Barker K, Dodd CA, Murray DW (2011) Minimally invasive Oxfor phase 3 unicompartmental knee replacement: results of 1000 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(2):198–204
Price AJ, Svard U (2011) A second decade lifetable survival analysis of the Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(1):174–179
Registro Regionale Di Implantologia Protesica Ortopedica Dati Complessivi interventi di Protesi d’anca, di ginocchio e di spalla in Emilia Romagna 2000–2009. https://ripo.cineca.it/pdf/relazione_globale_2009.pdf
Ridgeway SR, McAuley JP, Ammeen DJ, Engh GA (2002) The effect of alignment of the knee on the outcome of unicompartmental knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84(3):351–355
Sawatari T, Tsumura H, Iesaka K, Furushiro Y, Torisu T (2005) Three-dimensional finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty—the influence of tibial component inclination. J Orthop Res 23(3):549–554
Schai PA, Suh JT, Thornhill TS, Scott RD (1998) Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in middle-aged patients: a 2- to 6-year follow up evaluation. J Arthroplasty 13(4):365–372
Small SR, Berend ME, Ritter MA, Buckley CA, Rogge RD (2011) Metal backing significantly decreases tibial strains in a medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty model. J Arthroplasty 26(5):777–782
Sharma L, Song J, Dunlop D et al (2010) Varus and valgus alignment and incident and progressive knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(11):1940–1945
Simpson DJ, Gray H, D’Lima D, Murray DW, Gill HS (2008) The effect of bearing congruency, thickness and alignment on the stresses in unicompartmental knee replacements. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 23(9):1148–1157
Swank M, Stulberg SD, Jiganti J, Machairas S (1993) The natural history of unicompartmental arthroplasty. An eight-year follow-up study with survivorship analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:130–142
Tabor OB Jr, Tabor OB (1998) Unicompartmental arthroplasty: a long term follow-up study. J Arthroplasty 13(4):373–379
The Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register, Annual Report 2012. http://www.myknee.se/pdf/117_SKAR_2012_Engl_1.0.pdf
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zambianchi, F., Digennaro, V., Giorgini, A. et al. Surgeon’s experience influences UKA survivorship: a comparative study between all-poly and metal back designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23, 2074–2080 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2958-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2958-9